A Brain Tumor is a mass growth of neurons (or other brain cells) in the brain. The human skull has a high degree of rigidity. Hence, any increase within such an enclosed space will result in problems. A Brain Tumor can be either malignant (cancerous) or benign (noncancerous). When these Tumors spread, they can lead to internal pressure within the skull, which is dangerous and can be life-threatening! Brain Tumors that originate in the brain are referred to as primary Brain Tumors, while cancer that begins elsewhere in the body spreads to your brain as metastasized Tumors.
How fast a Tumor can grow varies greatly. The rate of growth, along with the location, determines how it will affect the functioning of the nervous system.
 How do you detect a Brain Tumor?
How do you detect a Brain Tumor?
The Brain Tumor symptoms vary more depending on where and how large the Tumor is. While some cancers directly affect the brain, others create pressure on the surrounding brain. Headaches are the most common symptom of a Brain Tumor. The patient may experience worse headaches in the morning, occur while sleeping and are made worse by sneezing or coughing too much. One may also experience vomiting, blurred vision, confused state of mind, seizures, weakness of a limp or change in mental functioning. Other common symptoms are clumsiness, memory loss, difficulty in writing or reading, difficulty swallowing, hand tremors, loss of balance, eye problems, dizziness, trouble speaking, changes in mood, emotions and behaviour, difficulty walking, muscle weakness in the face, arm or leg, loss of balance, difficulty in making decisions, inability to follow simple instructions and feeling very tired all the time.
What are the risk factors for a Brain Tumor?
Family history
Although it is rare for a Brain Tumor to be genetically inherited, it is recommended to talk to a doctor if several people in the family have been diagnosed with a Brain Tumor. The doctor might suggest a genetic counsellor for you.
Age
The risk for most Brain Tumors increases with age.
Chemical exposure
Consistent exposure to certain chemicals, such as those you encounter in your work environment, can heighten the risk for brain cancer.
Exposure to radiation
People who have been exposed to ionising radiation are comparatively at an increased risk of Brain Tumors. The nuclear power plant incidents in Fukushima and Chernobyl are examples of how people could be exposed to ionizing radiation.
How are Brain Tumors diagnosed?
The diagnosis begins with a physical exam and a study of medical history. The physical exam is a very detailed neurological examination, and the doctor conducts a test to see if the carnival nerves are intact. These nerves originate in the brain. The doctor will also look inside the eyes using an ophthalmoscope, an instrument that shines a light through your pupils and then onto your retinas. Doctors check how your pupils react to light and if there is any swelling of the optic nerve. When pressure increases inside the skull, there is usually a change in the optic nerve. The doctor further evaluates the strength of muscles, memory and ability to do mathematical calculations.
Further, there may be more tests after the physical examination, which include:
CT and MRI scan of the head
They are conducted to obtain a more detailed scan which helps doctors see some structures like blood vessels and brain more clearly.
Angiography
A dye is injected into your artery, which travels to the streets in the brain. It allows the doctor to see what the blood supply of Tumors look like
Skull X-rays
Brain Tumors may lead to fractures in the bones of the skull, which are detected through specific X-rays. They also check if there are calcium deposits that are sometimes contained within a Tumor.
Biopsy
Biopsy identifies if the cancerous cells are present in the Tumor. Then, a small piece of the Tumor is obtained, and a neuropathologist specialist examines it.
 What is the treatment of a Brain Tumor?
What is the treatment of a Brain Tumor?
The treatment primarily depends on the type of Tumor, size of cancer, location of the Tumor and overall health. The most common treatment for Tumors is surgery. The motive is to remove as much cancer as possible without damage to the healthy parts of the brain. While the location of some Tumors allows for safe removal, others may be located in an area that causes limitations to how much of it can be removed.
There are some risks of brain surgery, such as infection and bleeding. Surgery can be combined with other treatments such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech therapy help in speeding up the recovering process after neurosurgery.
What are the complications that are associated with a Brain Tumor?
People with Brain Tumors, whether it is cancerous or noncancerous, experience complications as the Tumor grows, which include:
- Difficulty in speech
- Faster or slower pulse rates
- Vision, smelling and hearing problems
- Weakness or inability to move arm or leg on one side of the body
- Decreased level of alertness
- Numbness that creates interference with feeling hot or cold on the body
While you cannot prevent a Brain Tumor, you can reduce the risk by refraining from smoke and excessive radiation exposure. However, after a Brain Tumor treatment, it is crucial to follow up with your doctor regularly.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.
 How do you detect a Brain Tumor?
How do you detect a Brain Tumor?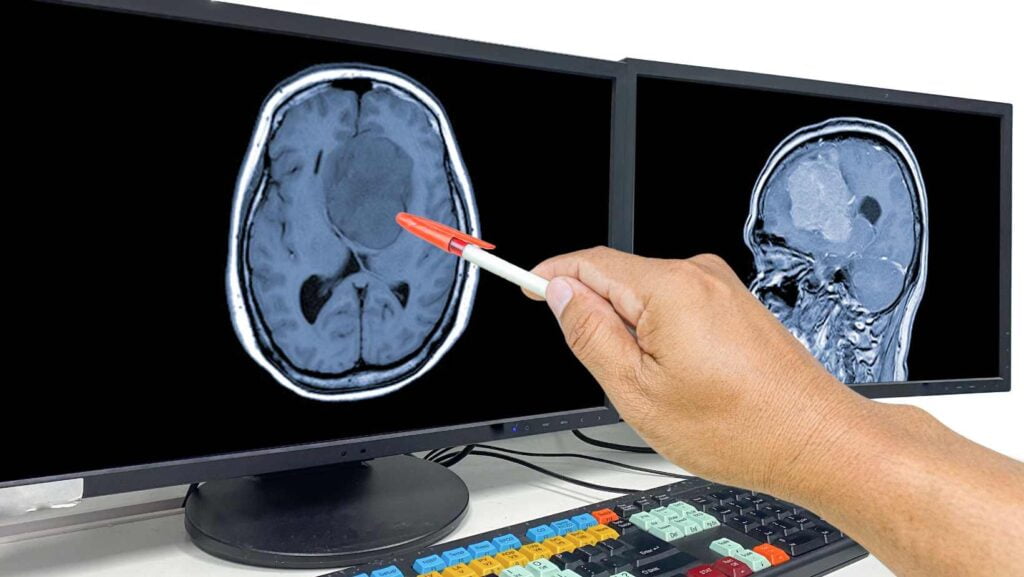 What is the treatment of a Brain Tumor?
What is the treatment of a Brain Tumor?


