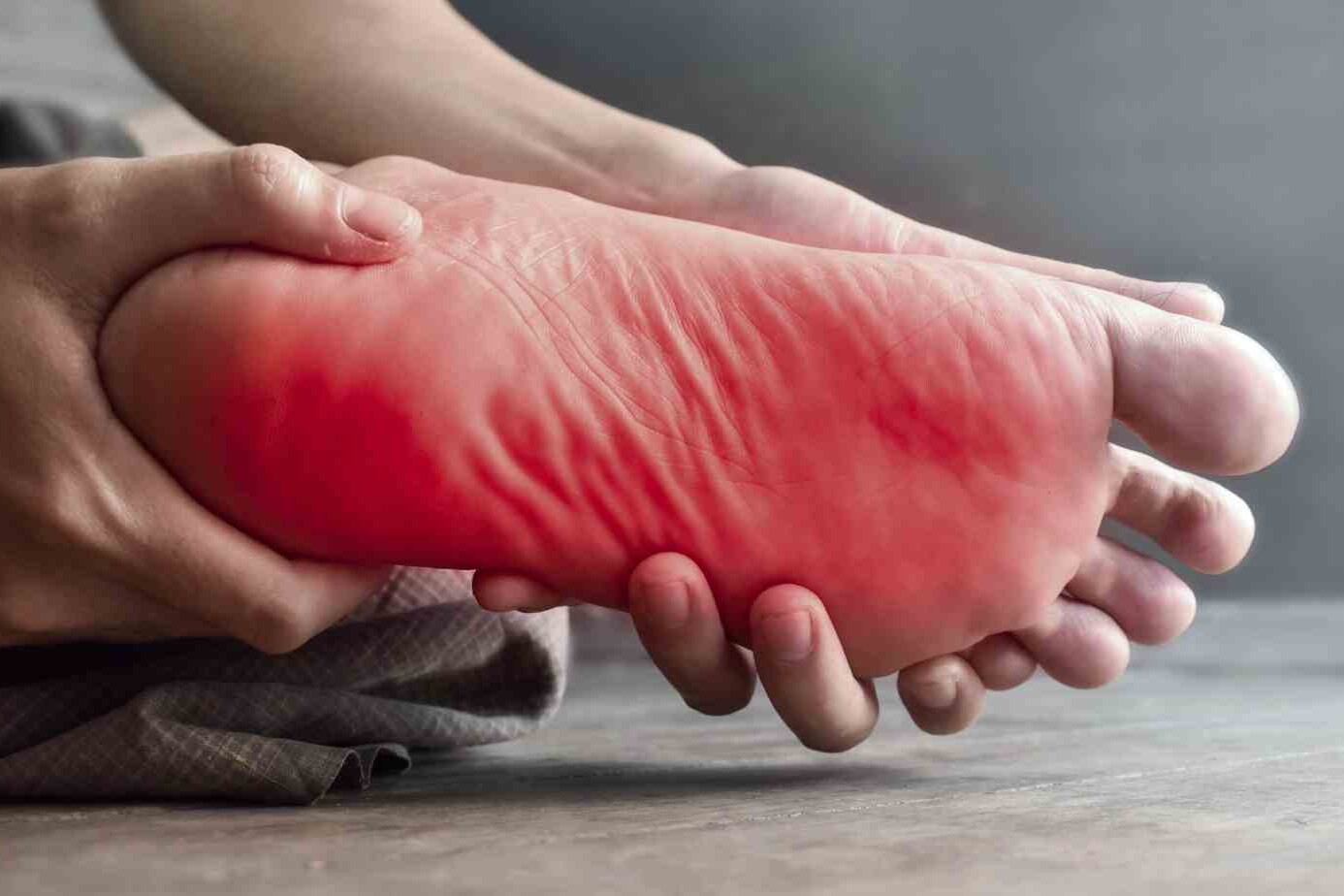
Neuropathy is when your nerves are damaged or not working right. It often affects the peripheral nerves. These nerves link the brain and spinal cord to the body. You might feel numbness, weakness, and pain in your hands and feet. Causes range from diabetes to autoimmune disorders and more. Learning about neuropathy helps in its recognition, diagnosis, and treatment.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a problem that affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves send and receive messages from the brain to the body. It includes nerves that control muscles, feel sensations, and manage body functions automatically. The signs of peripheral neuropathy change based on the kind of nerves involved and the cause of the problem.
Types of Peripheral Nerves
The peripheral nervous system has three main types of nerves:
- Motor nerves: They carry messages from the brain to the muscles. This helps with movement and muscle action.
- Sensory nerves: They send feelings like touch, heat, and pain from the body to the central nervous system.
- Autonomic nerves: They handle involuntary actions in the body, like heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and sweat production.
Issues with these nerve types can cause the symptoms and problems linked to peripheral neuropathy.
Common Symptoms of Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy leads to a wide range of symptoms. These symptoms differ based on the damaged nerves. It’s key to know the types of nerve damage and their symptoms. This helps in dealing with the condition effectively.
Sensory Nerve Symptoms
With sensory nerve damage, you may feel numbness or tingling. This often happens in the hands, feet, or other body parts. You might also lose feeling in those areas or feel sharp, jabbing, or burning pain. Some people become extremely sensitive to touch or changes in temperature.
Motor Nerve Symptoms
Motor nerve damage can cause muscle weakness or loss of muscle tone. Lack of coordination and a higher risk of falling are also common. Moving the affected muscles or limbs might become hard.
Autonomic Nerve Symptoms
Damaged autonomic nerves show different symptoms. These include not handling heat well, or sweating too much or too little. Some people experience digestive issues like constipation or diarrhea. They may also feel dizzy due to low blood pressure.
Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy has many causes. It can be due to autoimmune diseases or metabolic disorders. Infections, inherited conditions, and even exposure to toxins can also lead to it. It’s important to know these causes for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases make the immune system attack the body. This can cause peripheral neuropathy. Sjogren’s syndrome, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis are some autoimmune diseases. They can lead to neuropathy. So can conditions like Guillain-Barré syndrome and paraneoplastic syndrome, which are related to certain cancers.
Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Diabetes, especially when blood sugar isn’t controlled well, is a big cause of peripheral neuropathy. This condition can also be linked to metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome includes high blood sugar, blood pressure, and obesity.
Infections
Infections by certain viruses and bacteria can damage the peripheral nerves. For example, Lyme disease and shingles can lead to neuropathy. So can hepatitis B and C, HIV, and leprosy.
Inherited Disorders
Some people inherit the risk of peripheral neuropathy. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease runs in families. It’s a group of disorders affecting the peripheral nerves.
Tumors and Bone Marrow Disorders
Tumors, both cancerous and non-cancerous, and bone marrow disorders may press on nerves or damage them. Monoclonal gammopathies and amyloidosis, for example, are such conditions.
Other Diseases and Conditions
Certain other diseases can also cause peripheral neuropathy. These include kidney disease, liver disease, and an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
Exposure to Toxins and Medications
Some chemicals and toxins can harm the nerves. This can include industrial chemicals and heavy metals like lead and mercury. Also, some medications, especially some chemotherapy drugs, list neuropathy as a side effect.
Injury or Nerve Compression
Physical injuries from accidents or falls can hurt the nerves. Even activities like sports can be a cause. Nerve compression, which happens in carpal tunnel syndrome, can also bring on neuropathy.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Not getting enough certain vitamins and minerals can hurt your nerves. Deficiencies in B vitamins (like B1, B6, B12), copper, and vitamin E can lead to peripheral neuropathy.
Risk Factors for Neuropathy
Many factors can raise the chances of getting peripheral neuropathy. These include:
- Diabetes, especially with poor blood sugar control
- Alcohol misuse
- Low levels of vitamins, particularly B vitamins
- Infections, such as Lyme disease, shingles, hepatitis, and HIV
- Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus
- Kidney, liver, or thyroid disorders
- Exposure to toxins and chemicals
- Repetitive motions, such as those performed in certain jobs
- Family history of neuropathy
Complications of Peripheral Neuropathy
Without treatment, peripheral neuropathy can cause serious problems. These include skin injuries, burns, and wounds, often on the feet. People may not feel these injuries and end up with infections.
Falls and balance issues are also common. This comes from weaker muscles and loss of feeling. This is especially risky for those with diabetes. It’s crucial to manage and prevent peripheral neuropathy.
Diabetic foot ulcers are a major issue with this condition. It happens because high blood sugar harms blood vessels. This cuts off blood supply to the feet, slowing wound healing and raising the risk of gangrene.
Another problem is cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN). It can make exercise hard and cause low blood pressure. This can lead to dizziness or even faints. Steps to combat low blood pressure include standing up slowly and drinking more fluids. Wearing compression stockings and taking certain drugs like fludrocortisone and midodrine can also help.
Heart arrhythmias and, in the worst case, cardiac arrest can happen due to CAN. Doctors may prescribe medications like flecainide to help manage these heart problems. It’s vital for people with CAN to regularly check their heart health. This can help doctors treat any issues quickly and effectively.
Preventing Peripheral Neuropathy
The best way to stop peripheral neuropathy is by handling the health problems that start it. This means keeping your blood sugar level right if you have diabetes. It also means treating autoimmune diseases and infections linked to nerve damage.
Managing Underlying Conditions
If you have diabetes, it’s crucial to keep your blood sugar levels in check. Over half of diabetes patients face some neuropathy. Keeping diabetes under control helps avoid or slow down nerve damage.
Problems like Sjogren’s, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis can also trigger neuropathy. You can reduce the risk by treating these diseases with medications or other treatments.
Some infections, like Lyme disease and HIV, can harm your nerves. If you catch these early and treat them fast, it can help prevent neuropathy.
Adopting Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Stay healthy by eating right and exercising. This helps protect your nerves. And avoid things that can hurt your nerves, like toxic chemicals and too much alcohol.

By managing your health and life choices, you lower the risk of peripheral neuropathy. This also cuts down on its related problems.
What is neuropathy
Neuropathy is a broad term for issues with peripheral nerves, which are outside the brain and spinal cord. It causes symptoms like numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain, especially in the hands and feet. Various things, like diabetes, autoimmune diseases, infections, and even vitamin shortages can trigger neuropathy. So, knowing what neuropathy is helps in spotting, diagnosing, and treating it.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
To diagnose peripheral neuropathy, doctors start with a detailed medical history and a physical exam. They ask about symptoms, medical conditions, things you’ve been exposed to, and family disease history. This helps find out the possible reasons for the neuropathy.
Medical History and Physical Examination
In the medical history, you’ll talk about where, how bad, and how it changes your numbness or pain. Doctors also look into your medical past, lifestyle, anything toxic you’ve encountered, how much you drink, and if your family has nerve diseases.
Next, the physical exam checks things like your tendon reflexes, how strong your muscles are, and if you feel things as you should. It also looks at your balance and coordination, key in diagnosing neuropathy.
Laboratory Tests
Doctors might order many lab tests to figure out peripheral neuropathy. They check your blood for vitamin shortages, autoimmune problems, and infections. And they look at your liver, kidneys, and thyroid.
Your urine might be tested for Bence-Jones proteins, a sign of multiple myeloma.
Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography
Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) are special tests that doctors might do. These tests show how your peripheral nerves are working. They help find out what’s wrong and how bad it is.
Imaging Tests
In some situations, imaging tests like MRIs or CT scans are needed. These look for things like compressed nerves, tumors, or other issues in your body. They’re important as they show hidden problems.
Nerve Biopsy and Genetic Testing
Sometimes, for very challenging cases, a nerve biopsy or genetic test is done. This is more for rare or inherited forms of neuropathy. These tests are crucial for finding the exact cause.

Treatment and Management Strategies
The main goal of treating peripheral neuropathy is to deal with its main cause, if we can. Steps may include:
- Keeping blood sugar in check for those with diabetes
- Using drugs or therapies to fight autoimmune issues
- Treating any infections beneath the surface
Medications for Symptom Relief
Besides the root cause, doctors might give medications to ease peripheral neuropathy symptoms. These can include:
- Medicines for pain, like certain antidepressants and anti-seizure drugs
- Creams or ointments for pain in certain spots
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Physical and occupational therapy is key to peripheral neuropathy management. It aims to help patients:
- Better their muscle strength and coordination
- Improve balance and avoid tumbles
- Master skills to handle symptoms and keep doing daily tasks alone
Pain Management
For those with ongoing pain from peripheral neuropathy, docs might suggest pain relief methods. These can be:
- Drugs to ease the pain
- Scrambler therapy, an alternative method. It uses electrical pulses to lower chronic pain levels
Conclusion
Peripheral neuropathy is a serious issue that challenges life quality. It’s vital for both doctors and patients to know the causes, symptoms, and how to diagnose and treat it. This knowledge helps in spotting the disease early and dealing with it the right way.
It affects about 2.4% of the world and reaches 8% in the elderly, making it a big health issue. Causes like diabetes, infections, and genetic disorders signal the need for careful check-ups and specific treatments.
Keeping up with the latest neuropathy info is important for healthcare workers and patients. It aids in success in dealing with this complex illness. By working together, they can make real improvements in life quality and reduce the impact of this severe disorder.
FAQ
What is neuropathy?
Neuropathy is nerve damage or dysfunction. It mainly affects the nerves that link the brain and spinal cord to the body parts. You might feel numb, weak, or in pain, especially in your hands and feet.
What is peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These nerves help you feel and move your body parts by sending messages to and from the brain.
What are the main types of peripheral nerves?
The peripheral nervous system has motor nerves, sensory nerves, and autonomic nerves. Motor nerves help you move your muscles, sensory nerves let you feel touch, and autonomic nerves handle automatic body functions.
What are the common symptoms of neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy’s symptoms vary but often include numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet. You might also notice weakness, coordination problems, or changes in how you feel hot or cold.
What are some of the causes of peripheral neuropathy?
Many things can cause peripheral neuropathy. This includes diseases, like diabetes, and autoimmune conditions. Infections and physical injuries are also common culprits. Even exposure to certain toxins can play a role.
What are the risk factors for developing neuropathy?
Several things can raise your risk of getting peripheral neuropathy. These include diabetes, alcohol abuse, and low vitamin levels. Infections, autoimmune diseases, and a family history of neuropathy also increase your risk.
What are some of the complications of peripheral neuropathy?
Left untreated, peripheral neuropathy can lead to severe issues. These include injuries or infections due to reduced sensation. Balance problems and falls can also occur, making it crucial to manage the condition.
How can I prevent peripheral neuropathy?
To prevent peripheral neuropathy, handle related health issues like diabetes. Also, live a healthy life. Eat well, exercise, and avoid harm to your nerves. These steps can keep or slow neuropathy from getting worse.
How is peripheral neuropathy diagnosed?
Doctors use various tests to diagnose peripheral neuropathy. These may include checking your medical history, doing physical exams, and running lab tests. They might also use special nerve tests or even look at nerve tissue closely with a biopsy.
How is peripheral neuropathy treated?
There’s no cure for peripheral neuropathy, but treatments can help. These include pain medicines, therapies to improve movement, and sometimes alternative methods for pain relief. The aim is to ease symptoms and help you live better.
Source Links
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061
- https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/neuropathy
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/14737-peripheral-neuropathy
- https://www.webmd.com/brain/understanding-peripheral-neuropathy-basics
- https://www.houstonmethodist.org/blog/articles/2024/mar/what-are-the-early-warning-signs-of-neuropathy/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/causes/
- https://www.foundationforpn.org/types-risk-factors/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/complications/
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/peripheral-neuropathy
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20352067
- https://www.dana-farber.org/health-library/tips-for-managing-neuropathy
- https://www.foundationforpn.org/living-well/lifestyle/managing-peripheral-neuropathy/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542220/
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.



