Brachial plexus injury is a condition that affects the network of nerves in your shoulder, arm, and hand, known as the brachial plexus. This injury occurs when these nerves are damaged or torn, resulting in various symptoms and complications. It is essential to have a thorough understanding of the causes, symptoms, and proper care for managing this complex condition effectively.
There are several possible causes of brachial plexus injury, including trauma, birth complications, inflammation, tumors, and accidents. The severity of the injury can range from minor damage to complete paralysis of the arm. Seeking appropriate care and treatment is crucial for better management and improving outcomes.
Throughout this article, we will explore the anatomy and function of the brachial plexus, common symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention methods, and rehabilitation for brachial plexus injury. We will also touch upon the specific challenges faced by infants with neonatal brachial plexus palsy (NBPP) and the latest advances in treatment options.
Key Takeaways:
- Brachial plexus injury occurs when the nerves in the network known as the brachial plexus are damaged or torn.
- The injury can be caused by trauma, birth complications, inflammation, tumors, and accidents.
- Common symptoms include weakness or inability to use certain muscles, complete lack of movement and feeling in the affected area, severe pain, and numbness.
- Early diagnosis, appropriate care, and rehabilitation are essential for managing brachial plexus injury effectively.
- Prevention methods include range-of-motion exercises, protective padding, and promoting healthy development in infants at risk.
Table of Contents
ToggleBrachial Plexus Anatomy and Function
The brachial plexus is a complex network of nerves that originates in the neck and extends into the shoulder, arm, and hand. It plays a crucial role in controlling movement and sensation in the upper limb. Understanding the brachial plexus anatomy and its function is vital in comprehending the complexities of brachial plexus injury and its impact on daily life.
The brachial plexus consists of five major nerves:
- Musculocutaneous nerve
- Axillary nerve
- Median nerve
- Radial nerve
- Ulnar nerve
Each nerve has its own specific function:
| Nerve | Function |
|---|---|
| Musculocutaneous nerve | Controls the muscles involved in flexing the forearm and sensation in the lateral aspect of the forearm |
| Axillary nerve | Innervates the deltoid and teres minor muscles, which are important for shoulder movement and sensation in the shoulder joint |
| Median nerve | Responsible for controlling the muscles involved in finger flexion, as well as sensation in the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger |
| Radial nerve | Controls the muscles responsible for extending the forearm, wrist, and fingers |
| Ulnar nerve | Innervates the muscles involved in finger adduction and controls sensation in the little finger and half of the ring finger |
These nerves work together to transmit signals from the spinal cord to the muscles, allowing us to perform intricate movements in the arm and hand. Additionally, they provide sensory information, enabling us to feel pain, temperature, and touch in these areas.
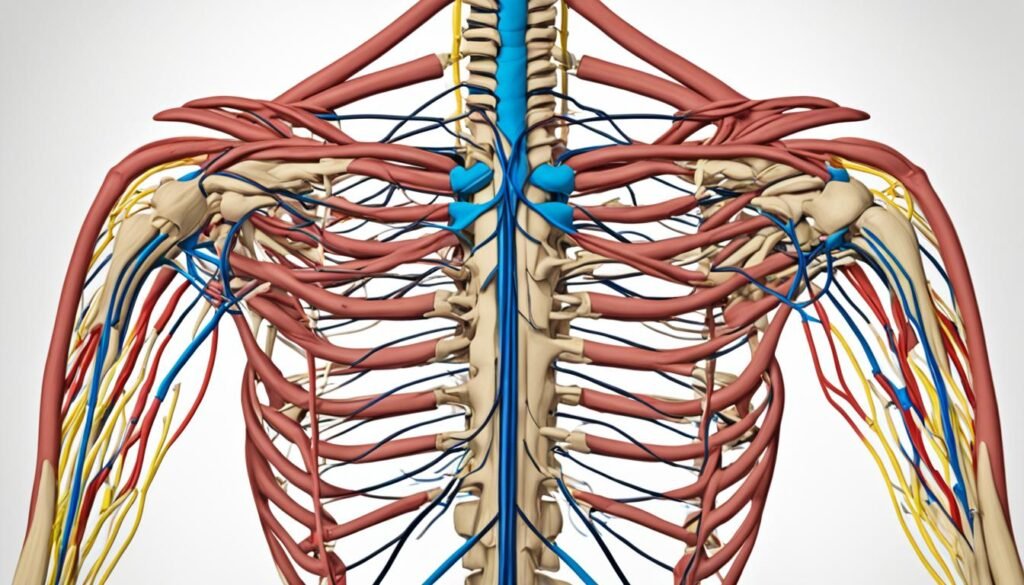
Common Symptoms of Brachial Plexus Injury
A brachial plexus injury can result in various symptoms, which can range in severity depending on the extent and location of the damage. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial in diagnosing and treating the injury effectively. Below are some common symptoms associated with brachial plexus injury:
- Weakness or inability to use certain muscles: Individuals may experience weakness or an inability to move specific muscles in the hand, arm, or shoulder due to nerve damage in the brachial plexus.
- Complete lack of movement and feeling: In some cases, a brachial plexus injury can lead to a complete loss of movement and sensation in the affected area.
- Severe pain: Pain is a prominent symptom of a brachial plexus injury and can range from mild discomfort to intense, debilitating pain.
- Numbness: Numbness or a tingling sensation in the affected arm or hand may indicate nerve damage in the brachial plexus.
- Recurrent burners or stingers: Some individuals may experience episodes of burning pain or electric shock-like sensations traveling down the arm, known as burners or stingers.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Brachial plexus injuries can potentially result in long-term complications such as arm paralysis and disability if left untreated.
Causes and Risk Factors of Brachial Plexus Injury
Brachial plexus injuries can occur due to various factors, including trauma, birth complications, tumors, and cancer treatments. The upper nerves of the brachial plexus are more likely to be injured when the shoulder is forced down while the neck stretches up, whereas the lower nerves are more likely to be injured when the arm is forced above the head.
Common causes of brachial plexus injury include:
- Participating in contact sports like football
- Being involved in high-speed motor-vehicle accidents
- Trauma from accidents or falls
- Tumors
- Cancer treatments
These activities and situations can increase the risk of brachial plexus injury as they put pressure or strain on the nerves.
Risk factors for brachial plexus injury:
- High birth weight: Babies with higher birth weights are more prone to brachial plexus injuries during delivery.
- Breech presentation during birth: When a baby is born feet-first or buttocks-first, it increases the likelihood of a brachial plexus injury.
- Prolonged labor: Long and difficult labors can increase the risk of brachial plexus injuries in newborns.
It is important to be aware of these causes and risk factors to take necessary precautions and seek appropriate medical care to prevent or manage brachial plexus injuries.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Brachial Plexus Injury
Diagnosing a brachial plexus injury involves a comprehensive evaluation to determine the extent of nerve damage. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- A physical examination: The doctor will assess your range of motion, muscle strength, and sensory function in the affected arm and hand. They may also test specific movements and reflexes.
- Sensation and function tests: These involve evaluating your ability to feel touch, temperature, and pain in the affected area. Additionally, the doctor may assess your grip strength and finger dexterity.
- Diagnostic imaging tests: X-rays, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), or Computerized Tomography (CT) scans may be conducted to obtain detailed images of the brachial plexus and identify any structural abnormalities or nerve damage.
The treatment of brachial plexus injuries varies depending on the severity and type of injury. Mild injuries may heal on their own with conservative methods, including:
- Physical therapy: Specific exercises and therapies aimed at improving range of motion, strength, and function in the affected arm and hand.
- Occupational therapy: Techniques to enhance your ability to perform daily activities and regain independence.
However, more severe brachial plexus injuries often require surgical intervention to repair or reconstruct the damaged nerves. Surgical treatments may include:
- Nerve grafting: A procedure in which a healthy nerve from another part of your body is used to bridge the gap and restore continuity in the damaged brachial plexus.
- Nerve transfers: The transfer of functional nerves from less important areas to restore function in the affected arm.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes and restoring function in the arm and hand. Seeking prompt medical attention and consulting with a specialist experienced in brachial plexus injuries can significantly improve your chances of a successful recovery.
| Treatment Options | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Mild to moderate | Involves exercises and techniques to improve range of motion, strength, and function in the affected arm and hand. |
| Occupational Therapy | Mild to moderate | Focuses on enhancing your ability to perform daily activities and regain independence. |
| Nerve Grafting | Severe | Transplanting a healthy nerve from another part of the body to reconstruct the damaged brachial plexus. |
| Nerve Transfers | Severe | Utilizing functional nerves from less critical areas to restore function in the affected arm. |
Early intervention and a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs are essential in maximizing recovery and improving quality of life.
Complications of Brachial Plexus Injury
Brachial plexus injuries can lead to various complications, especially if left untreated or if the injury is severe. These complications can include stiffness in the joints, chronic pain, numbness, muscle atrophy, and permanent disability. Stiff joints can make movement difficult, and lack of feeling in the affected area can lead to accidental burns or injuries. Muscle atrophy can occur due to lack of use during the healing process, and severe injuries may result in permanent muscle weakness or paralysis. Managing these complications may require ongoing physical therapy, pain management strategies, and lifestyle adjustments.
Stiffness in the joints is a common complication of brachial plexus injury. When the nerves are damaged, the affected muscles may become tight and rigid, leading to limited range of motion in the joints. This stiffness can significantly impair daily activities and make it challenging to perform tasks that require precise movement. Physical therapy can help improve joint flexibility and restore functional mobility.
Chronic pain is another complication that individuals with brachial plexus injuries may experience. The damaged nerves can send continuous pain signals to the brain, resulting in persistent discomfort. This pain can significantly impact quality of life and hinder the ability to carry out daily activities. Pain management strategies, such as medication, physical therapy, and alternative therapies like acupuncture, can help alleviate chronic pain and improve overall well-being.
Numbness is a common sensation experienced in the affected area of a brachial plexus injury. The damaged nerves can disrupt the transmission of sensory signals, leading to a loss of feeling in the arm, shoulder, or hand. This lack of sensation can increase the risk of accidental burns, cuts, or injuries, as individuals may not be aware of potential dangers. Proper precautions, such as avoiding extreme temperatures and using protective measures, can help mitigate the risk of accidental injuries.
Muscle atrophy, or the wasting away of muscle tissue, is a potential complication of brachial plexus injury. When the affected arm is immobilized or not used during the healing process, the muscles can weaken and shrink in size. This can result in reduced muscle strength and functionality. Physical therapy and targeted exercises are essential in preventing or minimizing muscle atrophy and promoting muscle strength and endurance.
In severe cases, brachial plexus injuries can lead to permanent disability. If the nerves are severely damaged or torn, it may not be possible to fully restore function and sensation in the affected area. This can result in long-term muscle weakness or paralysis, significantly impacting an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and participate in meaningful work or hobbies. Adaptive devices and assistive technologies, along with comprehensive rehabilitation programs, can help individuals with permanent disability regain independence and improve their overall quality of life.
Managing these complications requires a multidisciplinary approach that includes ongoing medical care, physical therapy, pain management strategies, and lifestyle modifications. It is crucial for individuals with brachial plexus injuries to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans and to stay vigilant in addressing any new or worsening symptoms. With proper care and management, individuals with brachial plexus injuries can minimize the impact of complications and optimize their recovery.

Prevention of Brachial Plexus Injury
While it may not always be possible to prevent brachial plexus injuries, there are measures that can be taken to reduce the risk and prevent complications. By incorporating a few simple strategies into your daily routine, you can help safeguard your brachial plexus and maintain optimal arm and hand function.
Range-of-Motion Exercises and Physical Therapy
Engaging in regular range-of-motion exercises and physical therapy can help prevent joint stiffness and maintain muscle strength, especially if you experience temporary loss of hand or arm function. These exercises aim to keep your joints flexible and improve circulation, promoting overall joint health and preventing the development of stiffness.
Range-of-motion exercises can include:
- Gentle stretching to improve flexibility
- Rotations and circular motions to maintain joint mobility
- Resistance exercises to strengthen muscles
Padding for Added Protection
If you participate in contact sports like football, wearing specific protective padding can provide an extra layer of safety for your brachial plexus. This padding is designed to cushion the area and reduce the risk of injury in case of impact or direct blows. By wearing appropriate padding, you can minimize the chances of sustaining a brachial plexus injury while actively participating in sports.
Preventing Brachial Plexus Injury in Infants
For infants who may be at risk of brachial plexus injury during birth, there are preventive measures that can be taken as well. Encouraging joint movement and maintaining muscle strength through exercises can be beneficial in preventing long-term stiffness and promoting healthy development. Consult with healthcare professionals or pediatric specialists for guidance on safe and effective exercises suitable for infants.

By implementing these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of brachial plexus injury and protect the intricate network of nerves responsible for arm and hand function. Remember, prevention is always better than treatment when it comes to ensuring the health and well-being of your brachial plexus.
Care and Rehabilitation for Brachial Plexus Injury
Effective care and rehabilitation are essential for managing brachial plexus injuries. Treatment plans often involve a combination of surgical intervention, physical therapy, occupational therapy, pain management strategies, and the use of assistive devices.
Physical therapy is a critical component of the treatment plan. It aims to improve range of motion, strengthen muscles, and enhance functional abilities. Through targeted exercises and techniques, physical therapy helps individuals regain mobility and regain control over their affected arm and hand.
Occupational therapy focuses on improving daily activities and tasks such as dressing, eating, and personal care. Occupational therapists work with individuals to develop strategies and adaptive techniques that enable them to perform these activities with increased independence and efficiency.
Pain management strategies may be incorporated into the treatment plan to alleviate discomfort associated with brachial plexus injuries. This may include the use of medication, acupuncture, or other alternative therapies, depending on the individual’s needs and preferences.
Assistive devices, such as braces or splints, may also be recommended to support the affected limb, promote proper alignment, and aid in functional recovery.
Rehabilitation for brachial plexus injury aims to restore function and promote independence in daily life. With the help of a comprehensive treatment plan and the guidance of healthcare professionals, individuals can achieve significant improvements and regain control over their lives.
Rehabilitation Goals for Brachial Plexus Injury
Rehabilitation programs for brachial plexus injury typically focus on achieving the following goals:
- Restoring range of motion and strength in the affected arm and hand
- Improving coordination and motor control
- Enhancing functional abilities for daily activities
- Promoting pain management and reducing discomfort
- Fostering independence and self-care
These goals are achieved through a combination of exercises, therapeutic interventions, and patient education. Physical therapists and occupational therapists work closely with individuals to develop customized treatment plans that address their unique needs and maximize their potential for recovery.
Rehabilitation for brachial plexus injury is a holistic process that requires dedication, patience, and active participation from the individual. It may take time, but with the guidance of healthcare professionals and a supportive environment, individuals can overcome the challenges of brachial plexus injury and regain their independence and functionality.
| Treatment Approaches | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy |
|
| Occupational Therapy |
|
| Pain Management |
|
| Assistive Devices |
|
Brachial Plexus Injury in Infants – Neonatal Brachial Plexus Palsy (NBPP)
Brachial plexus injuries can also affect infants during childbirth, resulting in Neonatal Brachial Plexus Palsy (NBPP). These injuries can occur due to complications such as shoulder dystocia or breech presentation. NBPP is often characterized by two specific conditions: Erb’s palsy and Klumpke’s palsy, which affect different areas of the brachial plexus.
Erb’s palsy is the most common form of NBPP and typically affects the upper brachial plexus nerves. It can result in weakness or loss of motion in the affected arm. On the other hand, Klumpke’s palsy affects the lower brachial plexus nerves and can cause weakness or paralysis in the hand and forearm.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing NBPP effectively. Medical professionals will assess the severity of the injury and determine the appropriate treatment options. In many cases, physical therapy and occupational therapy may be recommended to improve muscle strength, range of motion, and overall function of the affected arm.
In some instances, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged nerves. The goal of treatment is to promote healing, restore function, and help the infant achieve full or near-full recovery.

Research and Advances in Brachial Plexus Injury Treatment
Ongoing research and advances in medical technology are paving the way for improved treatment options for brachial plexus injury. Scientists and healthcare professionals are constantly striving to develop innovative approaches that can restore function and enhance outcomes for individuals with this condition.
One significant area of advancement is in surgical techniques. Nerve grafting and nerve transfers have shown promising results in helping to restore function and improve overall outcomes for patients with brachial plexus injuries. These procedures involve transferring nerves from healthy areas of the body or using grafts to bridge the gap between damaged nerves, facilitating nerve regeneration and promoting recovery.
Another promising avenue of research is regenerative therapies, specifically stem cell therapy. Stem cells have the potential to differentiate and develop into various cell types, making them a viable candidate for repairing damaged nerve tissue in the brachial plexus. While still in the experimental stage, initial studies have shown encouraging results, and researchers continue to explore the potential of stem cell therapy in treating brachial plexus injuries.
In addition to surgical and regenerative advances, there have been significant strides in rehabilitation strategies, pain management techniques, and assistive devices. Physical therapy and occupational therapy play crucial roles in helping individuals with brachial plexus injuries regain independence and improve their quality of life. These therapies focus on strengthening muscles, improving range of motion, and developing compensatory strategies to maximize function in daily activities.
Pain management strategies have also evolved, offering individuals with brachial plexus injuries various options to manage their pain effectively. This can include medication, physical modalities, acupuncture, and other alternative therapies tailored to each individual’s needs. The goal is to provide relief and improve overall well-being.
Assistive devices, such as splints and braces, can aid in supporting weakened or paralyzed muscles and help individuals maintain functionality. They are designed to promote independence and compensate for any limitations caused by the injury.
Overall, ongoing research and development in the field of brachial plexus injury continue to bring forth exciting advancements in treatment options. From surgical innovations to regenerative therapies, rehabilitation strategies, pain management techniques, and assistive devices, these advances provide hope for improved care and recovery for individuals affected by brachial plexus injury.
Conclusion
Brachial plexus injury is a complex condition that can have significant implications for your physical function and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial in managing this condition effectively. Prompt medical attention, appropriate care, and rehabilitation are key factors in achieving optimal recovery and minimizing complications.
To improve your outcomes and live a fulfilling life with enhanced functionality and independence, it is important to follow these care tips:
- Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any symptoms or suspect a brachial plexus injury.
- Follow the recommended treatment plan, which may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, pain management strategies, and assistive devices.
- Stay informed about advancements in treatment options and discuss them with your healthcare provider to explore all available options.
- Be proactive in managing your condition by adhering to post-treatment care instructions and attending regular check-ups.
- Engage in range-of-motion exercises and other recommended therapies to maintain joint mobility and muscle strength.
- Take necessary precautions in activities or sports that pose a risk of injury to the brachial plexus.
By following these care tips, seeking necessary treatment, and staying informed about advancements in treatment options, you can improve your outcomes and live a fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by a brachial plexus injury.
FAQ
What is brachial plexus injury?
Brachial plexus injury is a condition that occurs when the nerves in the brachial plexus network are damaged or torn.
What are the causes of brachial plexus injury?
Brachial plexus injuries can be caused by trauma, birth complications, inflammation, tumors, and accidents.
What are the common symptoms of brachial plexus injury?
Common symptoms include weakness or inability to use certain muscles, arm paralysis, severe pain, and numbness.
What are the risk factors for brachial plexus injury?
Common risk factors include trauma from accidents or falls, difficult births, contact sports, and certain cancer treatments.
How is brachial plexus injury diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis usually involves physical examination and imaging tests. Treatment options range from nonsurgical treatments to surgical intervention.
What are the complications of brachial plexus injury?
Complications can include stiffness, chronic pain, muscle atrophy, numbness, and permanent disability.
Can brachial plexus injury be prevented?
While not always preventable, measures such as range-of-motion exercises and wearing protective padding can help reduce the risk.
How is brachial plexus injury cared for and rehabilitated?
Treatment plans may include surgery, physical therapy, occupational therapy, pain management, and assistive devices.
What is Neonatal Brachial Plexus Palsy (NBPP)?
NBPP refers to brachial plexus injuries in infants, often caused by birth complications, and may require physical therapy or surgery for treatment.
What are the latest advancements in brachial plexus injury treatment?
New surgical techniques, regenerative therapies, and advancements in rehabilitation strategies offer hope for improved outcomes.
Source Links
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Board-Certified Neurologist
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.