How Can Diabetes Cause Nerve Damage?
Diabetes, a condition where sugar levels become higher than normal, causes damage to nerves. It is called diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes affects the blood supply to the nerves which in turn are unable to send and receive signals to and from the brain to the body leading to nerve damage. It mainly affects nerves in the feet and legs. Diabetes nerve damage is caused by high blood sugar levels, where the pain can potentially be unbearable and debilitating. Depending on the site of nerve damage and severity, the diabetes nerve pain symptoms can range from numbness in the feet and diabetes nerve pain in the legs to problems in the digestive system, blood vessels and heart. Diabetes nerve pain relief can be brought by consistent blood sugar management and adopting healthy lifestyle habits. Contact a neurologist who may advise diabetes nerve pain medication. You can also have online neurologist consultation. Following diabetes nerve pain home remedy like keeping blood pressure under control, eating healthy, not smoking and being active every day can effectively help in pain management. Learn from the neurosurgeon in Patna about the nervous system facts, foods that heal nerve damage, aspartame side effects on the brain,best food for nerve repair, complex ptsd and sleep, facts about the cns. These are the reasons to see a neurologist.
Diabetes and Nerve Pain Reasons
The reasons behind diabetes leading to nerve damage are not precisely known. It is understood that uncontrolled blood sugar levels damage nerves and affect the ability to send and receive signals. High blood sugar also damages the capillaries or the small blood vessels that take nutrients and oxygen to the nerves. In some people, low Vitamin B12 levels may also cause nerve damage. The online neurologist may prescribe blood tests to check for vitamin deficiency. Some other factors that cause diabetic neuropathy are:
- · Damaged blood vessels due to high cholesterol
- · Lifestyle factors like alcohol abuse or smoking
- · Mechanical injuries like those caused by carpal tunnel syndrome.
Diabetes Nerve Damage Symptoms
The symptoms depend on which nerves are affected and the type of diabetic neuropathy you have. Usually, you may not notice diabetes related nerve pain until considerable damage has occurred. A person can develop one or more than one of the four kinds of diabetic neuropathy:
- · Peripheral Nerve Damage: It is the most common type of nerve damage which affects lower limbs first, followed by damage to nerves of the upper limbs. Symptoms include numbness, tingling sensation, heightened sensitivity to touch, cramps and severe foot problems.
- · Autonomic Nerve Damage: It affects the nerves of the bladder, intestines, eyes, heart, stomach; symptoms include bowel problems, lowered sexual responses, lack of awareness of low blood sugar levels,
- · Proximal Neuropathy: It affects the nerves in the hips, legs, thighs, and buttocks. In some people, it can also affect the chest and abdominal area. Symptoms include severe pain, shrinking thigh muscles, severe stomach pain, and difficulty standing after sitting for a long time.
- · Focal Neuropathy: It refers to nerve damage of specific areas like the cranium. Symptoms include difficulty in focusing, pain behind one eye, numbness in fingers or hands, paralysis of one facial side, and inability to hold things due to weak muscles.
Diabetes Nerve Damage Diagnosis
The top neurologist in Jaipur will diagnose diabetic nerve damage with a physical examination, medical history and asking questions about your symptoms. He will also examine reflex actions, overall muscle strength and sensitivity to vibrations and touch. Some specialized tests like sensory, muscle response, and autonomic tests may be recommended depending on the type of nerve damage.
Diabetes Nerve Damage Risk Factors
Diabetes can eventually lead to nerve damage. But any of the following factors are likely to increase your chances of developing diabetic neuropathy:
- Uncontrolled levels of sugar in the blood heightens the risk of developing diabetic complications, including nerve damage.
- The longer you have had diabetes, the higher the chances of damage to the nerves. The possibilities become higher if diabetes has been uncontrolled.
- Being obese or having a Body Mass Index of more than 25 increases diabetes nerve damage risk.
- Smoking hardens and narrows the arteries, thus reducing the blood supply to the feet and legs. It leads to nerve damage.
- Diabetes affects the functioning of kidneys. Damaged kidneys are unable to process wastes efficiently and send toxins back into the blood causing nerve damage.
Diabetes Nerve Damage Treatment
Nerve damage is irreversible. However, the treatment is effective as the goals aim to:
- Reduce the progression of the disease
Maintaining the blood sugar levels within the range is critical to preventing or deferring the onset of nerve damage. When effectively managed, it may even reduce some of the associated symptoms. Consulting one of the top 5 neurologist in Patna will help you to identify your target range of blood sugar. Ideally, it should be between 80 and 130 mg/dL before meals and less than 180 mg/dL after meals for diabetic people.
- Reduce pain: Book a consultation with the top neurosurgeon in Patna if you are keen to consider medication for reducing pain. The medicines may not work for everyone. Each case has to be considered on an individual basis. The pain relief treatment includes anti-seizure drugs and antidepressants. The medications are known to relieve nerve damage pain even if you do not have seizures or are not depressed.
- Restore functioning by managing complications: The best neurologist in Faridabad can advise about the treatment depending on the type of neuropathy related complication. The complications could be problems associated with the urinary tract, digestive system, low blood pressure, or sexual dysfunction. You need to consult a specialist doctor along with your mind doctor in Delhi or mind doctor in Agra.
FAQs
How are nerves damaged from diabetes?
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels that supply oxygenated blood to the nerves. The damaged nerves cannot send and receive signals between the brain and other parts of the body. This causes the nerves to either send signals at the wrong time, not send at all, or send slowly. When this happens, the body responses become weak, and it causes loss of balance and numbness.
Why does diabetes cause problems for the feet?
Diabetes harms the nerves, causes infection, ulcers, and problems with blood circulation. Diabetic people are not able to feel any injury to the feet due to numbness. This exposes the person to further complications.
Is it possible to avoid diabetic neuropathy?
Yes, it is possible to avoid diabetic nerve damage by effective management of blood sugar levels.
Also Read:
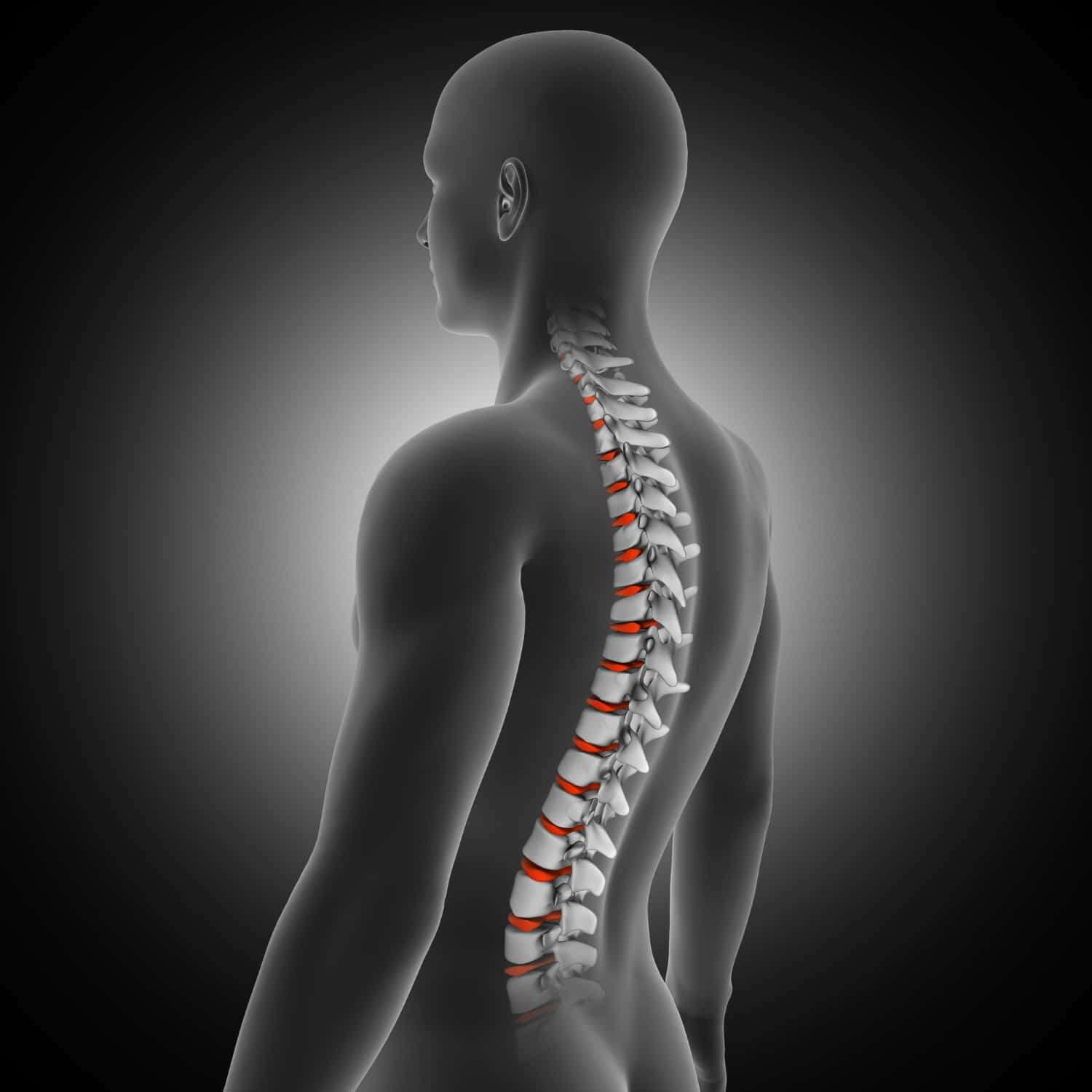
Types of Spinal Stenosis: Risk Factor & Diagnosis
Spinal Stenosis Meaning
Spinal stenosis is the shrinking of the areas within your spine. The shrinkage that generally occurs in the neck or lower back pressurizes the spinal cord or nerves that emanate from the compressed areas. An affected person will complain of severe pain in the calves, legs, and lower back while walking and standing. The pain generally eases by either sitting or leaning over, say, a chair or a countertop. The condition can cause pain, but spinal stenosis risk of paralysis has not been confirmed by scientific research. When considering if spinal stenosis can be cured, a consultation with an online neurologist can help you find treatments to relieve the symptoms.
The spinal stenosis causes are not known, and not everyone with this condition will develop symptoms. Some people may experience symptoms like numbness, pain, tingling, and muscle weakness. There are three main Spinal stenosis types: lateral recess stenosis in the thoracic region, central spinal stenosis in the cervical region, and foraminal stenosis in the lumbar region.
Spinal Stenosis Causes
The spine or the backbone extends from the neck to the lower back. The bones of the backbone form a canal that protects the spinal cord. The narrowing of the spaces within the spine may occur due to any of the following causes:
- Bone Overgrowth: Damage from osteoarthritis can cause wear and tear in the spinal bones. It leads to the formation of bone spurs that invades the spinal canal. Some bone diseases can also cause overgrowth in the spine bone.
- Thickening of Ligaments: The cords that hold the spinal bones together can become stiff, hardened, and thickened as we age. The thickened ligaments can protrude into the spine leading to reduced spaces.
- Spinal Injuries: Accidents or trauma can cause fractures in one or more spinal vertebrae. The dislocated bone may damage the spinal canal. Back surgery may cause swelling in the surrounding tissue thus, putting pressure on the spinal nerves.
- Herniated Discs: There is cushioning acting as shock absorbers present between the vertebrae that tends to dry as we grow old. Any crack in the disk may cause this soft material to break out and pressurise the spinal nerves.
- Tumours: Abnormal cell growth may occur inside the membranous covering of the spine, space between spinal cord and vertebrae, or inside the spinal cord. Such growth can press into the spinal nerves.
Spinal Stenosis Symptoms
Many people may not experience the stenosis symptoms even when their MRI and CT scans show the onset of spinal stenosis. The symptoms include:
- Tingling sensation or numbness in hands, feet, legs, or arms.
- Problems with gait, balance, and walking
- Neck pain
- Weakness in hands, foot, legs, or arms
- Pain or cramps in one or both legs that worsen on standing for long periods or walking extensively and which eases on standing or leaning forward.
Spinal Stenosis Diagnosis
Your neuro physician in Patna or the top neurologist in Patna will discuss your medical and family history to diagnose spinal stenosis. Additionally, he will also conduct a physical examination. He will prescribe several imaging tests to ascertain the cause of spinal stenosis. The imaging tests will include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI uses a combination of powerful magnetic and radio waves to produce multiple cross-sectional scans of the spine. The scan can detect tumours and damage to disks and ligaments. It can also highlight the area where spinal cord nerves are being pressurised.
- X- Rays: Creating an X-ray image of the back can show the changes in the bone structure, such as bone spurs that may be protruding into the spinal canal, thus narrowing it down.
- CT Scan: A CT scan involves staking multiple X-ray images taken from several angles to produce cross-sectional body images. If an advanced scan is done, it involves using a contrast dye to highlight the herniated disc, tumours, and bone spurs.
Spinal Stenosis Treatment
The suitability of the selected treatment depends on the location of the spinal stenosis and the severity of the condition. Talk today with a top neurosurgeon in Patna who will advise about the best option. If the symptoms are mild, the neurologist doctor in Jaipur may recommend self-care tips. If that does not help, the best neurologist in Faridabad will prescribe medications or psychotherapy. If any other treatment does not relieve the painful symptoms, one of the top 5 neurologists in Patna may advise spinal stenosis types of surgery.
- Medications: The doctor may prescribe medications. This includes pain killers, antidepressants, anti-seizure medicines, and opioids.
- Physical therapy: People with spinal stenosis usually become less active to tolerate pain. But idling can lead to the weakening of muscles which can lead to more pain on movement. A therapist can help build endurance and strength levels, improve balance, and help maintain the stability and flexibility of the spine.
- Steroid Injections: Steroidal injections do not directly treat stenosis but reduce inflammation, thus relieving pain.
- Surgery: It is considered only if other treatments do not seem to work. The surgery aims to reduce pressure on the spinal nerves by making a space within the spine.
Spinal Stenosis Risk Factors
Some factors that can heighten the risk of developing spinal stenosis are:
- Being over the age of 50
- Degenerative changes, if young
- Trauma
- Congenital spinal deformity such as scoliosis
- A genetic disease affecting muscle and bone development in the body
FAQs
Is Spinal stenosis type of arthritis?
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It leads to a loss of cushion between bones that causes them to brush against one another, causing pain, swelling and stiffness. When osteoarthritis worsens, the condition is called spinal stenosis.
Is Spinal stenosis type of neuropathy?
Spinal stenosis is an example of compressive neuropathy as it causes the spinal nerves to compress due to factors like herniated disks, bone spurs, etc.
What activities should be avoided with spinal stenosis?
Any extreme and excessive activity like back extension long walks, running, heavy sports, and certain poses that stretch the back should be avoided.
Also Read
6 Most Common Neurological Disorders
How Alcohol Affects Your Brain?
Top 12 Interesting Facts About The Nervous System
Effective Remedies To Get Rid of Migraine
Migraine is a severe headache that causes a pulsating sensation or a throbbing pain in one side of the head. The attacks can last for few hours to few days, and the intense pain can hamper your daily routine. The headaches are sometimes accompanied by vomiting, nausea, and extra sensitivity to light. Though science has not fully understood migraine reasons, environmental factors and heredity are thought to play a role.
Migraines often remain undiagnosed. Maintain a migraine report if you experience frequent headaches or throbbing pain in the head. Notice all the changes in the pattern of occurrence or if you find them suddenly different. See your doctor immediately for migraine relief. Research suggests that consuming migraine relief food rich in magnesium and omega 3 fatty acids may help people with migraines. Such foods include dark leafy green vegetables, fish like mackerel, whole grains, and legumes.
What Causes Migraine?
The causes behind the migraine attacks are not fully clear. It may be due to chemical imbalances and changes in nerves that manage pain in the nervous system. Some factors likely to trigger migraine are:
- Beverages, especially alcoholic ones and those that contain excessive caffeine
- Stress-related to work or at home
- Stimulus like bright flashing lights
- Drastic changes in sleep patterns
- Hormonal changes in women
- Certain medications like oral contraceptives
- Food additives and preservatives
How is Migraine Diagnosed?
Observe your headaches. If they occur frequently, or if you have a family history of migraines, then you need specialist treatment from a neurologist. He is likely to conduct a physical and neurological examination, consider your current symptoms and previous medical history to diagnose. Some tests like MRI and CT scans may be advised.
Ways to Get Rid of Migraines Headaches
Several migraine treatments are available that can help lessen the symptoms. It would be helpful to try different migraine remedy to identify the most effective ones. When having a migraine attack, some people might find relief by eating migraine remedy food like their comfort foods. Other people may find that lying or sleeping in a darkened room works best when experiencing a migraine attack. Some effective ways to get rid of migraines are:
- Consulting a Specialist: It is advisable to consult the best neurologist in Faridabad if you experience chronic migraine symptoms that never seem to go away. The specialist will investigate the causes and suggest further treatment.
- Pain killers: Many people who experience migraine attacks feel better with over-the-counter medications like paracetamol, ibuprofen, and aspirin. The painkillers are effective when taken on the first sign of a possible attack. This allows the body time to assimilate it into the bloodstream and reduce the symptoms. The medicines should be taken before the headache worsens to make it effective. It is advisable to contact a neurologist even if you are taking over the counter medicines as they may cause side effects. You should carefully read and follow the instructions given on the package.
Painkillers can make migraines worse in some people. The online neurologist may recommend you to stop using the painkillers if he feels that the frequent use contributing to the migraine. Talk with one of the top 5 neurologist in Patna to avoid medication overuse. The top neurosurgeon in Patna or Gwalior Neurologist doctor may advise more suitable medications or medicines with triptans.
- Triptans: If regular painkillers are not relieving the symptoms of severe headaches, you should immediately seek medical consultation with a top neurologist in Jaipur. He may advise taking triptan and some anti-sickness medicine. Triptans are special painkillers aimed at treating migraine headaches. The medicines are thought to reverse the brain alterations that cause migraines.
Like any other medicine, Triptans may also have mild side effects that include flushing, warm sensations, tingling, and feeling of heaviness in the chest, limbs, or face. Some people may also feel drowsiness, dry mouth and sickness. It is best to have a follow-up routine with your neurologist doctor in Jaipur. He will help you to assess the effectiveness of triptans. If there are little or no side effects, expect the treatment to continue. If you experience side effects, he may put you on a different triptan as everyone responds differently to medications.
- Anti-sickness medicine: These medicines are known to be effective for some people in treating migraines. Though they are prescribed for sickness, they are beneficial even if a person affected with migraine is not feeling sick. These prescription medicines, also called anti-emetics, can be taken along with triptans and other painkillers. They are more effective if taken before the onset of the attack. The medicine may also cause some side effects like drowsiness and diarrhea.
- Combination Medicines: It is best to consult a mind doctor in Delhi before buying medicines for treating migraines. However, some combination medicines are available at a pharmacy as over the counter meds. They are a combination of both anti-sickness medicine and painkillers. They may be convenient, but the potency is not strong enough to relieve the headache symptoms. In that case, it is best to take separate anti-sickness and painkillers.
- Acupuncture: When you are looking for ways on how to get rid of migraines fast, you may ask the help of your neuro physician in Jaipur or a famous neurologist in Patna. He may advise you to try acupuncture also along with medicines for a more effective migraine remedy.
FAQs
Are there any ways to get rid of migraines naturally?
Severe migraines need medical intervention for a cure. However, mild to moderate migraine symptoms can be relieved with natural methods like applying soothing oils like lavender oil, peppermint oil, eating ginger, trying relaxing techniques like meditation, massage, and yoga.
Does a migraine cause a stroke?
No migraine does not directly cause a stroke. Though stroke may be more common in people with migraines, but it is not a risk factor.
How can I know if my headache is a migraine?
Though a migraine is a type of headache, but all headaches are not migraines. When the pain occurs in one side of the head and stays for more than a few hours, it is called a migraine.
Also Read
Back Pain After Covid: Causes And Treatment
Top 6 Signs Of Nervous Breakdown
Signs Of Nervous Breakdown Meaning
A nervous breakdown describes a period of extreme emotional distress. The stress is so overpowering that the affected person is unable to undertake their regular activities. The nervous breakdown clinical term is not a medical term in the true sense. It implies an unhealthy response to stress and is indicative of an underlying issue such as anxiety or depression. No single factor can be attributed to nervous breakdown causes, but anything that leads to stress can trigger it. Managing factors that cause pressure can help in nervous breakdown recovery. Making lifestyle changes and speaking to someone like an online neurologist about stress-causing issues can help identify solutions and aid as a nervous breakdown cure.
Nervous Breakdown Is It Real?
The condition is real as it affects the quality of life. Being unable to manage stress may create a feeling of being overwhelmed that hinders your daily routine. In some people, a nervous breakdown may also cause complex PTSD and sleep disorder. One or more of the following factors can trigger a nervous breakdown:
- Traumatic experience
- Unstable work-life balance
- Family history of mental health conditions
- Chronic medical conditions
- Abusive relationships
- Grief and loss of loved one
- Persistent stress at work or burnout
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Abuse
- A tragic event
- Financial problems like loss of income
Nervous Breakdown Symptoms
A nervous breakdown is a temporary inability to function normally. It is one of the prime reasons to see a neurologist. A person experiencing a nervous breakdown or feeling overwhelmed may show a few or more of the following nervous breakdown signs and symptoms.
Here are the top 6 signs of nervous breakdown:
- Depression or Anxiety: It includes responses like low self-esteem, feeling irritated, worried, or getting angered on every pretext. It also means feeling helpless or crying uncontrollably. You may also feel like withdrawing from family, friends, and social activities, losing interest in otherwise favourite activities. The affected person may be having thoughts of suicide or try to inflict self-harm.
- Concentration problems: Long-lasting stress can cause structural changes to the brain, affecting memory and making concentration difficult.
- Insomnia: Stress most often makes people worried, full of anxiety and either unable to fall asleep or stay asleep. When you cannot sleep, the brain and body do not rest and cannot recover from stress, leading to worsened anxiety and stress. Sleep deficiency affects both physical output and mental performance. Some people may also oversleep as a response to stress which also is equally unhealthy.
- Fatigue: You may feel tired if you are either not getting enough sleep or are sleeping too much. The long-term exhaustion coupled with stress can cause a nervous breakdown.
- Changes in Appetite: Some people cope with stress by overeating which leads to excess weight gain. But for some other people, it may also lead to appetite loss. The twin problems of stress and anxiety can cause stomach problems like constipation, bloating, diarrhoea. Stress can aggravate irritable bowel syndrome.
- Hallucinations: In extreme stress, you may hear or see things that are not present.
Nervous Breakdown Diagnosis
As the term is not clinical, there is no way to diagnose a nervous breakdown. If you or someone you know feels distressed and overcome by feelings of stress or anxiety, they need to contact a neurologist doctor in Jaipur or a migraine doctor in Jaipur. The doctor will help to identify the factors that may be contributing to the problem.
Nervous Breakdown Treatment
Often life can be overwhelming. It may feel like it is getting out of hand or challenging to manage everything. But if it becomes a frequent occurrence, then you need to consult the best neurologist in Faridabad. Your mind doctor in Agra may refer you to a psychiatrist or psychologist.
The top neurosurgeon in Patna may advise a treatment plan according to the cause of a nervous breakdown and your emotional, behavioural, and psychological conditions. Some common treatments that may prove beneficial are:
- Lifestyle changes: Adding some form of exercise to daily activities to take the mind away from stressors. Make healthy and mindful eating a part of the diet, practising meditation, and taking a break from work or other things that cause stress. You can make it a point to spend some time in nature and reduce your obligations to make them manageable to finish.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medicines like antidepressants to help control and manage anxiety levels. The doctor may also advise on medicines or aids to help you sleep better. It can help in inducing sleep, breaking out of the sleeplessness cycle and reducing stress.
- Psychotherapy: A session with a psychotherapist or a mind doctor in Delhi can help you process your thoughts and figure out solutions to reduce stress. Speaking about your worries and concerns often helps in relaxing and making sense of everything.
Feeling overwhelmed and experiencing emotions is a part of the ups and downs of life. But if they frequently hamper the daily activities, the stress can become unmanageable and lead to a nervous breakdown. It would be best if you altered your lifestyle to manage it and get back to normal. Consulting a doctor or a psychologist can help you in this process.
FAQs
How can I know if I am having a nervous breakdown?
To assess if you have a nervous breakdown, look for symptoms like are you constantly worried, do you get easily irritated or angered, or feel helpless? You may also have lost interest in your favourite activities and not interested in meeting family and friends.
How do I manage my nervous breakdown?
To manage a nervous breakdown, you need to care more for yourself and bring out specific changes to your lifestyle. Make an effort to make friends and socialise with family, learn, and practise relaxation techniques like meditation. Aim to sleep at least eight hours a night. Spend some time alone to process your thoughts.
Is it possible to recover from a nervous breakdown?
Yes, a full recovery is possible from a nervous breakdown. It is not a disease in the medical sense but is indicative of underlying concerns like depression. Treatment may involve counseling sessions and medicines.
Also Read
How To Help Someone With Covid From Afar?
Superfoods For The Super Working Of The Brain
Brain Anatomy And How It Works
How Being Overweight Can Influence Your Risk Of Getting Stroke?
Have you ever wondered how your body weight could affect your brain? What if carrying a few extra kilos around your waist was silently raising your risk of getting stroke?
It might surprise you to know that being overweight isn't just about how you look; it deeply affects your blood vessels, your heart, and most importantly, your brain. In this blog, we will explore how body weight plays a crucial role in increasing your risk of getting stroke, backed by facts and practical health advice.
We will look at what happens inside your body when you're overweight, the real dangers it brings, and what you can do today to lower your chances. Let's break this down together in a way that's easy to understand.
What is a Stroke?
A stroke happens when blood can’t get to a part of your brain. This stops your brain cells from getting oxygen. When that happens, those cells start to die quickly.
There are two major types of strokes:
- Ischemic stroke: Caused by a blocked artery. This is the most common type and makes up about 87% of all strokes.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: Caused by bleeding in the brain due to a burst blood vessel.
According to the World Health Organization, stroke is the second leading cause of death worldwide. It’s also a major cause of disability.
Understanding this helps us realize why weight matters so much. Stroke isn't just an "older person" problem. It can happen at any age, especially when certain risk factors like obesity are present.
Read: 10 Healthy Habits for a Stronger Heart
What Role Does Weight Play in Brain and Heart Health?
Let’s look at how extra weight impacts key body systems that keep your brain safe:
When someone is overweight, the body has to work harder to pump blood. That causes pressure to rise. High blood pressure can damage the arteries that supply your brain.
Here’s how being overweight increases the risk of getting stroke:
- Blood pressure and stroke: Extra fat tissue means your heart needs to pump more blood, which increases pressure in the arteries.
- Cholesterol levels and brain health: Being overweight often means higher LDL (bad cholesterol), which clogs arteries.
- Blood sugar: Extra weight raises the chance of insulin resistance, which can lead to diabetes.
- Inflammation and vascular health: Fat cells release chemicals that cause inflammation, damaging the inner walls of blood vessels.
Also, where the fat sits matters. Abdominal fat (belly fat) is more harmful than fat in other areas because it increases cardiovascular risk more directly.
How Strong is the Link Between Obesity and the Risk of Getting Stroke?
This isn’t a loose connection. Medical research proves that weight and stroke are tightly linked.
Here’s what studies say:
- According to the CDC, people with obesity are 2.7 times more likely to have a stroke.
- The Framingham Heart Study found that for each 1-point increase in BMI, stroke risk goes up by 6%.
- A 20-year study in Europe showed that midlife obesity doubles the risk of getting stroke later in life.
This connection isn’t just a theory, it’s well-documented and powerful.
Does a High BMI Always Mean Higher Stroke Risk?
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a rough way to measure if someone is overweight.
Here’s what the ranges mean:
- Underweight: less than 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 to 24.9
- Overweight: 25 to 29.9
- Obese: 30 and above
But it's not just about the number:
- Some people with "normal" BMI still have high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- This is called metabolically unhealthy normal weight.
So while BMI gives us a guideline, it doesn’t tell the whole story about your overweight stroke risk.
Can Overweight Influence Your Risk Of Getting Stroke??
Obesity is on the rise in the adult population. As per a report, the prevalence of obesity has increased from 2.2 % to 5.1 % from 1998 to 2015. The study further stated that an estimated 27.8 % of all Indians would be overweight by 2030. Several published studies from 1983 to 2011 have examined the relationship between obesity and cardiovascular diseases and found it positive. Few essential things emerged from the research. Middle-aged people are more at risk of stroke than older individuals. Obesity and increased risk of stroke were also heightened by other associated factors like diabetes mellitus and hypertension.
Does overweight cause stroke?
Obesity increases the risk of stroke by several factors that include sleep apnoea, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Adipose tissue in our body plays an important role immunologically and endocrinologically. With weight gain, the tissue undergoes changes that include infiltration with inflammatory cells and lesser secretion of adiponectin, a protein hormone with positive vascular effects. Both the inflammation and reduced adiponectin lead to the build-up of insulin resistance. Obesity and the resultant insulin resistance condition may also stimulate other factors that lead to stroke.
How Can You Know If You’re at Risk?
Many people don’t realize how close they are to a medical emergency.
Here’s how you can tell if you may have a higher risk of getting stroke:
- Your BMI is above 25
- Your blood pressure is over 130/80
- You have a family history of stroke, diabetes, or heart disease
- You often feel fatigued, breathless, or get headaches
Regular checkups can reveal early signs. Ask your doctor to check your cholesterol, blood sugar, and do a carotid artery scan if needed.
Overweight Risk Of Getting Stroke
Being overweight to a large extent may be influenced by heredity. Your genes play a significant part in how food is digested, converted into calories, assimilated and how your body uses up the calories. However, the following factors also significantly influence obesity
- Lifestyle habits: A calorie-rich diet with more fried foods, sweetened beverages, oversized portions, and fast foods but lacking in fruits and vegetables is a significant contributor to weight gain. A sedentary lifestyle makes you take in more calories than you burn, an important factor in weight gain.
- Certain medications and diseases: Overweight causing stroke may occur due to hormonal imbalance caused by certain conditions that lead to weight gain. Medications such as antidepressants, steroids etc. may also lead to weight gain
- Social factors: If people you interact with are obese and have unhealthy eating habits, you are more likely to become obese as it will easily be accepted. Or it may be possible that you do not have access to healthy foods and safe places to exercise like parks making it challenging to prevent obesity.
- Age: Most people tend to reduce physical activities as they age. Aging brings on hormonal changes and reduced muscle mass. This reduces metabolism and a lesser need for calories making it harder to stave off extra weight.
- Other factors: Lack of sleep and stress make people crave comfort foods that are generally calorie-rich.
Is the Risk Different for Men and Women?
Yes, gender plays a role.
- Women often store fat in hips and thighs, while men carry more belly fat.
- After menopause, women tend to gain more abdominal fat, which increases their overweight stroke risk.
- JAMA research shows that women with obesity are 3x more likely to suffer a stroke than women with a healthy weight.
Can Children and Teens Also Be at Risk If They Are Overweight?
Sadly, yes. Childhood obesity has become a major concern.
- Kids with high BMI show early signs of artery thickening.
- These are warning signs for future body weight and stroke problems.
- Early prevention is key to breaking this cycle.
What Are Effective Ways to Reduce Stroke Risk if You're Overweight?
Simple lifestyle changes can go a long way. Here are stroke prevention tips that actually work:
| Strategy | Stroke Risk Reduction % | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DASH Diet | Up to 27% | Focuses on low sodium, fruits, veggies |
| 150 min/week exercise | 30-35% | Improves BP, sugar control |
| Weight loss of 5-10% | 20%+ | Major reduction in all risk factors |
Other changes to reduce stroke and high BMI problems:
- Quit smoking
- Cut back on alcohol
- Sleep 7-9 hours
- Manage stress using meditation or hobbies
What can you do?
Treating obesity involves weight management and lifestyle changes for losing weight and maintaining it successfully. It consists in combining physical activity with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Losing weight may be challenging but is the best way to reduce the risk of secondary diseases, especially stroke. Excellent services are offered by one of the top 5 neurologist in Patna Dr. Chandril Chugh , neuro physician in Jaipur, and brain specialist doctor in Faridabad. Also avail the benefits of the best neurologist doctor in Jaipur and a top neurosurgeon in Patna. You can also book an online neurologist consultation or neurologist online chat.
FAQs
Can stroke happen at a young age due to obesity?
Yes. More young adults are having strokes today than 20 years ago, and obesity and stroke are major links. If you’re in your 30s or 40s with high BMI, talk to Dr. Chugh today.
How fast does weight loss impact stroke risk?
Studies show that within 3-6 months, people who lose just 5-10% body weight see major drops in blood pressure and cholesterol, reducing the risk of getting stroke.
Are stroke symptoms different in overweight people?
Sometimes. They may be brushed off as fatigue or sleep issues. Always watch for face drooping, arm weakness, or slurred speech.
Is belly fat more dangerous than overall weight?
Yes. Belly fat, or visceral fat, is directly tied to fat deposits in arteries and high inflammation. It increases your risk of getting stroke more than fat stored elsewhere.
Do weight loss drugs help in lowering stroke risk?
In some cases, yes. Medications like GLP-1 agonists can lower weight and blood sugar. But they should be used under a doctor's care. Book a consultation with Dr. Chugh to discuss options.
Can thin people have a stroke too?
Yes. Thin people with metabolic syndrome (high BP, sugar, cholesterol) can still have strokes. It’s about what's happening inside the body.
What is the stroke belt and does obesity affect regional risk?
The "stroke belt" includes U.S. states like Mississippi and Alabama. High obesity rates in these regions raise the risk of getting stroke significantly.
Complication And Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis Amidst Covid 19 Pandemic
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects the spine, causing pain and stiffness. It can lead to the fusion of vertebrae, resulting in reduced flexibility and a hunched-forward posture. While there is no cure for AS, early diagnosis and appropriate management can significantly improve the quality of life. This article delves into Ankylosing Spondylitis: Symptoms, causes, and treatment options, offering a comprehensive overview of this condition.
What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Ankylosing Spondylitis is a type of arthritis that causes inflammation of the spinal joints, which can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort. Over time, this inflammation can cause some of the vertebrae in the spine to fuse, reducing flexibility and potentially leading to a hunched posture. In severe cases, it can affect the ribs, making breathing difficult. The disease often begins in early adulthood and is more common in men than women.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Causes
The exact cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, but genetic factors play a significant role. The presence of the HLA-B27 gene is strongly associated with the disease. However, not everyone with this gene develops AS, suggesting that other genetic and environmental factors may also contribute to its onset.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Symptoms
The symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis can vary greatly but typically include:
- Pain and Stiffness: Initial symptoms often include pain and stiffness in the lower back and hips, especially after periods of inactivity or in the mornings.
- Reduced Flexibility: Over time, affected areas, particularly the spine, may lose flexibility. This can result in a hunched-forward posture.
- Breathing Difficulties: If the ribs are affected, it can limit the chest expansion and cause difficulty breathing.
- Pain in Specific Areas: Pain can also occur in the areas where tendons and ligaments attach to bones, such as the spine, ribs, and pelvis.
Seek medical assistance if you experience persistent pain that worsens in the morning or after inactivity, as early intervention can prevent more severe complications.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Diagnosis
Diagnosing AS typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging, and laboratory tests:
- Physical Examination: A physician may check for symptoms like pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility in the spine. Tests may include asking the patient to bend in different directions to assess range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays and MRI scans can reveal changes in the spine and joints. MRI is particularly useful for early detection, as it can show inflammation before significant damage occurs.
- Lab Tests: Blood tests may be used to check for markers of inflammation or the presence of the HLA-B27 gene.
Consulting a qualified specialist, such as Dr. Chandril Chugh, is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Ankylosing Spondylitis Treatment
While ankylosing spondylitis cannot be cured, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and prevent progression:
- Medications: Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases, biologics and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be used.
- Therapy: Physical therapy is crucial for maintaining flexibility and strength. A therapist can design specific exercises, including stretching, posture training, and strengthening exercises, to help manage symptoms.
- Surgery: Although rare, surgical intervention, such as joint replacement, may be necessary in severe cases where joints are severely damaged.
- Lifestyle Changes: Staying active, practicing good posture, quitting smoking, and following a healthy diet can support overall health and reduce the impact of AS.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Risks and Complications
The risk factors for ankylosing spondylitis include:
- Gender: AS is more common in men than women.
- Age: The disorder often begins in early adulthood, typically between ages 20 and 40.
- Genetics: A family history of AS or the presence of the HLA-B27 gene increases the risk.
Complications can include:
- Spinal Fusion: In severe cases, the vertebrae may fuse, leading to reduced flexibility and a hunched posture.
- Eye Inflammation (Uveitis): AS can cause uveitis, leading to eye pain, sensitivity to light, and blurred vision.
- Heart Problems: Inflammation can affect the heart and aorta, potentially leading to aortic valve disease.
Managing Ankylosing Spondylitis During Covid-19
While ankylosing spondylitis does not directly increase the risk of contracting Covid-19, managing the disease during the pandemic is crucial. Vaccination can help reduce the risk of severe illness. If you have AS, discuss with your healthcare provider the best approach to vaccination and disease management.
For more detailed information on ankylosing spondylitis, visit Ankylosing Spondylitis.
Conclusion
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic, progressive disease that requires comprehensive management to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Early diagnosis and a combination of medical treatments, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes can significantly improve patient outcomes. If you experience any symptoms associated with AS, consult a healthcare provider promptly to begin an effective treatment plan.
FAQs
How does ankylosing spondylitis usually begin?
Ankylosing spondylitis often begins with stiffness in the joints and back pain, particularly noticeable in the morning or after periods of inactivity. The symptoms can progress gradually.
Can ankylosing spondylitis affect anyone?
Yes, ankylosing spondylitis can affect anyone, although it is more common in men. The disease usually starts in early adulthood, often between the ages of 20 and 40.
What is the most serious complication of the disease?
One of the most serious complications is difficulty breathing due to the fusion of the rib cage, which can limit chest expansion and lung capacity.
Is there a cure for ankylosing spondylitis?
There is currently no cure for ankylosing spondylitis. However, treatments can help manage symptoms and slow disease progression.
How can lifestyle changes help manage ankylosing spondylitis?
Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, maintaining good posture, quitting smoking, and following a healthy diet, can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
Is ankylosing spondylitis associated with other health conditions?
Yes, ankylosing spondylitis can be associated with other conditions, such as uveitis, heart disease, and osteoporosis, increasing the risk of fractures and other complications.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a disorder where inflammation causes few of the smaller bones in the spine or vertebrae to fuse. Ankylosing spondylitis affected areas tend to lose flexibility and bent forward posture. If the disease affects ribs, then it makes breathing difficult. Having the disorder does not raise the risk of contracting Covid-19, but it is safer to get the vaccine. But if you have ankylosing spondylitis after covid, the vaccine helps in reducing the exposure to deadly virus. While it is not fully curable, the Ankylosing spondylitis exercises and Ankylosing spondylitis diet can help in disease management.
Strategies for Managing Mood Swings Effectively | Dr Chandril Chugh
Mood Swings Meaning
The dictionary gives mood swings meaning as an unaccountable and sudden change of mood. It often describes a range of emotions from happiness, anger to contentment and irritability and more. Though mood swings affect both men and women, mood swings hormones changes affect women in particular. Emotional upheavals that occur frequently can be a symptom of psychiatric disorder or from medical conditions like mood swings brain tumours. Even a minor mood swing brain injury can cause mood swings brain fog. Your neurosurgeon in Patna will advise on mood swings how to deal with them. Consult a top neurosurgeon in Patna without delay.
Mood Swings Symptoms
Mood swings symptoms are a range of emotions that affect the everyday life of the affected person. Mood swings effects can hinder the daily routine. Being a mental health disorder, mood swings negative effects are more commonly seen. Mood swings positive effects are rare. Immediately seek medical assistance from the top 5 neurologists in Patna if you or someone you know is affected by one or more of the following symptoms:
- Tendency to forget, confusion
- Difficulty in maintaining attention
- Anxiety, boredom, irritability
- Frequent changes in behaviour, mood
- Difficulty in thinking, comprehension, talking, reading or writing
- Extreme swings of mood from elevation to depression
- Delusions
- Reckless behaviour
- Rapid speech and racing thoughts
- Feeling sad for most of the time
Mood Swings Causes and Risks
Experiencing some mood changes from time to time is natural. But if the changes become frequent or intense enough to disturb your work, life, and relationships, there is a need to address the underlying causes. The mood swings may happen due to some internal or external changes. Internally, they refer to how we feel, how our body feels, and our responses to the environment around us. Mood swings caused by stress often get heightened to cause other issues like depression. Externally, emotions are influenced by changes in our home and work life and our environment. Here are some of the causes that demand attention:
- Bipolar Disorder: Mood swings cause bipolar disorder. The emotions will range from one extreme to another. It could likely be extremely sad at one time to extremely happy at another. The changes are likely to happen a few times a year. People with bipolar disorder may also be excessively energetic, talk a lot and speedily, and tend to engage in risky activities.
- Injury and illness: The shift in emotions can be attributed to severe injuries or chronic diseases that impact the brain, like a stroke, concussion, or dementia. Some neurological conditions can also lead to mood swings like sleep disorders, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, thyroid disorders etc.
- Allergies: People with seasonal allergies may often find themselves moody at the time when allergens are present. They might find themselves irritable and difficult to concentrate when they are feeling unwell. Some of the symptoms like headaches, watery eyes, itchiness, and constant sneezing can cause mood swings.
- Medications: Some of the medications prescribed can cause mood swings as a side effect. Additionally, starting and stopping certain medications can also affect the mood.
- Hormones: Mood swings caused by hormones affect women primarily. Changes in hormone levels, especially estrogen, is known to cause mood swings. It can also occur due to other factors like pregnancy and menopause in women.
- Depression: People who remain sad for a prolonged period tend to be depressed. Usually, Mood swings caused by depression take the affected person from irritation to sadness to anger. They also have trouble sleeping, feeling hopeless, exhausted. Mood swings cause difficulty in decision making. People with severe depression, also called chronic depression, tend to have suicidal thoughts.
- Borderline Personality Disorder: It is a mental health disorder that causes mood shifts to last from a few hours to a few days. The mood is often intense with a variety of emotions. Several other symptoms include risky behaviour, extreme emotions like rage, feeling restless, attempts at suicide and others.
- Substance Abuse: People experience emotional turmoil when addicted to a substance like a drug or alcohol. Mood swings caused by alcohol can be managed by trying to quit the substance addiction. Though you may experience withdrawal symptoms, they can be effectively treated with medications along with the patient's willingness to change.
Mood Swings Diagnosis
The doctor may undertake a preliminary physical examination to rule out an illness like mood swings brain tumour, or thyroid. The neuro physician in Jaipur will ask about your medical history, medications, and any blood relation has previously been diagnosed with mood swings disorder.
Mood Swings Management and Treatment
It is normal and even reasonable to have some days when you feel good and other days when you are not up to it. The mood swings become a matter of concern when they begin to interfere in routine everyday activities. It would help if you discussed with your neurologist doctor in Jaipur for a deep dive into the reasons and possible line of treatment.
The brain specialist doctor in Faridabad will prescribe an appropriate line of treatment. It generally is a combination of psychotherapy (counseling through talk sessions) and medications.
- Antidepressants: Medicines are prescribed to treat depression. Though all antidepressants are equally effective, some may be more effective depending on mood swings and the cause behind them. The medicines need to be taken for at least 4 to 6 weeks before any effect can be seen.
- Mood Stabilisers: These medicines are prescribed to regulate the mood swings occurring due to bipolar disorder. They may also be prescribed along with antidepressants.
- Psychotherapy: Talking about issues that are bothering a person often releases bottled-up emotions and helps the person get better. The psychotherapy or talk sessions include interpersonal, cognitive, problem-solving, and brain stimulation therapies.
Mood swings are a mental health disorder caused by the turbulent state of a person’s emotional state. The affected person experiences alternating periods of different emotions that disturb normal daily functions. Immediate medical assistance consisting of medications and therapy can help the affected person to recover.
For getting expert advice or consultation, call +91 98994 79984 and book your appointment.
Also Read
Dementia Vs Depression: Are They Related?
Can Covid 19 Cause Brain Damage?
Common Symptoms Of Known Neurological Disorders
Trauma And Its Gradual Impact On Health
Trauma Meaning
Trauma is a response to destructive events like natural disasters, rape, or accidents. The event could be harmful, emotionally, or physically threatening. The emotions can affect the traumatized person immediately after the event or till long after. Trauma and emergency patients have life-threatening injuries that need immediate care. Trauma and recovery can be different for everyone. However, they can work on their trauma and anxiety to rebuild their life with support from the best online neurologist.
Trauma attack Causes
Stressful events like trauma and depression disturb the sense of security and make the affected person feel helpless and vulnerable in a dangerous world. It can make him disconnected and unable to have trust in anyone. The trauma and injury, both psychological and emotional, can be caused by:
- Events such as injury, violent attacks, accidents, or any harmful event happened unexpectedly or happened in childhood.
- Ongoing stress like bullying, life-threatening illness, abuse, living in a crime-infested neighbourhood, domestic violence, or childhood neglect.
- Sudden events like the death of someone close, humiliating experience, the breakup of a meaningful relationship, or a profoundly disappointing experience.
- It is improbable that we will be a direct victim of mob violence, terrorist attacks or a mass shooting. However, such events are constantly played on social media and news channels. Viewing the constant bombardment of such horror images can create stress and traumatize us.
Contact a neurologist if you or someone you know experiences trauma and health issues.
Trauma Attack Symptoms
Everyone reacts to trauma differently with different emotional and physical reactions. Some physical symptoms include insomnia, racing heartbeat, fatigue, nightmares, being startled easily, aches, pain, and feeling edgy and agitated. Whatever be the response, it is entirely normal. Consult an online neurologist for some of the common symptoms:
- Difficulty in concentrating
- Confused state of mind
- Irritable stature
- Shock, disbelief, or denial
- Anger, sadness, and mood swings
- Self-blame, shame, and guilt
- Withdrawing into shell
- Feeling of hopelessness
- Feeling numb or being disconnected
Trauma and Depression
It takes time to recover from trauma. However, if several months have passed and the symptoms are not easing, the affected person could fall into depression. They may need help from an expert migraine doctor in Jaipur.
Seek help from a top neurologist in Jaipur if the affected person
- Is suffering from fear or anxiety.
- s unable to form relationships.
- Experiencing terrifying thoughts, nightmares, or memories
- Avoiding everything
- Feeling disconnected from others
- Is getting dependent on alcohol
Finding the right mind doctor in Agra may take some time. Healing from trauma can be painful, so it works best to find a trauma specialist with which they are comfortable. It is crucial to have an excellent quality relationship with the therapist.
Effects of Trauma
Science has developed deeper insights into how the nervous system regulates stress. It is one of the nervous system facts that when it is normal and regulated, it will experience anxiety but will be able to calm itself when the threat has passed. However, trauma pushes this ability of the system to self-regulate. One of the reasons to see a neurologist is to find someone who can help understand the trauma and guide you about the best food for strengthening nerves.
Trauma and Healing
It can take some time to overcome the pain and feel safe again. With self-help and support from an online neurologist, recovery can be ensured. The affected person will need to remove the bottled-up feelings, refurbish the memories they are avoiding, control the intense emotions, and rebuild trust in people. A trauma expert may use different approaches to see what works best. They may help to release the stress through crying or shaking. They may also undertake comfortable talking sessions where the traumatized person can speak without fear. Cognitive Behavioural therapy helps to process the thoughts about the trauma, which is one of the good reasons to see a neurologist.
Trauma Healing Diet
Trauma and stress affect the organ systems such as the nervous system and digestive system. The diet needs to nourish the body and support trauma and health outcomes. The diet should include foods that heal nerve damage, decrease stress levels. Some of the best food for nerves repair are whole foods, fruits, colorful vegetables, plant proteins, and supplements.
Trauma And Recovery
The symptoms usually last from a few days to several months. They slowly fade away with memories as time passes. Even though the affected person will get better day by day, they may still be troubled by painful memories by something that reminds them of the traumatic event, like a similar event happening to someone else or an anniversary of the event.
Eventually, the traumatized person should ease up and move on with therapy and counseling from the top neurosurgeon in Patna. However, suppose the symptoms of psychological trauma do not let the person normalize. In that case, they are unable to move on and remain with the event's emotions, then they are experiencing Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). While the reactions to the trauma are normal, if the person is overwhelmed, they remain in a state of psychological disbelief, unable to come out of it for a prolonged period, it means they have a complex PTSD and sleep disorder.
People with PTSD have a heightened sense of danger, making them feel fearful even when they are safe. Changes due to trauma and brain function occurs as a response to changes in the neural and chemical pathways of the brain is a nervous system fact. The presence of trauma and brain fog does not mean one is weak. People with prolonged PTSD may experience trauma and brain damage.
As a survivor, the traumatized person needs to learn to cope with the harmful event and its after actions for their safety. They can:
- Try to incorporate exercise into the routine. A thirty-minute routine for several days a week or as many as possible is good. It is best to indulge in an activity that engages both limbs. To get more benefit, focus on body movements rather than focusing on their thoughts or trying to distract themselves. Reach out to a mind doctor in Delhi for therapy.
- Isolating and withdrawing into a shell will only make matters worse. Connect with others, maintain relationships, and try not to spend time alone. Ask for support and do not talk about the traumatic event.
- Participate in social activities. Either make new friends reconnect with old ones.
- Volunteering can bring a deep sense of purpose and reduce the feeling of helplessness. Helping others can help to realize their inherent strengths and potential.
- No matter how much trauma and health anxiety the traumatized person may be having, it is important to calm oneself. If they often feel disoriented and confused, learn mindful breathing techniques.
- Take complete care of their health. Get an adequate amount of sleep. Eat a nutritious and balanced diet. Do activities that relax like meditation, yoga, etc.
For getting expert advice or consultation, call +91 98994 79984 and book your appointment.
Also Read
Nervous System Facts
Aspartame Slows Metabolism
Stroke During Sex
Sudden Neck Pain And Its Relation With Neurology
Neck pain causes
Neck pain or stiffness can arise for a combination of reasons.
Muscle tension and strain-
This is typically due to activities and behaviors such as:
- Poor posture
- Working at a table for too long whereas not
- Dynamic position
- Jerking your neck throughout the exercise
Injury-
The neck is particularly at risk of injury, significantly in falls, automotive accidents, and sports, where the muscles and ligaments are forced to maneuver
If the neck bones (cervical vertebrae) are broken, the funiculus is also broken. Neck injury due to sharp jerking of the head is typically stated as whiplash.
Heart attack-
Neck pain is also a sign of cardiomyopathy, but it always presents with entirely different symptoms of a cardiopathy, such as:
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Arm or jaw pain
Other causes embrace the following-
- Rheumatoid arthritis induces pain, inflammation of the joints, and bone spurs. Once these happen inside the neck area, neck pain might occur.
- Osteoporosis weakens bones and would possibly end in minor fractures. This condition sometimes happens in the hands or knees, but it will occur inside the neck.
Neck pain symptom
Signs and symptoms include:
- Pain that's sometimes worsened by holding your head in one place for long periods, like once driving or engaging at a laptop
- Muscle tightness and spasms
- Decreased ability to manoeuvre your head
- Headache
Neck pain nerve pinch
Usually, a pinched nerve can last from a day to 6 weeks — or, in some cases, even prolonged. Pinched nerve signs and symptoms include:
- The nerve provides the diminished sensation inside the area.
- Sharp, hurting or burning injury, which may spread outward.
- Tingling, pins and needles sensations (paresthesia).
Neck pain nerve headaches
One of the extra common medical causes of headaches is pinched nerves inside the neck. Pinched nerves inside the neck cause headaches by pressuring the nerve that generates a way of pain on the nerve's pathway. Cervical Radiculopathy is also a medical condition where a nerve inside the upper spine becomes compressed.
Neck pain nerve inflammation
Cervical radiculopathy, unremarkably stated as a "pinched nerve," happens once a nerve inside the neck is compressed or irritated where it branches off from the funiculus. This might cause pain that radiates into the shoulder and arm, additionally as muscle weakness and symptoms. A pinched nerve in your neck happens once soft tissues inside the body apply an associate degree of excessive pressure to a nerve and limit its ability to work correctly. Bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and tissue can all press against a nerve, inflicting irritation, inflammation and pain.
Neck nerve pain on left side
Discomfort on the left side of the neck is due to various causes, from muscle distress to a pinched nerve. Most cases don't seem to be serious. A sore neck is maybe due to sleeping in an associate degree odd position or holding your neck at a degree angle that stresses the muscles and tendons on that side. To induce relief from left neck pain, Keep moving, but avoid jerking or painful activities. This assists calm your indications and decline inflammation. Do slow range-of-motion workouts, up and down, side to side, and from ear to ear.
Neck pain risk factors
- Psychosocial, physical, and neurobiology factors affected the prospect for neck pain.
- The unhappy mood was the powerful predictor for the expansion of chronic neck pain.
- Diffuse harmful restrictive management was impaired in those developing chronic neck pain.
- Poor cervical muscle endurance enhanced the prospect of developing chronic neck pain.
Neck pain treatment
Treatment for neck pain depends on the diagnosis. To boot to radical history and physical communication by your doctor, you'll to boot would love one or extra of the following imaging studies and tests to help your doctor verify the rationale behind your neck pain:
- Blood tests
- X-rays
- CT scans
- MRI scans
Depending on the results, your doctor would possibly refer you to a specialist. Treatment for neck pain would perhaps include:
- Ice and heat medical care
- Experience, stretching, and therapy
- Pain medication
- Corticosteroids injections
- Muscle relaxants
- Neck collar
Neck pain treatment exercise
Down below, we've listed some exercises for neck pain nerve treatment
- Keep your head over your shoulders and your back straight up.
- Slowly turn your head to the right until you're feeling a stretch in the side of your neck.
- Hold the stretch for 15-30 seconds, so slowly flip your head forward yet again.
- Repeat on your left side. Do up to 10 sets.
Neck pain nerve relief
If you have got mild symptoms, you'll notice relief from:
- Rest.
- Soft cervical collar.
- Hot or cold compress.
- Practicing sensible posture.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Acupuncture.
- Massage.
- Yoga.
When a patient is undergoing neurological disorders there are many reasons to see a neurologist. So, to solve your conditions, get in touch with Dr. Chandril Chugh or book an appointment with an online neurologist. You can find him among the top 5 neurologists in Patna, neurologist doctor in Jaipur, and neuro physician in Jaipur. Dr.Chandril Chugh is considered one of the best neurologists in Faridabad, a mind doctor in Agra, a neurosurgeon in Patna, a mind doctor in Delhi, brain specialist doctor in Faridabad. Also, his ability to treat patients online with compassionate care is remarkable.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of nerve pain nerve damage?
Symptoms of pinched nerves inside the neck include sharp pain inside the arm, pain inside the shoulder, a way of sign or pins and needles inside the arm, weakness of the arm and worsening pain once you progress your neck or flip your head.
Can you have neck nerve pain in your chest?
Nerve pain inside the chest can come from any chest nerves pinched, cut, or crushed by trauma. However, one provides that shingles cause burning and sharp pain inside the trunk.
Is it okay to have neck pain from a nerve block?
It is normal to experience discomfort or soreness that will improve within a few days of injection. The long anesthetic doesn’t persist for some patients; it may take a while for the steroids to function and deliver a long-term benefit. The effect of the steroid usually lasts for 4 to 10 days.
Also Read
Can Covid 19 Cause Brain Damage?
How Pandemic Is Messing With Our Brains?
Is Brain Transplantation Possible?
Back Pain After Covid : Causes And Treatment
Back Pain After COVID
Many people have developed back pain after Covid recovery. This is because of less movement of joints and muscles during and post-Covid. It leads to aches, pain, muscle stiffness, and weakness. This can result in difficulty with activities like climbing stairs, standing, lifting heavy objects with your arms.
Some of the treatments during the Covid illness can put a patient under extra stress, strains on their joints and muscles. These days experts get to hear common problems after getting well with Covid. Those problems are shoulder, back pain, joint, and muscle weakness. Some people also experience numbness in their arms and legs.
Back pain due to Covid vaccine
Many individuals have faced common side effects after Covid 19 vaccine. The symptoms include fatigue, headache, fever, vomiting, dizziness, sweating, and also back pain. There is nothing to worry about these symptoms; they don’t persist for a long time. Mostly lead to side-effects during your first dose.
Back pain after exercise
The moment you push your limits on physical exercise, it may cause discomfort during the recovery time. A long run can leave you short of breath and lifting heavy weights can lead to back pains. While a moderate level of soreness is expected as you increase your physical capabilities. However, back pain may be a symptom of some underlying disease.
In most cases, running might not be the direct cause of back pain. Researchers have seen athletes, including competitive runners, experience less back pain than average people. Some common disorders that cause back pain are muscle strains, springs, hyperlordosis. If your back pain is persisting or increasing, you should get medical assistance.
Back pain after sex
Low back pain can have a serious impact on some individuals after intercourse. That’s why many people with chronic back pain bring sexual problems into their life. Such sexual problems related to back pain often have diseases like arthritis, but patients who are recovering from back surgery may also struggle with the same. If you are constantly facing such problems don’t hesitate to contact a neurologist, Dr. Chandril Chugh.
During intercourse, the bacteria can be forced into the urinary bladder. This leads to UTI, which is a urinary tract infection. Symptoms include pain while urinating, frequently passing urine, back pain, and others. This kind of condition is treated with antibiotics.
Back Pain Due To Nerve Compression
Nerves extending from your spinal cord send messages to your body. If you have damage from a pinched nerve your body may send warning signals such as pain. Don’t ignore such signals. Damage from a pinched nerve can be severe or minor. It may cause temporary or long-lasting problems. The earlier the cause is diagnosed the quicker the treatment can be. Nerve compression occurs when there is pressure on a nerve. The pressure can be the result of repetitive motions. Or it may be because of holding your body in a position for a long time such as keeping elbows bent while resting.
If your symptoms don't minimize consult a doctor. You may require treatments to shrink swollen tissues around your nerves. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like Aspirin may reduce your swelling.
Back Pain Due To Nerve Damage
Sciatica is a common disorder of back pain due to nerve problems. Pain that illuminates from your lower backbone to your hips and down your leg is a hallmark of Sciatica. In this condition, mostly one side of your body is affected. Sciatica occurs when narrowing of the spine compresses part of the nerve. This leads to swelling, inflammation, pain, and sometimes even numbness in the affected leg. When the symptoms are mild they might go away in some time. But when you see the symptoms are progressively getting worse, call a doctor. You might experience symptoms like sudden or severe pain in your lower back or leg, the pain follows a violent injury. You may also have difficulty controlling your bladder movement.
Back Pain Treatment
Any back pain can be treated at home till it is mild and moderate. Once the symptom gets severe, one should seek immediate assistance from a doctor. Some common ways to treat back pain are -
- Change your sleeping posture- When you have back pain, sleeping can be hard. A poor sleep posture can enhance the pain. Try lying down on either side. Place a pillow between your knees to support your spinal cord. Make sure you have a comfortable mattress.
- Good posture- Your back pain can get worse if you sit for a long time in the wrong position. Try to sit upright with your shoulders relaxed and your body supported by a chair. Try putting a pillow or a cushion between your lower back and the seat and keep your feet on the floor.
- Physical therapy- You can get help from a physical therapist to teach you how to sit, stand and move your spine in proper alignment. They will also help you with specialized exercise which supports your back and makes your core strong. Records show that an increase in strength and flexibility can decrease the pain.
- Ice and heat- Regular application of ice or a warm towel on the painful area of your back can help reduce inflammation and pain. Try this every day for around 20 minutes.
When a patient is undergoing neurological disorders there are many reasons to see a neurologist. So, to solve your conditions, get in touch with Dr. Chandril Chugh or book an appointment with an online neurologist. You can find him among the top neurologists in Jaipur, migraine doctor in Jaipur, and top neuro physician in Jaipur. Dr.Chandril Chugh is considered one of the best neurologists in Faridabad, a mind doctor in Agra, a mind doctor in Delhi, brain specialist doctor in Faridabad. Also, his ability to treat patients online with compassionate care is remarkable.
FAQs
Is it normal to experience pain after sex?
Both women and men can have pains after intercourse. The medical term used for pain after sex is called dyspareunia. Cramps may range from mild to underlying conditions that require treatment, so it’s always safe to contact a neurologist.
How to get relief from back pain due to nerves?
When it comes to self-care the patient can implement physical exercise, ice packs, massages, and acupuncture in their treatment. If the pain is getting severe you might need medications like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or nerve pain medications. Remember to talk to an online neurologist before taking any medicine.