Epilepsy is a long-term brain condition where sudden changes in brain signals cause repeated seizures. Alternative therapies for epilepsy come into focus when seizures continue despite medication or when side effects limit daily life. These approaches include diet-based treatments, stress control methods, mind-body practices, and supportive therapies that aim to reduce seizure triggers rather than directly stop seizures.
Alternative therapies for epilepsy do not cure the condition but can support seizure stability when used with medical treatment. The strongest evidence exists for dietary therapy, while other options show mixed or limited results.
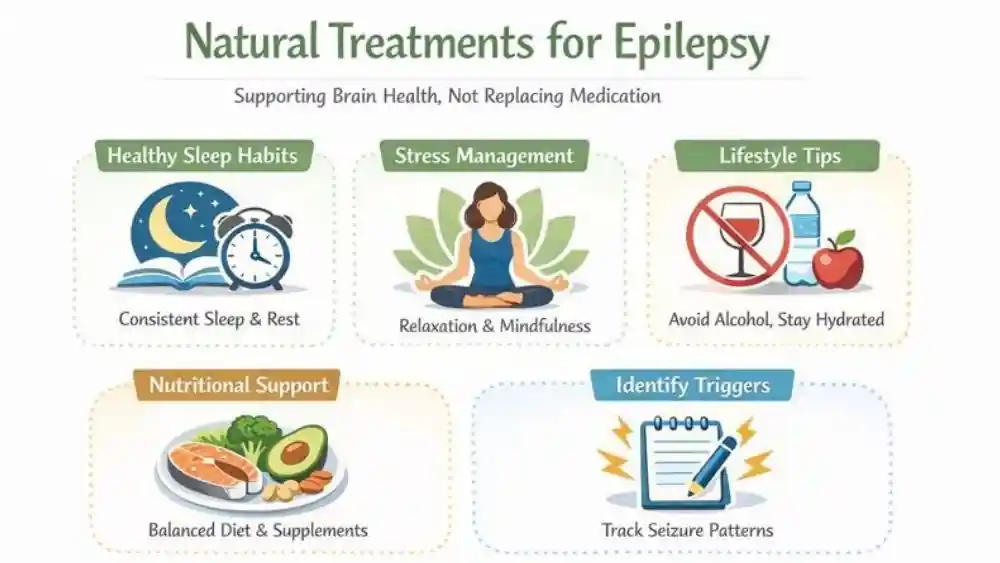
Natural Treatments For Epilepsy
What Are Natural Treatments For Epilepsy?
Natural treatments for epilepsy include lifestyle changes, sleep support, stress control, and nutrition-focused methods that aim to lower seizure triggers. You often see these options described as gentle or holistic. In reality, they work by reducing factors that stress the brain, such as sleep loss, dehydration, or emotional strain. Alternative therapies for epilepsy in this group do not act directly on seizure pathways like medicines do.
Common natural approaches include regular sleep schedules, avoiding alcohol, staying hydrated, and managing illness quickly. These steps matter because disrupted sleep and fever raise seizure risk. Consistent routines reduce seizure frequency in some people, especially those with reflex seizures, meaning seizures triggered by specific factors.
Scientific Evidence Behind Natural Epilepsy Treatments
Evidence for natural treatments for epilepsy remains limited. Results vary between seizure types. For example, stress reduction may help focal seizures (seizures starting in one brain area) but show little effect on generalized epilepsy.
Alternative therapies for epilepsy based on lifestyle changes improve overall health, not seizure cure. Sleep regulation and stress control support brain stability. They do not replace anti-seizure drugs. Experts caution against over-interpreting personal stories since placebo effects remain common in epilepsy studies.
When Natural Treatments May Help Alongside Medication
You may benefit from natural methods if your seizures stay mostly controlled, but triggers still exist. Poor sleep, skipped meals, and emotional stress increase seizure risk. Addressing these factors improves seizure consistency. Alternative therapies for epilepsy work best when added after seizure control begins, not before.
Doctors often recommend these strategies early because they carry low risk. However, they still require honesty with your care team. Even simple supplements can interfere with medication levels.
Risks Of Replacing Prescribed Anti-Seizure Drugs
Stopping medication remains dangerous. Sudden drug withdrawal increases seizure clusters and raises the risk of status epilepticus (a seizure lasting longer than five minutes). This condition causes brain injury and can be fatal. Alternative therapies for epilepsy should never replace medication unless a neurologist supervises the change.
Alternative Medicine For Epilepsy
Overview Of Alternative Medicine Approaches
Alternative medicine for epilepsy includes herbal remedies, traditional healing systems, and non-conventional practices. Examples include Ayurveda, traditional Chinese medicine, and homeopathy. These systems often describe epilepsy as an energy imbalance rather than a neurological condition.
Scientific support remains weak for most of these methods. Alternative therapies for epilepsy in this category vary widely in safety. Some herbs affect liver enzymes that process seizure drugs. This interaction can lower drug levels and trigger seizures.
Herbal Remedies Commonly Used For Epilepsy
Herbs like valerian, ginkgo, kava, and passionflower appear in epilepsy discussions. Some claim calming effects on the nervous system. Evidence does not support seizure control benefits. Ginkgo has been linked to increased seizure risk in case reports.
Alternative therapies for epilepsy involving herbs require extreme caution. Natural does not mean safe. Many herbs lack quality control, and dosage varies between products.
Vitamins And Supplements Studied In Epilepsy
Vitamin B6 helps rare genetic epilepsy types diagnosed in infancy. Outside of deficiency states, extra supplementation shows little benefit. Magnesium and omega-3 fatty acids receive attention, but results remain inconsistent.
Clinical guidance stresses that alternative medicine for epilepsy involving supplements should address confirmed deficiencies only. High doses may worsen seizures or interact with drugs.
Safety Concerns and Drug-Herb Interactions
Drug-herb interactions represent one of the biggest risks. Herbs can speed up or slow down drug breakdown in the liver. This change alters blood levels without warning. Studies from epilepsy clinics show that seizure breakthroughs often follow unreported supplement use. Alternative therapies for epilepsy must always be shared with your neurologist.
Dietary Therapy For Epilepsy
Ketogenic Diet And Seizure Control
Dietary therapy for epilepsy shows the strongest scientific support among non-drug options. The ketogenic diet uses high-fat and very low-carbohydrate intake to shift the brain’s energy source from glucose to ketones (fat-based fuel). This shift stabilizes nerve signaling in some patients.
Clinical trials confirm seizure reduction in many children with drug-resistant epilepsy. Adults also benefit, though success rates remain lower. Alternative therapies for epilepsy using diet require strict medical supervision.
Modified Atkins And Low Glycemic Index Diets
The modified Atkins diet allows more protein and slightly more carbohydrates. The low glycemic index diet focuses on slow-digesting carbs that avoid blood sugar spikes. These options improve tolerance while maintaining seizure benefits.
Doctors often recommend these plans when strict keto proves difficult. Dietary therapy for epilepsy works best with a dietitian’s support to prevent nutrient deficiencies.
Who Benefits Most From Dietary Therapy
Children with drug-resistant epilepsy benefit most. Certain genetic epilepsy syndromes respond especially well. Adults may see moderate improvement and show better results when dietary therapy starts early.
Long-term success depends on consistency and monitoring. Alternative therapies for epilepsy using diet require commitment and family support.
Side Effects And Long-Term Nutritional Concerns
Side effects include constipation, kidney stones, slowed growth in children, and vitamin deficiencies. Regular lab testing helps detect problems early. Dietary therapy for epilepsy remains safe when monitored but risky when self-directed.
Yoga And Meditation For Epilepsy
How Stress Affects Seizure Frequency
Stress does not cause epilepsy, but it can increase how often seizures happen. When you feel stressed, your body releases stress hormones. These hormones change brain signals and sleep patterns.
Emotional stress and poor sleep often appear in seizure diaries before breakthrough seizures. Alternative therapies for epilepsy that focus on stress control aim to reduce these triggers, not the seizures themselves.
Stress also affects medication adherence. You may miss doses or sleep poorly during stressful periods. This combination raises seizure risk. Managing stress supports stability, especially in focal epilepsy.
Role Of Yoga In Seizure Management
Yoga combines movement, breathing, and body awareness. Yoga may help reduce seizure frequency in some people, but results remain inconsistent. The benefit likely comes from improved sleep, reduced anxiety, and better breathing control.
Yoga does not change seizure pathways in the brain. Alternative therapies for epilepsy, like yoga work indirectly. Certain poses that involve breath-holding or extreme neck movement may increase risk. Neurologists advise gentle forms only, with the instructor’s awareness of your condition.
Meditation And Breathing Techniques For Epilepsy
Meditation trains attention and emotional control. Slow breathing lowers heart rate and reduces nervous system activation. Some small clinical studies report fewer seizures with regular meditation practice. Others show no clear change.
The strongest benefit appears in anxiety reduction. Anxiety acts as a seizure trigger for many people. Alternative therapies for epilepsy that calm the nervous system may help reduce seizure-provoking stress, but they do not replace medication.
Evidence Limitations Of Mind-Body Therapies
Most studies involve small groups and short timeframes. Placebo effects remain strong. No large randomized trials confirm seizure control through meditation or yoga alone. Medical groups agree that mind-body approaches work best as supportive care.
Supportive Therapies For Epilepsy
Biofeedback And Neurofeedback Therapy
Supportive therapies for epilepsy include biofeedback and neurofeedback. Biofeedback teaches you to control body responses like muscle tension or heart rate. Neurofeedback focuses on brain wave patterns using EEG (brain signal recording).
Some studies show seizure reduction in select patients, especially those with focal epilepsy. Other studies show no benefit. Results depend on training quality and patient consistency. These methods require specialized centers and trained professionals.
Music Therapy And Sensory-Based Interventions
Music therapy uses rhythm and sound to influence mood and relaxation. Calming music lowers stress hormones. Rare cases report seizure reduction with specific music patterns.
Sensory-based methods remain experimental. Supportive therapies for epilepsy in this category mainly improve emotional well-being rather than seizure control.
Acupuncture and Epilepsy: What Research Shows
Acupuncture involves placing thin needles at specific body points. Some clinical trials report reduced seizure frequency. Others find no difference compared to placebo treatment. Results remain mixed.
Safety depends on practitioner training. Acupuncture should never replace medication. Alternative therapies for epilepsy, like acupuncture, require realistic expectations and medical oversight.
Physical And Occupational Therapy Support
Physical therapy helps with balance, strength, and injury prevention. Occupational therapy supports daily skills and independence. These therapies do not reduce seizures but lower injury risk and improve quality of life. Supportive therapies for epilepsy focus on living safely with seizures, not stopping them.
Combining Alternative Therapies With Medical Treatment
Why Alternative Therapies Should Not Replace Medication
Anti-seizure medicines have the strongest evidence for seizure control. Even in drug-resistant epilepsy, stopping medication increases seizure severity. Alternative therapies for epilepsy lack consistent proof for seizure prevention.
Replacing medication without supervision leads to emergency hospital visits and long-term harm. Doctors stress that alternatives work as add-ons, not substitutes.
Coordinating Care With A Neurologist
You should inform your neurologist about every supplement, diet, or therapy you try. This helps track interactions and seizure changes. Neurologists use blood tests and seizure logs to adjust treatment safely.
Coordinated care reduces risk and improves outcomes when using alternative therapies for epilepsy .
Monitoring Seizure Control And Side Effects
Seizure diaries help identify triggers and trends. Lab tests monitor drug levels and nutritional status. Diet-based therapies need regular follow-up to prevent deficiencies. Monitoring keeps alternative therapies for epilepsy from causing silent harm.
Risks And Limitations Of Alternative Therapies For Epilepsy
Unproven Claims And Misinformation
Online sources often promise cures. These claims rely on testimonials, not data. Epilepsy remains a chronic brain condition for most people. No alternative method cures it. Alternative therapies for epilepsy should raise caution when claims sound absolute or guaranteed.
Financial And Emotional Risks
Some treatments cost thousands without proof. Repeated failure causes stress and frustration. Stress itself increases seizure risk. False hope creates emotional strain for families and patients.
Delayed Access To Effective Medical Treatment
Delaying proper treatment allows seizures to continue uncontrolled. Repeated seizures damage brain networks over time. Early seizure control improves long-term outcomes.
Who May Consider Alternative Therapies for Epilepsy?
Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Cases
Drug-resistant epilepsy means seizures continue after trying two appropriate medications. In these cases, dietary therapy, surgery, or neurostimulation receives priority. Alternative treatments for epilepsy may support care but not replace proven options.
Children Vs Adults: Different Considerations
Children respond better to dietary therapy. Adults show mixed results. Growth, learning, and nutrition matter more in children, so monitoring becomes stricter.
Individualized Treatment Planning
Epilepsy varies by cause, seizure type, and age. Treatment plans must match individual needs. Alternative therapies for epilepsy require personalization, not general advice.
When To Avoid Alternative Therapies For Epilepsy
Frequent Or Uncontrolled Seizures
If seizures remain frequent, medical treatment comes first. Alternatives may delay life-saving care.
History Of Status Epilepticus
This history raises risk during treatment changes. Any therapy adjustment requires close supervision.
Pregnancy And Epilepsy Safety Concerns
Pregnancy alters drug metabolism. Supplements may harm fetal development. Changes should happen only under specialist care.
FAQs
Can Alternative Therapies Cure Epilepsy?
No evidence shows a cure through alternative approaches. Epilepsy treatment focuses on seizure control and safety. Alternative therapies for epilepsy support care but do not remove the condition.
Are Natural Treatments Safe For Children With Epilepsy?
Some lifestyle-based options may help when supervised. Supplements and herbs carry a higher risk. Pediatric neurologists should guide all decisions involving alternative therapies for epilepsy .
How Long Do Alternative Therapies Take To Work?
Dietary therapies may show effects within months. Other approaches show unclear timelines. Results vary by seizure type and consistency.
Which Alternative Therapy Has The Strongest Evidence?
Diet-based approaches show the strongest evidence, especially for drug-resistant epilepsy. Other alternative therapies for epilepsy show limited or mixed support.
Can Drug Herb Interactions Worsen Seizure Control?
Yes. Many herbs alter medication levels. This interaction can trigger seizures or side effects without warning.
How Does Dietary Therapy Help Manage Epilepsy?
It changes brain energy use and stabilizes nerve signals. This effect reduces seizures in some people.
How Does The Ketogenic Diet Reduce Seizure Frequency?
The diet shifts the brain’s energy source from glucose to ketones. This change affects how neurons send signals.
What Is The Modified Atkins Or Low Glycemic Index Diet?
These diets reduce carbs without strict ketosis. They improve flexibility while keeping seizure benefits.
Who Benefits Most From Dietary Therapy For Epilepsy?
Children with drug-resistant epilepsy benefit most. Adults may also improve with careful monitoring.
Epilepsy is a long-term brain condition where sudden changes in brain signals cause repeated seizures. Alternative therapies for epilepsy come into focus when seizures continue despite medication or when side effects limit daily life. These approaches include diet-based treatments, stress control methods, mind-body practices, and supportive therapies that aim to reduce seizure triggers rather than directly stop seizures.
Alternative therapies for epilepsy do not cure the condition but can support seizure stability when used with medical treatment. The strongest evidence exists for dietary therapy, while other options show mixed or limited results.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.