Spinal Cord Injury: Complications & Treatment
Spinal Cord Injury: Complications & Treatment
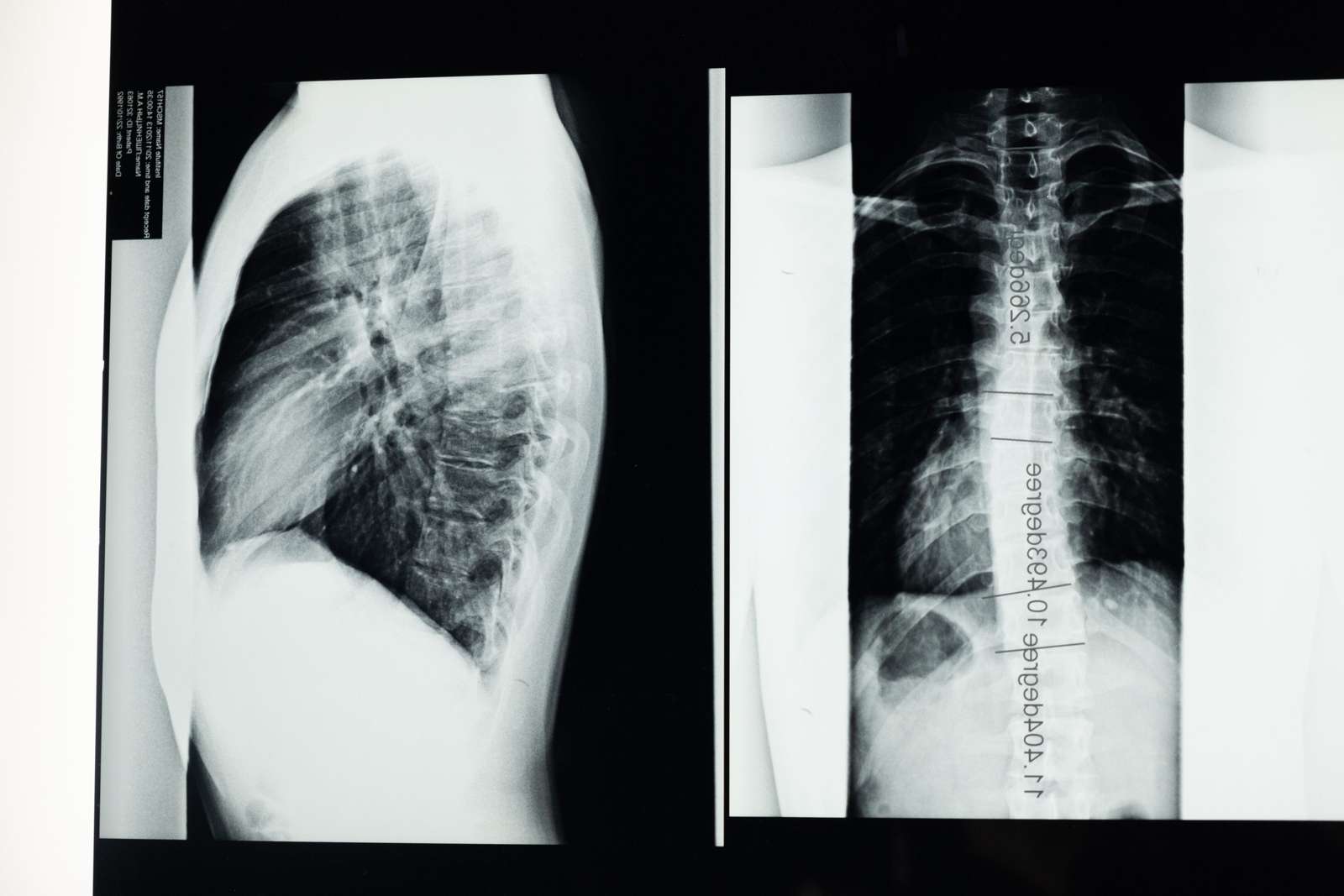
The spinal cord that forms a part of the central nervous system; is a column of nerve tissue that extends from the base of the skeleton to the center of the back. The spinal cord forms a pathway for messages sent by the brain to the body. Alongside the brain, it helps in carrying out motor, sensory and autonomic functions. Thus, any damage caused to the spinal cord can lead to some serious dysfunction in the body.
The spinal cord is an important and very sensitive part of the human body. It is prone to injury, and unlike other parts of the human body, it does not have the ability to repair itself. Thus, damage to the spinal cord can lead to permanent harm to movement, sensation, and other body functions below the site of injury. Some of the best neurologists in Gwalior or neurologist in Agra can help in treating spinal cord injury.
Causes Of Injury
Spinal cord injuries (SCI) may occur as a result of external trauma, loss of blood, or non-traumatic spinal cord injuries. Some of the causes are listed below:
- Automobile accidents
- Collisions in sports
- Hitting or falling hard on the head
- Cancer
- Arthritis
- Inflammation
- Disk degeneration of the spine
Symptoms of Spinal cord Injury
The symptoms of spinal cord injury may depend from person to person. Some of the common symptoms of SCI are listed below. Although they may not necessarily mean a spinal cord injury, it is better to seek medical attention.
- Extreme pain felt in the head, neck, or the back region
- Weakness in the limbs or difficulty walking
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Trouble while breathing
- Trouble in balancing and coordination
- Numbness or tingling sensation in hands, fingers, feet, or toes
- An oddly twisted neck or back
It is recommended that people with a backbone injury should restrain themselves from lifting heavy objects or moving them. One should consider seeking immediate medical care from the famous neurologist in Patna or from the famous neurologist in Gwalior
Some of the long term signs and symptoms of SCI are -
- Loss of movement
- Alterations in senses, such as loss of touch, inability to feel hold, cold, etc
- Loss of bladder and bowel control
- Severe, throbbing pain at the back (this is felt due to the nerve fibers in the spinal cord)
- Abnormal or exaggerated reflex activities
- muscle spasms
- Changes in sexual function, sexual sensitivity
- Infertility
- Difficulty while breathing or coughing
In times of lockdown and social distancing, one can also get online neurologist consultation.
Spinal cord Injury types
There are several types of spinal cord injuries. The type of injury is based on the spinal cord injury symptoms. Usually, the injuries are categorized into two types- complete and incomplete injuries. The severity of the injury is called ‘completeness’.
- Complete
- Incomplete
Get a neurologist online consultation for a quick diagnosis of spinal cord injury.
Complications
There are several changes and complications that can take place after the spinal cord is injured. It is necessary that one seeks quick medical care to prevent any further losses. Some of the complications are -
- Bladder and Bowel control - Although your kidneys, stomach, and intestines may continue to function as earlier, your brain will have no control over your bowels or bladder. This is because the message carrier, your spinal cord is affected.
- Muscle spasms- Uncontrolled muscle movements and spasticity, due to contracting of the muscles
- Respiratory issues - Injuries on the upper part of the spinal cord can affect your breathing. Cervical or thoracic spinal cord injury increases the risk of lung problems such as pneumonia etc.
- Mental health conditions - Some spinal cord injuries may lead to permanent loss of function, or even, spinal cord injury disability. Coping with the changes taking place and the trauma of the accident may lead to a decline in mental health.
- Infertility - Men may face issues in erection or ejaculation, whereas women may notice changes in lubrication. Getting pregnant can also be difficult for women.
It is important to get Spinal cord injury treatment from the top best neurologist in Jaipur.
Spinal cord Injury pain - Treatment
Although there are no treatments available for reversing the damage caused to the spinal cord, researchers are constantly working on different ways to cure the injury. However, at present, the treatment for spinal cord injury focuses on the rehabilitation of the person to their daily life and preventing any further damage.
The recovery time of spinal cord injury depends on the type and severity of the injury. Surgery is the norm for treating spinal cord injuries. It helps in preventing any further damage. Spinal cord injuries in the upper neck can cause some serious problems, hence it is necessary that one checks the heartbeats and breathing of that person, immediately after the injury takes place. Wounds at the lower end of the spinal cord may lead to loss of bowel and bladder control, loss of sexual function, weakness, and loss of muscle function, etc.
X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help in Spinal cord injury diagnosis as well as aid in knowing the exact location of the wound. Occupational therapy, physical training therapy, and rehabilitation are recommended in most cases. This helps the patient in maintaining their physical strength and mobility, as well as preventing them from any long-term effects. One of the best neurologists in Saket can help in providing the best treatment for spinal cord injuries. You may also seek medical care and an appropriate spinal cord injury diet from the best neurologist in South Delhi, Dr. Chandril Chugh. You can also find him as a neurologist in Punjab, the best neurologist in Faridabad or brain specialist doctor in Faridabad, a top neurologist in Jaipur or neurologist doctor in Jaipur, the best neurologist in Saket, best neurologist in South delhi, neurologist in Agra, mind doctor in Delhi, top neuro physician in Patna and a top neurologist in Gwalior or neurologist doctor in Gwalior. He is also amongst the top 5 neurologist in Patna. You can also go for neurologist online chat or online neurologist consultation.
Top 12 Interesting Facts About The Nervous System
Nervous system introduction
The nervous system function is one complex and tremendously organized body system. It coordinates the action and sensory information. This information is received from different organs and is transmitted via nerves through the spinal cord. It is then processed by the brain and the nervous system structure is spread around the whole body to function suitably. This system directs the body’s function and controls our reaction to the outside world. It’s like a hyperactive connection that sends signals, electrical and chemical in lighting speed between cells. One should consult a famous neurologist in Patna in case any damage is caused to the nervous system.
Given below are some interesting nervous system facts and functions.
Nervous system facts A-Z:
The two main nervous systems
The nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord as the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves and sensory organs. Together with the help of CNS and PNS, it transfers sensory information, and along with that, it coordinates body functions. Sensory organs send data to the brain and spinal cord (CNS) from the nerves throughout the body. The CNS is the control center that processes this information and sends the command back. The nerves carry out the signals that are outgoing and incoming. Any damage to these nervous systems may require the help of a brain doctor in Patna for a quick recovery.
The Neurotransmitter effect
A neurotransmitter is a chemical that is released when signals reach the end of the neuron. The message passes through neurons as electrical signals, and they facilitate the release of this chemical. It travels between neuron spaces and even other body tissues or cells. It has two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters enable the electrical signal in neurons that encourage responses from body cells. On the other hand, an inhibitory transmitter discourages these signals and cellular responses. These chemicals assist in controlling the activities of muscles, glands, and nerve pathways. If you suspect any malfunction of the muscles or other body parts, consult the best neurologist in Saket.
The nerve branches of the nervous system
The nervous tissue from the brain to the spinal cord and further nerve trunk includes cells called neurons. Neurons are charged cells as they conduct electrical signals to pass information throughout the body. A basic neuron consists of a dendrite, axon, and axon terminal. Body tissues or neurons pass signals to dendrite, and it is transmitted into the cell body. An outgoing signal is zipped in the axon and passed ahead through the axon terminal to the targeted cell. It has a huge capacity to send a signal from the nerve pathway and via the central nervous system too. One should consult the best neurologist in Gwalior or the famous neurologist in Gwalior, Dr. Chandril Chugh for proper treatment of damaged nerves. You can also find him as a neurologist in Punjab, the best neurologist in Faridabad or brain specialist doctor in Faridabad, a top neurologist in Jaipur or neurologist doctor in Jaipur, the best neurologist in Saket, best neurologist in South delhi, neurologist in Agra, mind doctor in Delhi, top neuro physician in Patna and a top neurologist in Gwalior or neurologist doctor in Gwalior. He is also amongst the top 5 neurologist in Patna. You can also go for neurologist online chat or online neurologist consultation.
The roadway of nerves
The spinal cord is covered up by connective tissues and bones. It’s made up of neuron cells and a stack of axons. The brain’s medulla oblongata is connected down to the vertebral column. It’s a super track and part of the CNS. It enhances the nervous system factors of sensory information that motors command up and down to and from the brain. These signals speed in and out via spinal nerves. The spinal cord can pass on a reflex command without including the brain responses.
The brain- the engine of the body
This Nervous system organ connects perceptions and memory. Passing information might be the basic process command of the nervous system, but when you smell a familiar perfume do you feel nostalgic? It happens because of the limbic system that forms two rings paired within the brain. It consists of the amygdala, the hippocampus, the cingulate gyrus, and the dentate gyrus. The limbic system is involved in different nervous system function that helps our memory, olfaction (Our sense of smell) and even our range of emotions. The aroma that makes you happy and you reach out to the meal is the collective work of the limbic system.
Neurons can look different
While one may assume that all neurons look the same, it’s not true. Neurons have different sizes and shapes depends upon their location in the body and their functionality. Sensory neurons are connected by a long axon with dendrites on both ends and a cell body in middle. Whereas, motor neurons have a long axon in the middle. A cell body and dendrites on each end.
Two types of the nervous system
The voluntary and non-voluntary nervous system exists in the body along with PNS and CNS. The voluntary system controls action that a human being is aware of and even control consciously, like moving head, legs, arms, and different body parts. The other system controls the processes that the body can’t control consciously. The system is always active and governs an individual’s breathing, heartbeat rate, metabolism, and other critical body processes. One may get an online neurologist consultation if they experience any trouble in their routine bodily processes.
A nervous system prepares the body for action
The sympathetic nervous system notifies the body to get active for physical and any mental activities to face them. When the body is active, it makes breathing easy, and the heartbeat faster. Even the digestion in the body is temporarily stopped due to this system and activeness load. Seek guidance from a neurologist in south Delhi for the treatment of neurological disorders.
Controlling the body at rest
The sympathetic nervous system facts were referring to activating the body for work. On the other hand, the parasympathetic nervous system restraint body function when it is at rest. It includes activating metabolism, stimulating digestion, and settling the body in a relaxed state.
The handler of bowel movement
The bowel movements in our body are controlled by the enteric nervous system. It automatically regulates bowel movements as a part of digestion. Consult the top best neurologist in Jaipur if you face troubles with passing bowels
The different types of neurons
Neurons have four types:
- Motor: Motor neurons are the ones that carry signals from the central nervous system to the outside parts of the body.
- Sensory: Sensory neurons carry the signals into the central nervous system from the outer part of the body – the glands, muscles, and skin.
- Receptors: Receptors sense the surrounding environment like light, sound, touch, and chemicals around you. Further, it converts into electrochemical energy and is sent by sensory neurons.
- Interneurons: This neuron is promised to send messages from one neuron to another one.
The loss of neurons
Neurons too have a lifespan. We start losing our neurons at around 20 years of age and till we reach the age of 75, 1/10 of our neurons are gone by the age of 75.
Common Symptoms Of Known Neurological Disorders
Neurological disorders: Introduction
The disorder of the nervous system is known as neurological disorders. The nervous system is responsible for carrying out all the functions of the body. It is the engine of the human body, without which the body would not function. The nervous system is divided into two primary regions- the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system or CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system or PNS consists of everything else. Thus, the malfunctioning of the brain, the spinal cord or disruption in the connection of the nerves in the body, can lead to neurological disorders.
Lack of consciousness, stroke, paralysis, poor coordination, loss of memory, tremors and seizures, headache, etc are some of the common symptoms of neurological disorders. Often the symptoms originate from the peripheral nervous system. This could be, a result of injury or some illness. The neurological disorder symptoms can also arise from nerve damage or autoimmune diseases. Apart from this, it is also important to notice the signs and symptoms of neurological disorders in newborns. Some of the signs are- fuzziness, abnormal movements, difficulty in feeding, changes in body temperature, missing important developmental milestones, etc.
Given the rise in Covid-19 cases, one can get easy online neurological consultation or neurologist online chat from the best neurologist in Saket. Given below are the neurological disorders list and their symptoms:
Headaches and their types
Although headaches are quite common, they can be a serious neurological disorder. The location of the headache, its intensity, duration, the neurological disorder causes, vary according to the type of headache. Here are some of the symptoms based on the different types of neurological disorder headache.
Cluster headache
- Pain felt on one side of the head
- Red or tearing eyes
- Agitation
- Runny nose/nasal congestion
- Sweating
Migraine
- Throbbing, intense pain in a particular area
- Pain felt in the face, the eyes, or neck
- Sensitivity to light, distorted or blurred vision, seeing flashes of light
- Sensitivity to noise
- Nausea
Sinus
- Pain, pressure on cheeks, brow or forehead
- Pain felt while bending forward
- Stuffy nose
- Fatigue
Post-traumatic headaches
- Dizziness
- Insomnia, flashbacks, nightmares
- Memory problems
- Sensitivity to sound and light
- Anxiety, depression, etc.
Get online neurologist consultation from the top neurologist in Agra for your headaches.
Stroke
Strokes can be a life-threatening neurological disorder. A person is said to be having a stroke when the flow of blood and oxygen supply is cut off from a part of the brain, causing a breakdown and arrest in functioning. A stroke needs immediate medical attention, otherwise, it can be fatal. There are several reasons why a person may have a stroke. Smoking tobacco, high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, genetic factors, obesity, etc are some of the many causes of stroke. One must know It is important that one knows the signs and symptoms of a stroke. Some of them are -
- Blurred vision or loss of sight
- Trouble walking, sudden paralysis, stiffening of muscles
- Numbness
- Dizziness, confusion, difficulty in understanding
- Severe headache
One should definitely consult the best brain doctor in Patna for the treatment of strokes.
Seizures
When the connection between brain nerve cells is disturbed, one is said to have seizures. Thus, almost all people are at risk of having a seizure, however, a single seizure doesn’t mean a person has a seizure disorder. Epilepsy is a chronic condition where one has recurrent seizures. The nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, thus causing frequent outbursts of electrical energy. If you have frequent episodes of seizures, consider consulting the top best neurologist in Jaipur, for the treatment of epilepsy.
Most of the time, seizures are noticeable and you can make out if a person is having a seizure. However, sometimes, it may escape your eye. Here are some symptoms that a person is having a seizure-
- Uncontrollable muscles spasms, jerking of the arms and legs
- Loss of consciousness
- Drooling, Biting of tongue or clenching of teeth
- Uncontrolled bowels or bladder
- Loss of consciousness, having a blurred vision
- Dropping things, falling on ground/fainting
Neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases, as the name suggests is the deterioration of nerve cells over a period of time. The nerve cells of the brain or the peripheral nervous system, start to degenerate and ultimately die. Neurodegenerative diseases affect one’s personality and impair their ability to function. Some common types of neurodegenerative diseases and their symptoms are-
Dementia (a common neurological disorder in elderly)
- Loss of memory is a common symptom of dementia
- Inability to speak, disorientation
- Depression, mood swings, nervousness, anxiety
- Difficulty to walk, stiffness of muscles
- Sleep disorder
Parkinson’s disease
- Tremors felt in the hand, limbs, etc
- Difficulty in movement, muscle contraction, slow body movement
- Difficulty in speech, difficulty in swallowing food, etc.
- Stiffness of body parts
- Depression,
Huntington’s disease
- Abnormal movement, problems with coordination
- Amnesia , delusion, confusion,
- Depression, hallucination, mood swings,
- Memory loss
- Difficulty in functioning
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- Twitching of muscles in the arms, legs, shoulder, tongue
- Spasticity
- Slurred and nasal speech
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Muscle cramps
Consult the famous neurologist in Gwalior, also the best neurologist in Gwalior for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is characterized by the inability to concentrate and difficulty controlling their own behavior or actions. ADHD is common among both adults and children. Brain injuries, abnormal brain development or genes are some of the causes of ADHD. The symptoms of ADHD include -
- Trouble focusing or concentrating on tasks
- Having trouble completing tasks or forgetting about them
- Distraction
- having trouble sitting still
- Having a habit of interrupting people while they’re talking
Ignoring the symptoms of neurological symptoms can worsen the condition of the patient in the future. Thus, it is important that one seeks quick treatment from a professional. Consult a neurologist in South Delhi, Dr. Chandril Chugh for quick recovery and treatment of neurological conditions. You can also find him as a neurologist in Punjab, the best neurologist in Faridabad or brain specialist doctor in Faridabad, a top neurologist in Jaipur or neurologist doctor in Jaipur, the best neurologist in Saket, best neurologist in South delhi, neurologist in Agra, mind doctor in Delhi, top neuro physician in Patna and a top neurologist in Gwalior or neurologist doctor in Gwalior. He is also amongst the top 5 neurologist in Patna.
Brain Exercises: Improve Concentration, Memory And Cognition Ability
Human Brain, the most complex structure of the human body, starts developing in the mother’s womb itself. It is responsible for carrying out almost all functions of the body. Thus, it is important that the brain is active and no harm is caused to it.
Doctors often suggest brain exercises to patients, to help them steer free from neurological disorders. A simple exercise like reading a book for 30 minutes, can help in improving concentration level. One needs to train their brain and monitor it, to boost their brainpower. An online neurologist consultation can help answer your brain exercise questions. A study also proves that regular exercise changes the brain to improve memory and your thinking skills too.
Age is an important factor in determining the type of exercise one needs. The brain exercises change as per the level of different potentials of an individual.
Following are some exercises divided as per age factor.
Brain exercises for kids
- Double Doodling Brain Exercises
It’s a bilateral drawing exercise where children have to draw two images with their hands. It helps in improving skills like writing, spelling accuracy, and symbol recognition. Get to know more of the variations in these exercises from the top best neurologist in Jaipur.
- Lazy Eight’s Brain Exercises
Here the child draws the number eight on paper or in the air using their hands. It improves eyesight and opens the creative side of the child.
- Earth Buttons Brain Exercises
Let your child sit or stand in a comfortable place. Now, tell them to put their right hand on the lips and the left one on the naval. Ahead let the children rotate both hands in a circular motion. It enhances mental alertness and improves whole-body orientation. Other than exercises if any symptoms or neurological problem is found, an expert brain doctor in Patna.
Brain exercises for Adult
- Jigsaw Puzzles Brain Exercises
Solving jigsaw puzzles assists one in multiple cognitive abilities. They are one protective factor for visuospatial cognitive ageing. Finding pieces and completing a whole picture helps to exercise your brain
- Cards Games Brain Exercises
A study in 2015 has found that card games lead to greater brain volume in different regions of the brain. The game requires memory and thinking skills, so the brain formulates these skills while playing.
- Dancing Brain Exercises
Dancing is a great way to enhance brain functioning and memory. Remembering new steps enables your brain to improve brain’s processing speed and memory.
- Building Vocabulary Brain Exercises
The brain gets involved when it comes to developing a strong vocabulary. Especially the areas that are important for visual and auditory procedures. It’s one of the great brain exercises for memory.
How to do this exercise- Read a book and note down a new word and learn its definition or meaning. Use the same word five times the next day.
All the exercise helps in developing your brain and making improvements in your body’s neurological movements too. Even some patients who are recovering from a stroke can do certain exercises to improve the stroke recovery process. Some habits restore several cognitive abilities and improve their quality of life.
Here are some brain exercises for stroke recovery individuals.
- Board games
Board games are good for engaging someone. It requires concentration, and the use of memory is also essential. It reduces boredom and stress while reducing the anxiety level. This leads to better cognition in stroke cases. The best neurologist in Gwalior can guide you ahead with medications and exercises.
- Cooking
Cooking requires patience and basic skills. However, concentration is a must when it comes to adding ingredients. Keeping an eye on the food as it cooks, definitely adds to memory senses. It also boosts cognition. The sensory stimulation is strengthened, and the process itself stimulates the various parts of the brain. The best neurologist in Saket can help with stroke recovery.
Not just cooking, but sometimes eating can help improve your memory as well. Read about the food items that can contribute to improving brain function.
- Listening to music
This activity is for everyone, and most people do it daily. An easy and helpful way to increase the attention span with focusing abilities is listening to music. People may face some speaking and language challenges while recovering from a stroke, but music can help improve memory if they sing along with the song.
- Yoga
Along with games for brain exercise, yoga can be a great method to improve your body movement and memory. It calms your mind and reduces stress. Yoga asanas need focus and concentration to perform, which helps in the sympathetic nervous system. As the nervous system controls the moment and the body’s coordination, the famous neurologist in Patna can guide you with the treatment that is trusted for any neurological disorder.
 Following are some good asanas of yoga as a brain exercise:
Following are some good asanas of yoga as a brain exercise:
- Padmasana
- Sarvangasana
- Paschimottanasana
- Padahastasana
- Halasana
These should be done carefully as it requires practice as well as physical strength.
However, if you’ve been suffering from a long term neural disease, exercises might not yield the best results for you. Booking a consultation with a trustworthy brain doctor is a must for the right medication and treatment.
Also, Read
Top 5 Neurological Disorders in Children
Neurological Disorders in Children
A growing child is vulnerable to several diseases. Attention must be paid to the nourishment and development of the child in the initial growing years. The nervous system is of utmost importance for the functioning of the body. The spinal cord, the brain, and the nerves make up the nervous system. There are four nervous system development stages in a child. At birth, the bones in the skull of the newly born baby are soft and flexible. Later, as the baby grows, the bones become strong and hard. The development of the central nervous system which comprises the brain and the spinal cord starts right when the child is in the womb. Although the nerves are formed before the birth itself, the nerve connections start to develop after birth until adolescence. Genes, infections, accidents, immune disorders, etc can cause neurological disorders in children. If the health of a child is neglected in the developmental years, it could lead to permanent damage in the future.
Given below is neurological disorders list –
Headaches
Although most headaches are not a cause of concern, one should not totally neglect them. Headaches in some cases at times can be an indicator of some serious underlying conditions. Headache is a sharp sensation of pain in the head. Based upon the symptoms, one can identify the underlying cause of the headache. Migraine, stress, cluster headache, dental problems, headache due to straining of the eye, etc are some of the underlying conditions that may cause headache among children. Consult a neurologist in Delhi if your child has persistent headaches.
Autism
Autism also called Autism spectrum disorder(ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by problems with communication and social interaction. Children with autism may have difficulty in achieving developmental milestones at the same rate as their peers. They could have poor communication skills and may refrain from interacting in groups. The exact cause of autism is unknown. Usually, a child is at the risk of having autism if an immediate family member has it, or because of genetic mutations. Being born with low weight, or to older parents, being exposed to toxins or heavy metals, etc are some of the possible causes of autism. One needs to pay close attention to children to know whether they have autism or not. The symptoms are quite evident when the child is 2 to 3 years of age. Delayed speech, lack of eye contact, repeated use of words or phrases, narrow range of interests, etc. are some of the symptoms of autism in children.
ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a chronic mental health disorder. It is mainly characterized by hyperactivity and impulsive behaviour. Children with this disorder find it difficult in paying attention, focusing on a single task or sitting for long hours. ADHD is common in both adults and children. However, ADHD often begins in childhood itself. Genes and heredity, reduction of dopamine, head injuries, prematurity, etc are some of the factors of ADHD. Generally, CNS stimulants are prescribed in cases of ADHD. Mindfulness meditation is another option for this brain disorder in a child. If a child is dealing with ADHD, parents and teachers need to work together, to ensure they cope up with studies at school.
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that affects a person’s movement, maintaining balance, and posture. A common motor disability in childhood, CP is caused due to abnormal brain development in the brain. The symptoms of cerebral palsy may differ from person to person. Some children may face problems with walking or sitting, others may find it difficult swallowing food, or maintaining eye muscle balance. Being too stiff or floppy, delays in motor skill milestones, difficulty in speaking, swallowing food, drooling, lack of muscle coordination, etc are some of the symptoms of Cerebral Palsy.
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is rather a common condition in children. Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by seizures. The nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, thus causing frequent outbursts of electrical energy. Caring for children with epilepsy can be difficult as one does not know when or where the seizures occur. Most children outgrow epilepsy by the time they are teenagers with the help of proper neurological disorder treatment. It is necessary that parents pay serious attention to children. Identifying a seizure is an important task. Rapid blinking, staring continuously, confusion, unusual breathing and facial expressions, muscle movements, etc are some of the signs of a child having a seizure.
If you suspect your child has any of the above-mentioned disorders, or any other neurological disorders, you must consider online neurological consultation.
How do I know if my child has a neurological disorder?
It is necessary that as parents, you have a neurological disorders introduction and a fair idea of the symptoms. Although it’s difficult to know when your child needs specialized medical assistance, there are few signs that you should look out for –
- Delays in reaching developmental milestones
- Lack of coordination
- Abnormal head growth
- Seizures, variations in muscle tone
- Slurred speech
- Persistent headaches
- Hyperactivity
For treatment, appoint a neurologist online consultation, consult the online the famous neurologist in Patna, Dr Chandril Chugh, a best neuro physician in Patna or top neurosurgeon in Patna. He is also the top neurologist doctor in Jaipur, a brain specialist doctor in Faridabad or top neurosurgeon in Patna, neuro physician in Jaipur , a best neuro physician in Patna or neurologist doctor in Gwalior, neurosurgeon in Patna and brain specialist doctor in Delhi. He is also amongst the top neurosurgeons in Patna. You can also go for a neurologist online consultation or neurologist online chat. You can also learn about what causes brain hemorrhage, aspartame side effects of the brain, can a neck massage cause a stroke or not, which mattress is good for spondylitis elders dural, the best food for nerve repair, pillow for ankylosing spondylitis, and brain attack symptoms in Hindi from the best neuro physician in Patna. You can get the best advice from the top neurosurgeon in Patna and also from the best neuro physician in Patna. Not only is he a famous neurologist in Patna but also a Gwalior neurologist doctor.
Also Read
Complication And Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis Amidst Covid
Can Covid 19 Cause Brain Damage?
Body Positivity And Its Importance
All You Need To Know About Dementia
Dementia Meaning : Dementia is a general term for disorders of the brain characterized by cognitive decline. Dementia is not a specific disease rather a common term to describe symptoms of memory loss, impairment in thinking, language judgement, and behaviour. These are the main dementia features. If one has any two of these symptoms, they may have dementia. Dementia meaning is very essential to know and it can be progressive in nature i.e they develop over time whereas some dementia can be cured and reversed as well.
Dementia symptoms can be divided into two types. These symptoms may vary
Dementia Symptoms
Dementia symptoms can vary from person to person depending upon the type of disorder they have. Here are a few possible Dementia symptoms that someone with dementia may experience.The main Dementia symptoms are:
- Memory loss- this could be as simple as forgetting names, dates or phone numbers.
- Difficulty in completing daily tasks
- Struggling with words, language, difficulty in communication
- Impairment in judgment and problem solving
- Disorientation and confusion
- Impaired coordination and motor functions
- Weakened visual abilities
Some of the psychological changes one may experience are –
- Anxiety, frustration
- Changes in behaviour
- Personality changes
- Paranoia
- Agitation
- Hallucinations
- Sudden mood swings
- Feeling lost and losing interest in things
If you are facing any of these symptoms, you should consider consulting a neurologist in Faridabad. You can also find him as a famous neurologist in Patna or brain doctor in Patna, top best neurologist in Jaipur, best neurologist in Gwalior or famous neurologist in Gwalior, neurologist in South Delhi, best neurologist in Faridabad. You can also go for neurologist online consultation or talk to a neurologist online.
Dementia Causes
Generally, dementia disease is caused by the degeneration of neurons. Disturbances in other body parts and their effect on the working of neurons, too can cause dementia disease. Another cause of dementia disease is neurodegenerative diseases. In neurodegenerative diseases, the brain cells stop function gradually and eventually end up dying. This type of dementia disease is seen in elderly people which is dementia in elderly. Dementia elderly care should be taken.Thus, the neuron connection is lost in dementia elderly and one is unable to function properly. Vascular dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Dementia, tumours, etc are some of the neurodegenerative diseases which mostly happens in dementia elderly. Dementia elderly care should be taken positively. If Dementia elderly care is not taken, then it can lead to further complications.
For any problems related to the brain you can consult the brain specialist doctor in Delhi . The Patna clinic provides you with a top neurologist doctor in Jaipur or neuro physician in Jaipur, best neurologist in Saket, best neurologist in South delhi, neurologist in Agra, mind doctor in Delhi, brain specialist doctor in Faridabad , top neurosurgeon in Patna and a best neuro physician in Patna or neurologist doctor in Gwalior.
Dementia Types
Dementia disease can be of several types. Here are a few types.
- Progressive Dementia – here, the disease grows over a period of time.
- Alzheimer’s Disease – Very often, people believe Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease to be one and the same thing. However, Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia. A person suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, the brain cells progressively degenerate and wipe out the person’s memory. It is usually common in people with dementia aged 65 or above. Treating Alzheimer’s Disease may require a lot of patience and care.
- Vascular Dementia – This is usually caused due to several strokes, often known as silent strokes. The most common symptom of vascular dementia is poor judgement and reasoning.
- Lewy body Dementia – Also known as dementia with Lewy bodies, this disorder is associated with abnormal deposits of the protein alpha-synuclein in the brain. Common symptoms include hallucinations, acting in one’s sleep, problems with focus and attention.
- Frontotemporal Dementia – This is an umbrella for a group of disorders that affect the frontal and temporal lobes. These are the parts of the brain responsible for personality, behaviour and language.
- Mixed Dementia – Mixed dementia as the name suggests is a combination of disorders. This is common among people over the age of 80. Most often it is a combination of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
For any neurological problem, you can also go for neurologist online consultation or neurologist online chat. You can also get to know about what causes brain haemorrhage , aspartame side effects of the brain , can a neck massage cause a stroke or not, which mattress is good for spondylitis, elders dural , best food for nerve repair, pillow for ankylosing spondylitis and brain attack symptoms in hindi from the best neuro physician in patna.
Dementia like disorders
- Huntington’s disease – here, dementia is caused due to inherited genetic conditions. This genetic condition causes nerves in the brain and spinal cord to degenerate. The symptoms usually start to show up between 30 to 50 years of age.
- Parkinson’s disease – This is a progressive movement disorder that causes problems like stiffness, tremors, difficulty in walking, maintaining balance and coordination problems among people suffering from the disease.
These days, teleconsultation is available for online neurologist consultation for all neurological disorders. For further complications A prior check-up with a famous neurologist in Patna, Dr. Chandril Chugh, who is also a Gwalior neurologist doctor is a must for the right medication and treatment of neurological disorders. He is one of the top 5 neurologists in Patna. He is also amongst the top neurosurgeons in Patna. You can get the best advice for any nervous disorder from the top neurosurgeon in Patna and also from the best neuro physician in Patna.
Dementia treatment
Dementia treatment depends upon the type of disorder one has. Since brain cell death cannot be reversed, medications and non-drug therapies are the two treatments that can alleviate symptoms of dementia.
Medications –
- Cholinesterase inhibitors- These try to improve communication between nerve cells. Cholinesterase inhibitors increase the chemical acetylcholine. This may help in improving memory and judgment.
- Memantine – Memantine may help with memory, attention, reasoning, and language. It works by regulating glutamate and delaying cognitive and behavioral symptoms.
- Other medications – doctors may prescribe other medications to alleviate symptoms of dementia such as anxiety, depression,
Therapies –
- Occupational therapies – An occupational therapist can help the patient to make their homes safer, teach them how to be more safe and secure with tasks such as walking, cooking, driving, etc. They will also teach the patient coping behaviors.
- Modifying the environment – decluttering the patient’s room and reducing the noise enhances their ability to function and focus. It’s best that harmful objects such as knives are out of the patient’s reach. You can even keep track of the patient through monitoring systems in case they wander, or are lost.
- Modifying tasks- With the help of a therapist and healthcare provider, daily tasks such as cooking, bathing or grooming, etc can be broken down into simple manageable tasks.
For neurological disorders, you can consult Dr. Chandril who is a neurosurgeon in Patna as well as a famous neurologist in Patna.
Also Read
Body Positivity And Its Importance
Why Do Elder’s Suffer From Alzheimer’s?
Epilepsy Vs Seizures
Bell’s Palsy: Its Uncertainty & Ways To Treat It?
What is Bells Palsy?
Bell’s palsy, also known as ‘acute peripheral facial palsy of unknown cause’, is a medical condition that causes a temporary paralysis or weakness of the facial muscles. Facial paralysis can be a daunting problem as it damages the aesthetics of the face. A person suffering from Bell’s Palsy usually has one side of the face that droops or becomes stiff. This is because of swelling, compression or inflammation in the nerves that control your facial muscles. This disorder can occur anytime at any age. However, by following Bells palsy: Treatment guidelines 2021, this condition can be cured.
Symptoms
The symptoms of bell’s palsy may appear suddenly and abruptly. They may also appear after you’ve had an infection in the eye or the ear, or if you have a severe cold.
Some of the symptoms are given below -
- Drooling
- Stiffening of the face
- Difficulty in eating, drinking
- Difficulty in moving face, or facial expressions
- Dry eyes and mouth
- Sensitivity to sound on the affected side of the face
- Irritation of eye on the affected side
- Headache
Most often bell’s palsy is mistaken for a stroke. However, it’s not a stroke if the paralysis is limited to the face. In rare cases, the face can be affected on both sides.
How to prevent Bells Palsy?
Currently, there’s no way to prevent or avoid bell’s palsy. However, if you have any of the symptoms above, consult a neurologist in Jaipur or top best neurologist in Jaipur. You can also find him as a famous neurologist in Patna or brain doctor in Patna, best neurologist in Gwalior or famous neurologist in Gwalior, neurologist in South Delhi, best neurologist in Faridabad. You can also go for neurologist online consultation or talk to a neurologist online.
Causes of Bells Palsy
The main cause of this disorder is not known. However, according to several doctors, it’s generally because of damaged facial nerves. There are other studies that point out the various causes of Bells Palsy. Some of them are-
- Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV (Infectious mononucleosis)
- Mumps virus
- Flu or influenza B
- Coxsackievirus (Hand-foot-and-mouth disease)
- Cold sores and genital herpes (herpes simplex)
- Chickenpox and shingles (herpes zoster)
- Cytomegalovirus infections
- Adenovirus (Respiratory illnesses)
- German measles (rubella)
What is the fastest way to cure Bells Palsy?
Usually, for a person to recover from bells palsy, it takes roughly around 6 months. However, for a speedy recovery, it’s best if one gets the bells palsy physiotherapy treatment. A physiotherapist will evaluate your situation based upon your medical history and your present condition, symptoms. They will identify the patterns of weakness on your face by conducting a physical examination. According to what suits you, they will suggest some exercises that will help in quick recovery.
Given below are a few Bells Palsy treatment exercises that one can practise at home.
Facial stimulation
To begin with facial stimulation, you need to first sit in front of the mirror and scrunch up your face. Begin with trying to move the affected part of your face. You may notice that one side of the face can make the movements faster and higher as compared to the drooping side.
- Gently and slowly try to copy the movements similar to the unaffected part.
- You may use your hands to aid you in the process.
- Do this once or twice every day.
Exercises for the eye
It’s important that people with Bells Palsy take good care of their eyes. Bells palsy makes it difficult to close the eye, thus making the eye and the parts of the eye vulnerable to damage. Your eye can go completely dry and debris can cause harm to it. Using a patch to protect the eye from any external damage. Apart from this, you may try some exercises that will help you regain control over your eye movements.
- Practise shutting your eyelid with your fingers.
- Practise shutting your eyes and opening them wide open.
- Alternate raising your eyebrows and lowering them. Gently massage your eyebrows and try shutting them.
Nose and cheek exercise
The cheeks and the nose are yet another crucial part of the face. Stiffness or weakness in this region can affect the entire face as you recover. One needs to practise the exercises of the cheeks and nose on a daily basis.
- To improve the movement of the nose and the cheek muscle, try scrunching up your face.
- Puff up your cheeks and blow the air out. This may seem difficult at the start however, one needs to practise this on a daily basis. Repeat this at least 10 times a day.
- Try inhaling through the affected part of the nose to flare up the nostrils. You may do this by covering the unaffected nostril, and forcing the affected part to inhale harder. If you have difficulty breathing through the affected nostril, you may try various combinations of deep and slow breathing to inhale better.
- Practise wrinkling your nose and use your fingers to lift up the cheek.
Mouth exercise
While working on your mouth, try engaging your lips and tongue. Many a time, people find it difficult to eat or drink as the muscle movement is limited. Some also have no control over the saliva, and often find it dribbling from the mouth. Here are a few exercises for the mouth that one can practise on a daily basis (at least 10 to 20 times a day) -
- Practise smiling and frowning.
- Try puckering your lips and relaxing them.
- With the help of your fingers try lifting the affected side of your mouth.
Nerve Strengthening Exercises: Boost Your Nervous System with Food and Fitness
The nervous system acts as the command center of your body, orchestrating every movement, thought, and reflex. Its intricate network of nerves ensures seamless communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body. However, like any system, it requires care and maintenance to function optimally. Engaging in nerve strengthening exercises and consuming the right foods are effective ways to enhance nerve health, support reflexes, and maintain mental sharpness.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the best exercises and foods for strengthening your nervous system, alongside precautions and tips for maintaining its health.
The Importance of a Healthy Nervous System
A robust nervous system ensures quick reflexes, efficient coordination, and sharp cognitive abilities. It helps regulate vital functions, including:
- Heart rate and breathing.
- Muscle movements and reflexes.
- Sensory perception.
- Emotional responses.
When the nervous system is compromised, symptoms like numbness, tingling, slow reflexes, and cognitive decline may occur. To prevent such issues, it’s essential to incorporate practices that support its health, such as exercise and a nutrient-dense diet.
Top Nerve Strengthening Exercises
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in maintaining and improving nervous system health. The following exercises are particularly effective for strengthening nerves:
1. Daily Walks

Walking is one of the simplest yet most effective activities to enhance nervous system function.
- How It Helps: Walking boosts blood circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the brain and nerves. It also reduces stress and improves mood by increasing endorphin levels.
- How to Start: Begin with 15-minute walks and gradually increase to 30 minutes or more each day.
2. Aerobic Exercises

Aerobic activities, such as swimming, cycling, and jogging, promote nerve health by encouraging deep breathing and better circulation.
- Benefits:
- Increases oxygen supply to the brain and nerves.
- Enhances neuroplasticity, which is the brain's ability to adapt and form new connections.
- Boosts production of endorphins, which reduce stress and improve mental clarity.
- Recommendation: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week.
3. Stretching Exercises

Stretching improves flexibility and promotes better communication between nerves and muscles.
- Benefits:
- Enhances nerve-muscle coordination.
- Reduces tension in the muscles, alleviating pressure on nerves.
- Example Stretches:
- Hamstring Stretch: Loosens the back of the legs and improves nerve mobility.
- Cat-Cow Stretch: Promotes spinal flexibility and relieves tension.
4. Yoga for Nerve Health

Yoga integrates physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to strengthen the nervous system holistically.
- How It Helps:
- Reduces cortisol levels (the stress hormone).
- Improves balance and coordination through specific poses.
- Promotes relaxation, which enhances nerve regeneration.
- Recommended Poses:
- Child’s Pose (Balasana): Relaxes the nervous system.
- Tree Pose (Vrikshasana): Enhances focus and balance.
- Bridge Pose (Setu Bandhasana): Stimulates the nervous system and improves blood flow to the brain.
Top Foods to Strengthen Nerves
A healthy diet complements exercise in promoting nerve health. Certain foods are particularly beneficial due to their nutrient profiles.
1. Eggs

Eggs are rich in choline, a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that supports brain and nerve communication.
- Benefits: Enhances memory, learning, and nerve repair.
2. Avocados

Avocados are nutrient-dense and packed with healthy fats, vitamin K, and folate.
- Benefits:
- Improves nerve function by stabilizing blood flow to the brain.
- Supports concentration and reduces the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
3. Green Leafy Vegetables

Spinach, kale, and broccoli are loaded with vitamins and antioxidants essential for nerve health.
- Key Nutrients:
- Vitamin B Complex: Supports neurotransmitter function.
- Magnesium: Reduces nerve excitability and promotes relaxation.
- Vitamin C and E: Protect nerves from oxidative stress.
4. Fish

Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and mackerel are rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, which are crucial food for nerve repair
- How It Helps:
- Maintains the myelin sheath, a protective covering around nerves.
- Enhances communication between neurons.
5. Pumpkin Seeds

These tiny seeds are rich in magnesium, zinc, iron, and copper—all of which are essential for proper nerve function.
- Benefits:
- Prevents oxidative stress in nerves.
- Enhances signal transmission between neurons.
6. Nuts

Almonds, walnuts, and hazelnuts are excellent sources of Vitamin E and healthy fats.
- How They Help:
- Protect nerve cells from damage.
- Support nerve signaling and overall brain health.
7. Foods Rich in Vitamin B

Foods like lentils, sardines, and almonds are packed with Vitamin B6 and B12, which are crucial for nerve health.
- Benefits:
- Promote nerve repair and regeneration.
- Prevent nerve damage associated with deficiencies.
For more insights into nerve-friendly foods, read Foods That Can Heal Damaged Nerves.
Precautions While Strengthening Nerves
While exercise and diet are crucial, taking precautions ensures safe and effective nerve strengthening.
1. Start Slowly
Avoid jumping into high-intensity exercises. Gradually increase the intensity and duration to prevent overexertion.
2. Avoid Strain
If you have injuries or conditions like peripheral neuropathy, opt for low-impact exercises such as swimming or yoga.
3. Seek Professional Guidance
- Consult a neurologist if you experience persistent nerve pain or discomfort.
- Consider booking an Online Neurologist Consultation for personalized advice.
4. Use Recovery Aids
Tools like acupressure mats or foot massagers can alleviate tension and improve circulation in the nerves.
The Science Behind Exercise and Nerve Health
Regular exercise offers the following benefits for the nervous system:
- Enhanced Neuroplasticity: Exercise promotes the formation of new neural pathways, improving learning and memory.
- Improved Blood Flow: Increases oxygen and nutrient delivery to the brain and nerves.
- Reduced Stress: Lowers cortisol levels, which can otherwise harm the nervous system.
- Nerve Regeneration: Stimulates the growth of new nerve cells, particularly in damaged areas.
FAQs About Nerve Strengthening Exercises
1. What are the best exercises to strengthen nerves?
Daily walks, aerobic exercises, stretching, and yoga are highly effective for supporting nerve health.
2. Can exercise help repair damaged nerves?
Yes, regular exercise promotes nerve regeneration and enhances overall function.
3. Are there any foods that improve nerve health?
Yes, foods rich in Omega-3s, Vitamin B, and antioxidants—like fish, nuts, and leafy greens—are excellent for nerve repair and protection.
4. How soon can I see results from these exercises?
Consistent exercise and a balanced diet can lead to noticeable improvements in nerve health within a few weeks to months.
5. Can I exercise if I have a neurological condition?
Yes, but consult a healthcare professional to create a safe and effective exercise plan tailored to your condition.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy nervous system is essential for physical and mental well-being. Incorporating nerve strengthening exercises such as walking, yoga, and stretching into your routine can enhance nerve function and overall health. Pairing these exercises with nutrient-rich foods like eggs, fish, and green leafy vegetables further supports the nervous system.
By starting slowly, staying consistent, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can strengthen your nerves and enjoy improved reflexes, mental clarity, and physical coordination. Small lifestyle changes today can lead to a stronger, healthier nervous system for years to come.
Stay active, eat well, and take charge of your nerve health today!
6 Most Common Neurological Disorders
The nervous system is divided into two primary regions- the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous systems. The central nervous system or CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system or PNS consists of everything else. Neurological disorders are disorders of the brain, the spinal cord and all the nerves present in the body.
Here is the most common neurological disorders list :
- Alzheimer’s disease
One of the most common disorders in the elderly, Alzheimer’s, is a progressive disorder. Alzheimer’s and phantom pain is a prevalent condition among people over the age of 65. Depending on the intensity of the disease, a person may experience mild, moderate or severe symptoms. Alzheimer’s disease may start with minor invisible symptoms such as forgetting names, events, phone numbers, etc. It is a progressive disease, and over some time, one may experience extreme symptoms such as difficulty in swallowing or breathing, etc. This is because neurons that used to carry out functions in the body previously start to degenerate rapidly. With proper care and appropriate medications, this neurological disease can be treated. Talk to a neurologist online if you need guidance for this disorder.
Migraine
Migraine headache is one of the most common neurological conditions. It is a recurrent headache, usually affecting just one side of the brain, and is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and light sensitivity. The impact of a migraine headache can last for several days, thus impairing the person’s ability to perform and carry out the daily tasks. Migraine can take place in several stages- prodrome, aura, attack and postdrome. Hormonal changes, stress, anxiety, changes in the environment such as loud noise, strong smells, bright lights, etc., can trigger a migraine. While there is no cure for migraine, with the help of certain medications, the frequency and severity of migraine headaches can be reduced. If you suffer from this condition, you should consult a neurologist. They will give you the proper treatment for migraines.
Stroke
Strokes are yet another most common neurological disorders. Strokes are life-threatening conditions that can happen to anyone. Strokes occur when the vital flow of blood and oxygen supply is cut off from a part of the brain, causing it to break down and stop functioning. A stroke needs immediate medical attention. Otherwise, it can be fatal or cause a haemorrhage in the brain or permanent disability. One should immediately call for help and get the required medical attention that the patient needs to help the person having a stroke. Special care needs to be taken of the patient as a stroke can have a considerable impact and shock. Can a neck message cause stroke? is an often asked question. Generally, craniotomy is one of the most common neurosurgery procedures used to treat strokes.
Epilepsy
Very often, epilepsy and seizures are the two most common neurological terms that are used interchangeably. Epilepsy is a chronic condition where one has recurrent seizures. The nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, thus causing frequent outbursts of electrical energy. It is common among children and older adults. Epileptic people often have recurring seizures, which can cause harm to them. These seizures are, as we know, broadly of two types - focal and generalised. Epilepsy seizures can be different for different people. There are several reasons why a seizure can be triggered. While some people can live on their own and manage their seizures by themselves, others, on the other hand, may need a lot of care and attention.
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s is yet another progressive neurological disorder. Here, the part of the brain responsible for movement is affected. The onset of this disease usually starts when the person is in their 60s. Some of the common symptoms are trembling hands, slow movements, stiffness in hands, legs, etc. The problems with balancing, low volume speech, reduced swinging of the arms while walking, etc., genetic factors or environmental factors can cause Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor may prescribe a few medications and a few exercises and lifestyle modifications to reverse this disease’s effects. For treatment, consult the top neurophysician in Patna. He is also the top neurologist doctor in Jaipur, a brain specialist doctor in Faridabad, mind doctor in Delhi, best neurologist in South Delhi, Best neurologist in Saket, a top neurologist in Gwalior or neurologist doctor in Gwalior.
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a long term disorder affecting the central nervous system that affects the brain, the spinal cord and the optic nerves. In this disease, the immune systems attack the protective layer (myelin) covering the nerves. Multiple sclerosis causes inflammation and lesions, making it difficult for the brain to send signals to the body. Loss of vision, pain, fatigue and impaired coordination are some of the symptoms of Multiple sclerosis. The exact cause of this disorder is unknown; however, according to several types of research, toxins and virus can be one of the causes of this disease. Treatment usually focuses on physiotherapy and slowing the progression of the disease.
Apart from these, Bell’s palsy, Third nerve palsy, Fourth nerve palsy, Sixth nerve palsy are some of the most common neurological disorders of cranial nerves. Neurological disorders are challenging to deal with. However, with proper treatment and friends and family, one can cope with neurological disorders.
Epilepsy vs Seizure
Epilepsy vs Seizure: Key Differences, Causes, and Treatments Explained
Often epilepsy and seizures are mistaken and used interchangeably by people. This is where the confusion arises, as both epilepsy and seizures are neurological disorders with somewhat similar characteristics. However, in reality, there’s a lot of difference between epilepsy and seizures.
Knowing the difference between epilepsy and seizures could help save someone’s life—or at least help them get the right care sooner.
In this blog, we will break down the epilepsy vs seizure topic clearly and simply. You’ll understand what each term means, how they’re related, how doctors diagnose them, and what treatment or lifestyle changes might be needed.
What is a seizure?
Seizures are sudden bursts of electrical activity in the brain. They may last only a few seconds or go on for minutes. Not every seizure is a sign of epilepsy.
Definition of a seizure
A seizure is a temporary disturbance in brain function caused by abnormal electrical signals. These bursts can lead to shaking, staring spells, confusion, or even loss of consciousness.
Common causes of seizures
- High fever (especially in young children)
- Head injuries
- Very low blood sugar
- Sleep deprivation
- Use or withdrawal of drugs or alcohol
- Stroke or brain infections
Epilepsy vs seizure: These causes are often one-time events and don’t always mean a person has epilepsy.
Types of seizures
There are many types of seizures, but here are the most common:
- Focal Seizures: Start in one part of the brain; may cause twitching or odd sensations.
- Generalized Seizures: Affect both sides of the brain; can include shaking and blackouts.
- Absence Seizures: Brief staring spells, often missed.
- Tonic-Clonic Seizures: The most dramatic body stiffens, then jerks.
Statistics: Prevalence of one-time seizures
According to the CDC, 1 in 10 people may have a seizure during their life. But only 1 in 26 will develop epilepsy.
Table: Types of Seizures and Their Characteristics
| Type | Brain Area Affected | Symptoms | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focal | One side | Twitching, confusion | 30 sec - 2 min |
| Generalized | Both sides | Jerking, loss of consciousness | 1-3 min |
| Absence | Both sides | Staring, lip-smacking | < 30 sec |
| Tonic-Clonic | Both sides | Body stiffening, then jerking | 1-5 min |
A seizure disorder refers to having frequent episodes of unprovoked seizures. Unprovoked seizures are caused out of the blue, unlike provoked seizures triggered by events such as a stroke, traumatic brain injury, etc.
Several factors can increase the risk of you having a seizure. Having a brain injury or infection in the past, severe Alzheimer’s disease, exposure to toxic substances such as alcohol, smoking, drugs, etc., having a brain tumour, frequent strokes, etc. are some of the risk factors that may lead to the debilitating condition of seizures or seizure disorder.
Epilepsy is more than just one seizure. It’s a chronic brain condition where a person has repeated seizures without a clear cause.
Definition of epilepsy
Epilepsy is a long-term disorder marked by two or more unprovoked seizures. It affects how the brain sends signals and can impact behavior, memory, and awareness.
They have further divided as-.
- Focal seizures-
- Simple partial seizures
- Complex partial seizure
- Generalised seizures-
- Absence seizure
- Tonic seizures
- Atonic seizures
- Clonic seizures
- Myoclonic seizures
- Tonic-clonic seizures
Diagnostic criteria
Doctors look for:
- Two or more unprovoked seizures
- Results from EEG (to check brain waves)
- MRI scans (to find brain damage or growths)
Underlying causes of epilepsy
- Genetic disorders
- Brain injury (car accidents, falls)
- Stroke
- Brain tumors
- Infections like meningitis or encephalitis
Epilepsy vs seizure: While seizures have triggers, epilepsy causes are usually long-term and related to the brain’s wiring.
Prevalence and demographics
WHO estimates about 50 million people have epilepsy worldwide. It's more common in children and older adults.
Epilepsy can also lead to convulsions. There is a very thin line between epilepsy, seizures, and convulsions. While epilepsy is a seizure disorder, a convulsion is a type of seizure, which may result from a medical condition. Many a time, epilepsy may involve having convulsions.
Caring for a person with epilepsy can be difficult, as the person is at constant risk of hurting themselves because of the sudden epilepsy attacks.
Here is everything you need to know about how to support someone with epilepsy:
Firstly, attention must be paid to the seizure treatment of the epileptic person. A doctor may suggest epilepsy sedative such as anti-epileptic drugs, to reduce the seizures. The doctor may also prescribe other medication, depending upon the type and intensity of epilepsy, which will help the patient recover soon. Consult the best neurologist in Delhi to attain the best treatment for epilepsy.
Attention must also be paid to the diet of the patient. Generally, a keto diet is deemed beneficial for a person suffering from epilepsy disease. Often, people with epilepsy may resort to alcohol and drugs, which must be strictly avoided.
Epilepsy vs Seizure: What’s the Difference?
This is where most people get confused. So let’s simplify it.
One-time seizure vs chronic seizure disorder
Having a seizure once doesn’t mean you have epilepsy. Epilepsy means you have had multiple seizures without a clear cause.
Diagnosing epilepsy vs identifying a seizure event
A seizure might be diagnosed after a fever or head bump. But epilepsy diagnosis takes more tests, EEG, MRI, medical history.
Why seizures don’t always mean epilepsy?
Because seizures can be caused by reversible things like fever or drugs, doctors don’t call it epilepsy unless they happen again without reason.
Table: Comparison - Epilepsy vs Seizure
| Feature | Seizure | Epilepsy |
| Frequency | One-time | Repeated |
| Cause | Often triggered (fever, injury) | Often unknown or chronic brain issue |
| Duration | Short, usually < 5 mins | Episodes over time |
| Diagnosis Tool | Observation | EEG, MRI, medical history |
| Treatment | May not be needed | Medication, lifestyle change |
Treatment Options for Seizures and Epilepsy
Treatment depends on what you’re dealing with: a one-time seizure or long-term epilepsy.
Medications
- Anti-seizure drugs like carbamazepine, valproate, and lamotrigine
- These work for 70% of people with epilepsy
- Side effects may include drowsiness or mood changes
Surgery
- Done when seizures come from one brain spot (focal epilepsy)
- Removes damaged brain area
Dietary approaches
- Ketogenic diet may help some children with drug-resistant epilepsy
- Low in carbs, high in fat
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS)
- A device placed in the chest
- Sends signals to calm the brain
Emergency seizure first-aid
- Stay calm
- Lay the person on their side
- Time the seizure
- Don’t put anything in their mouth
Table: Common Treatments and Their Success Rates on Epilepsy vs Seizure
| Treatment | Success Rate | Notes |
| Medication | ~70% seizure control | Works best with regular use |
| Surgery | ~60-80% | For focal epilepsy |
| Ketogenic diet | ~30-50% | Often used in children |
| VNS | ~40-50% improvement | For those who don’t respond to meds |
When to See a Doctor
It’s better to get help early.
After first-time seizure
Even one seizure needs evaluation.
Recurrence or worsening symptoms
If seizures become more frequent or severe, consult a neurologist.
Side effects of medication
Tell your doctor if meds make you tired, dizzy, or moody.
Emergency signs
Call emergency services if:
- Seizure lasts over 5 minutes
- Person doesn’t wake up
- Repeated seizures with no break
When Should You Book an Appointment with Dr. Chandril Chugh?
If you or someone you love has had a seizure (whether it was one time or recurring), it’s time to get answers. Dr. Chandril Chugh is a US-trained, board-certified neurologist who treats conditions like seizures, epilepsy, stroke, migraines, and more. His deep expertise in understanding epilepsy vs seizure makes him a trusted name for diagnosis and treatment.
Book your consultation now. Don’t wait until the next seizure.
Conclusion
Seizures are an important characteristic of epilepsy. Thus, a caretaker must always be ready with a first aid box and tool kit in order to handle the seizure. They must also observe and keep a record of when a seizure occurs and how frequently. In order to get someone to overcome their seizure, the caretaker should know how to help them relieve their stress and anxiety. Teaching them relaxing techniques will help them soothe themselves and calm them down. Stress is one of the reasons for seizures. By learning relaxing techniques such as meditation or yoga, you can ease out the anxiety.
Thus, epilepsy vs seizure are different. However, one must never overlook a seizure, as it could be the onset of epilepsy. Both seizures and epilepsy are critical conditions and need to be taken care of. With the love and support of close ones, one can overcome these neurological disorders.
FAQs
Is a seizure the same as epilepsy?
No. A seizure is a single event. Epilepsy is when you have two or more unprovoked seizures. If you’ve had a seizure, book a consultation with Dr. Chugh to find out if it’s epilepsy.
Can you have a seizure and not have epilepsy?
Yes. Many things like fever, drugs, or trauma can cause a seizure without epilepsy.
What triggers seizures in non-epileptic people?
Common seizure triggers include stress, lack of sleep, high fever, or alcohol withdrawal.
How is epilepsy diagnosed differently from a seizure?
Doctors look for a pattern of unprovoked seizures using tools like EEG and MRI. A single seizure doesn’t mean epilepsy diagnosis.
Can epilepsy go away?
In some children, epilepsy may go into remission. But regular care and meds are key. Ask Dr. Chugh if your type of epilepsy can improve.
Are all seizures caused by epilepsy?
No. Seizures can happen for many reasons. That’s why knowing the difference between epilepsy and seizures is important.
Can stress or lack of sleep trigger seizures?
Yes, these are common triggers and can make both epilepsy and one-time seizures worse.




 Following are some good asanas of yoga as a brain exercise:
Following are some good asanas of yoga as a brain exercise:




