Trauma brings strong feelings that don’t go away unless you deal with them. If you don’t process these feelings when they happen, they stay in your mind and body. The best way to handle childhood emotional wounds is to understand the harm done, feel the right emotions, and know it doesn’t define you.
But this doesn’t always happen naturally. Often, you might push away your feelings instead of facing them. This can lead to carrying those emotional scars into adulthood. They can affect your relationships, job, happiness, and health.
To heal from childhood trauma, you must finish the healing process that started long ago. This is crucial for your well-being.
Therapies focused on trauma, learning to cope, and finding support are key steps towards healing. With hard work and the right help, you can overcome childhood trauma and improve your life.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Childhood Trauma
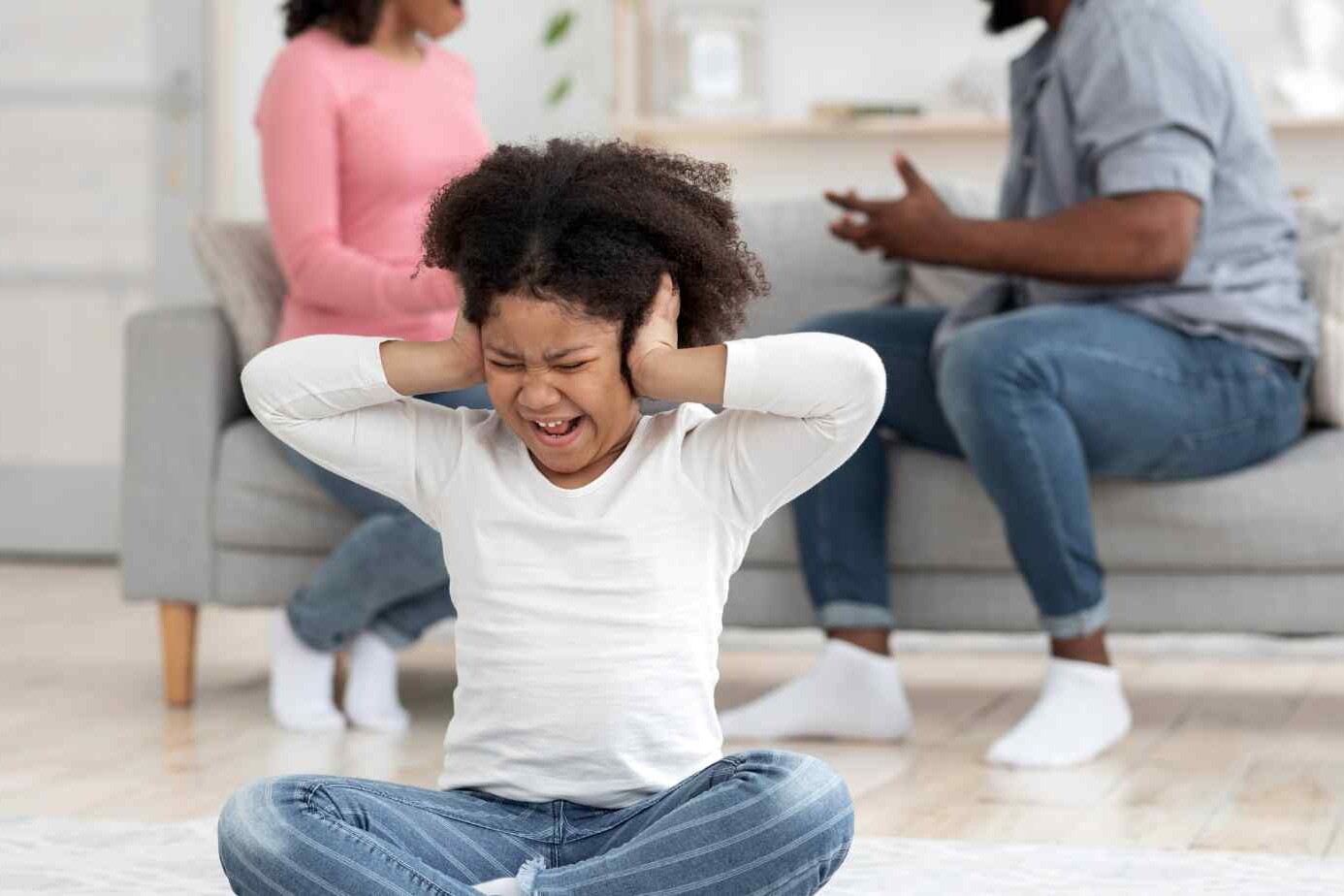
Our childhood experiences shape us in ways we might not realize. Some events can be traumatic, known as adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). These are negative events that affect a child’s well-being and health. They include abuse, neglect, or being in harmful environments.
Types of Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma comes in many forms, including abuse and neglect. Here are some examples:
- Physical or sexual abuse
- Sudden death of a loved one due to murder or suicide
- Kidnapping
- Witnessing violence in the household
- Emotional or physical neglect
These adverse childhood experiences can deeply affect a person’s mental, emotional, and physical health. Knowing about the different types of childhood trauma helps us understand and deal with its effects.
Recognizing the Signs of Childhood Trauma in Adults
If you’ve faced childhood trauma, you might notice its effects in adulthood. The signs of childhood trauma in adults can be varied. They often include trouble forming healthy relationships, being overly alert, feeling depressed, and anxious.
As an adult trauma survivor, you might always feel on edge. Even in safe places, you might feel threatened. Childhood trauma can also lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). This can cause flashbacks, nightmares, and panic attacks.
Adult trauma survivors often struggle with unhealthy relationships, depression, and anxiety. They may also experience dissociative episodes. The journey to healing is tough, but recognizing these signs is the first step to taking back your life.
You’re not alone in this fight. There are resources and support out there to help you deal with childhood trauma’s lasting effects. With the right tools and support, you can manage these effects and move towards healing and growth.
The Impact of Childhood Trauma on the Brain and Psyche
Childhood trauma can deeply affect both the brain and the mind. When kids go through traumatic events, their brains change in big ways. This can lead to lasting effects. The brain changes can make it hard for kids to handle emotions, remember things, and make good choices.
How Early Life Distress Affects the Brain and Psyche
When kids face trauma, their stress system gets too sensitive. This messes with the brain’s balance. It can make parts of the brain that control feelings, memories, and decisions not develop right.
These kids often feel a lot of fear, anxiety, and always be on the lookout for danger. Trauma can also make it hard for them to trust others or feel safe in relationships. If not treated, trauma can cause anxiety, depression, social issues, PTSD, and trouble with forming healthy relationships.
It’s important to see how big of an impact childhood trauma can have on the brain and mind. By understanding this, we can help those who have been through trauma. We can guide them towards healing and building resilience.
Emotional Regulation and Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma can deeply affect how well someone can handle their feelings. Those who have gone through this often find it hard to notice and share their emotions. They might act impulsively or avoid feeling things altogether. Learning to manage emotions is key to healing for adults dealing with childhood trauma.
Sudden memories of trauma can bring strong feelings that are hard to deal with. Therapies like trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) offer help. These methods teach skills for dealing with emotions and stress, improving emotional health.
Working on emotional control and finding better ways to cope, adults with past trauma can take back control of their feelings. With help from mental health experts and a dedication to healing, they can learn to handle all kinds of emotions better.
Attachment Styles and Relationships
Childhood trauma can deeply affect how we connect with others in adulthood. Trauma during our early years can make it hard to trust and depend on people. It can also make us fear being open, set unclear boundaries, and struggle with trust.
This trauma can make forming healthy relationships tough. It’s key to understand how trauma impacts our attachment styles. This knowledge helps us heal and build better relationships.
How Trauma Affects a Child’s Attachment Styles and Relationships
Kids who go through trauma, like abuse or loss, might develop insecure attachment styles. These styles can make relationships in adulthood hard.
- Avoidant attachment: Trouble trusting others, avoiding closeness, and fearing being open.
- Anxious-ambivalent attachment: Feeling intense, mixed emotions in relationships, needing closeness but fearing being left.
- Disorganized attachment: Feeling confused and unsure in relationships, lacking a clear way to find comfort or safety.
These styles can stick with us into adulthood, affecting our relationships. Therapy, like trauma-informed approaches, can help. It can teach us to form secure attachments, set clear boundaries, and trust ourselves and others.
Dealing with childhood trauma and Addiction Risk
Recent studies have found a strong link between childhood trauma and the risk of addiction in adults. People who faced trauma, like abuse or neglect, during their youth are more likely to develop substance abuse and addictive behaviors. It’s key to understand this link to tackle addiction’s root causes and offer the right treatment.
The Effects of Childhood Trauma on the Brain and Psyche
Childhood trauma deeply affects the brain and mind, raising the risk of addiction. It can cause problems with managing emotions, making poor choices, and a strong stress response. These issues make people more prone to use addictive substances or behaviors to cope with hard feelings.
Also, trauma changes the brain’s reward and motivation systems. It makes it tough for people to feel joy or satisfaction without addictive substances or behaviors. This can start a cycle where the person keeps seeking these substances or behaviors to ease their pain, making the addiction worse.
- Emotional dysregulation
- Impaired decision-making
- Heightened stress response
- Altered brain reward and motivation systems
Dealing with the trauma is key for those with addiction and a past of childhood trauma. By grasping the link between childhood trauma and addiction, we can create better ways to help those in need. This can help break the cycle of addiction.

Healing from Childhood Trauma
Healing from childhood trauma is a deep journey of self-discovery and growth. It can feel tough at first, but it’s also rewarding. The first step is to understand the trauma and see how it affects you.
Be patient with yourself as you heal. Trauma often makes us feel bad about ourselves, making healing harder. Getting support from loved ones or mental health experts is key.
Talking to therapists who know about trauma can help. They use methods like cognitive behavioral therapy and EMDR. These methods help you deal with feelings, learn to cope, and grow stronger. They guide you to feel safe, in control, and valuable again.
Healing from trauma is not straight forward; it has ups and downs. Be gentle with yourself, celebrate your wins, and ask for help when needed. With time, kindness, and support, you can move past your past and create a better future.
You’re not alone in this journey. Many have been where you are, and there’s help and communities out there for you. Embrace the healing process, and believe you can overcome childhood trauma with time and effort.
Trauma-Informed Therapies
Healing from childhood trauma can seem tough, but the right therapies can help. These therapies are made to meet the special needs of people who’ve faced trauma. This includes abuse, neglect, and other tough experiences from childhood.
Effective Trauma-Informed Therapies
Some of the best therapies for trauma are:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapy looks at how your thoughts, feelings, and actions are linked. It helps you change negative patterns.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): This method helps you handle strong feelings, learn healthy ways to cope, and improve your relationships.
- Trauma-Focused Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT): Made for those affected by trauma, this therapy aids in managing emotions and learning to live healthier.
These therapies offer a safe space for you to look into your trauma, feel your emotions, and learn new skills. With a skilled therapist who knows about trauma care, you can start healing. You can build a life that’s more fulfilling and resilient.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Dealing with the effects of childhood trauma can feel overwhelming. But, by learning healthy ways to cope, you can take back control and grow stronger. Using tools like mindfulness, meditation, and journaling can help manage your feelings and work through your trauma.
Mindfulness and meditation can make you feel more grounded and present. They lessen the effect of scary thoughts and memories. Journaling is great for expressing and understanding your feelings safely.
Physical activity is also a key way to cope. It helps release stress, boosts your mood, and releases happy chemicals in your brain. Having a circle of friends and family who get you is crucial too. They offer a safe place to talk and feel supported.
Healing from childhood trauma is a personal journey. But, by using healthy coping methods, you can move forward and look to the future with hope.
- Practice mindfulness and meditation to regulate emotions
- Engage in journaling to process and express your feelings
- Incorporate physical activity to release tension and improve well-being
- Surround yourself with a supportive network of trusted individuals
Seeking Support and Building Resilience
Healing from childhood trauma takes a lot of effort. It’s important to seek support and build resilience. Getting help from professionals and connecting with others who have gone through similar things can be very helpful. It gives you a sense of not being alone and understanding others better.
Self-care is key to building resilience. This means getting enough sleep, eating well, and doing things that make you happy. Over time, you can grow stronger and learn to handle your feelings better.
There are many resources out there for trauma recovery. You can find articles, books, and support hotlines online. These can give you new ways to deal with your feelings and help you feel better.
Remember, healing from childhood trauma is a long journey. Be kind to yourself and don’t rush. With the right support and tools, you can overcome the past and move forward.
Conclusion
Childhood trauma deeply affects your mental, emotional, and physical health. But, healing is possible with the right support and strategies. Understanding different types of trauma and recognizing signs in adulthood helps you start healing.
Talking to therapists and using therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy and EMDR can help. Building healthy coping skills and a strong support network is also key. This can be through therapy, support groups, or self-care.
Recovering from trauma is hard, but it’s worth it. By facing the trauma, you can take back your life and look forward to a better future. You’re not alone, and there are many resources and professionals ready to help you. With determination and kindness towards yourself, you can beat the effects of childhood trauma and live well.
FAQ
What is the healthiest response to childhood emotional wounds?
The best way to deal with childhood emotional wounds is to understand the trauma’s impact on your self-image. It’s important to feel the emotions that come with it. Realize that the trauma doesn’t define who you are.
But, this process isn’t easy. Many people hide their feelings instead of facing them.
How can childhood trauma affect adults?
Childhood trauma can make it hard to form healthy relationships. Adults may feel always on guard, suffer from depression and anxiety, and even have PTSD. They might act in unhealthy ways in relationships, feel threatened all the time, and struggle with depression and anxiety.
They might also have flashbacks, nightmares, and panic attacks.
How does childhood trauma impact the brain and psyche?
Trauma in childhood changes the brain, making the stress response too strong. This messes with the brain’s balance. It affects areas that handle emotions, memory, and making decisions.
This leads to a lot of fear, anxiety, and always being on high alert. People may see the world in a twisted way. Trusting others and feeling safe becomes hard.
How does childhood trauma affect emotional regulation and expression?
Traumatic memories can come back without warning, making emotions stronger. Adults with childhood trauma often feel more sensitive and have trouble controlling their emotions. They might not know how they feel, act impulsively, and avoid dealing with emotions.
They might also act in self-destructive ways or avoid feeling anything at all.
How does childhood trauma influence attachment styles and relationships?
Trauma can make it hard to trust others and feel safe in relationships. People may have trouble forming close bonds. They might fear being open, struggle with setting boundaries, and keep repeating patterns from the past.
This can make forming healthy relationships as an adult tough.
How does childhood trauma increase the risk of addiction and mental health disorders?
Trauma can lead people to use substances or behave addictively to cope with their feelings. It changes the brain and makes it easier to become addicted. This includes problems with managing emotions, making decisions, and handling stress.
What are the steps to heal from childhood trauma?
First, acknowledge the trauma and its effects on you. Be kind to yourself, as self-blame is common. Getting help from loved ones or professionals is key.
Talking to a therapist can help you process your feelings and learn to cope better. This can help you build strength and resilience.
What types of trauma-informed therapies can be effective in treating childhood trauma?
Good therapies include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), which links thoughts, feelings, and actions. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) helps manage emotions and find healthy ways to cope. Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) is made for dealing with trauma’s effects.
What are some healthy coping mechanisms for individuals dealing with childhood trauma?
Good ways to cope include mindfulness, journaling, and exercise. Having a strong support network of friends and family is also crucial for healing.
How can seeking support and building resilience aid in the healing process for individuals dealing with childhood trauma?
Joining support groups or online communities with others who’ve gone through trauma can be very helpful. Taking care of yourself, like sleeping well, eating right, and doing things you enjoy, can also boost resilience.
With the right support and ways to cope, people can learn to deal with trauma’s effects. They can grow stronger and feel better about themselves over time.
Source Links
About The Author

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.
→ Book a consultation to discover which remedies suit your needs best.




