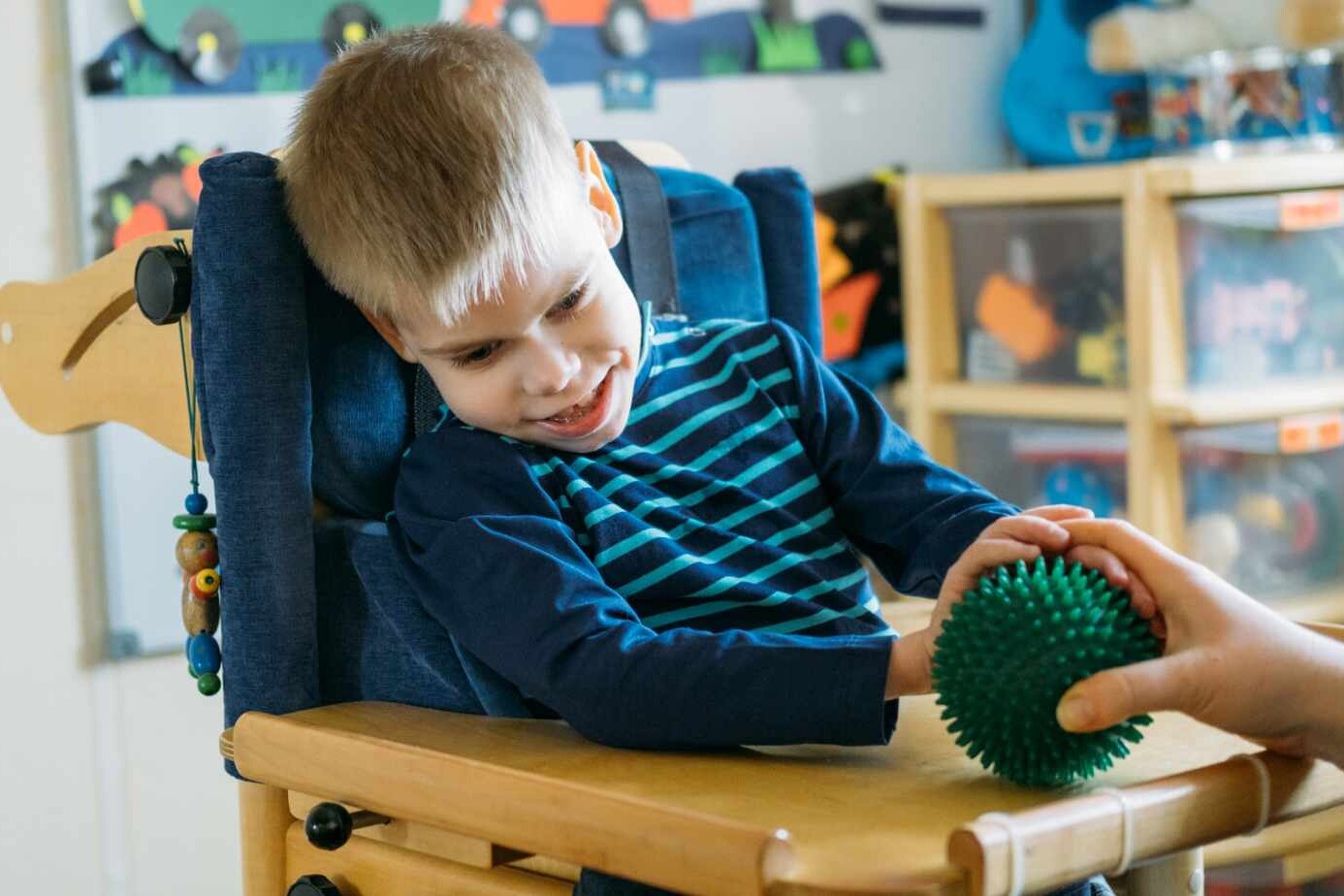
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy affects both the arms and legs, as well as the trunk and face, making movements jerky and awkward. This type of cerebral palsy is the most severe, and children with this condition often face challenges with mobility and multiple associated conditions such as speech difficulties and seizures.
The underlying cause of cerebral palsy, including spastic quadriplegia, is brain damage or abnormal brain development. Various factors can contribute to this damage, including prematurity, fetal infections or stroke, maternal infections or medical conditions, exposure to toxins, or medical negligence.
Although there is no cure for spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy, early interventions and treatments can make a significant difference in improving a child’s quality of life. However, individuals with this condition will require lifelong support and care.
In this article, we will explore the symptoms, diagnosis, complications, treatment options, prognosis, and causes of spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy. With a better understanding of this condition, you can make informed decisions and provide the necessary care and support to those affected by it.
Table of Contents
ToggleSymptoms and Diagnosis of Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy is characterized by more severe symptoms compared to other types of cerebral palsy. Common symptoms include:
- Rapidly contracting and releasing muscles
- Joints that cannot stretch or move
- Muscle tightness and spasticity
- Muscle tremors
- Difficulty walking
- Limb scissoring
- Speech impediments or language disorders
- Seizures
- Cognitive disabilities
The early signs of spastic quadriplegia are usually apparent and can be easily identified. Babies may exhibit stiff muscles, including rigid or crossed legs and arms, spastic limbs, tense muscles, and tremors. They may also miss developmental milestones such as holding up their head, rolling over, and sitting.
Diagnosis of spastic quadriplegia typically occurs during infancy when doctors observe significant delays in a baby’s development. Physical exams, observations of motor skills and reflexes, as well as brain imaging tests like CT and MRI scans, may be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions.
Early Signs of Spastic Quadriplegia Cerebral Palsy
- Stiff muscles, including rigid or crossed legs and arms
- Spastic limbs and tense muscles
- Developmental delays and missed milestones
- Tremors
Diagnosis of Spastic Quadriplegia Cerebral Palsy
Medical professionals use various methods for diagnosing spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy:
- Physical exams: Doctors assess motor skills, reflexes, and muscle tone.
- Observations: Developmental milestones and patterns of movement are observed.
- Brain imaging tests: CT and MRI scans may help identify brain abnormalities or damage.
Complications and Treatment Options for Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy can present various complications that significantly impact a child’s well-being. These complications may include limb deformities, scoliosis (a curvature of the spine), ankle deformities, joint contractures (permanent shortening of the muscles around a joint), malnutrition, seizures, constipation, and incontinence.

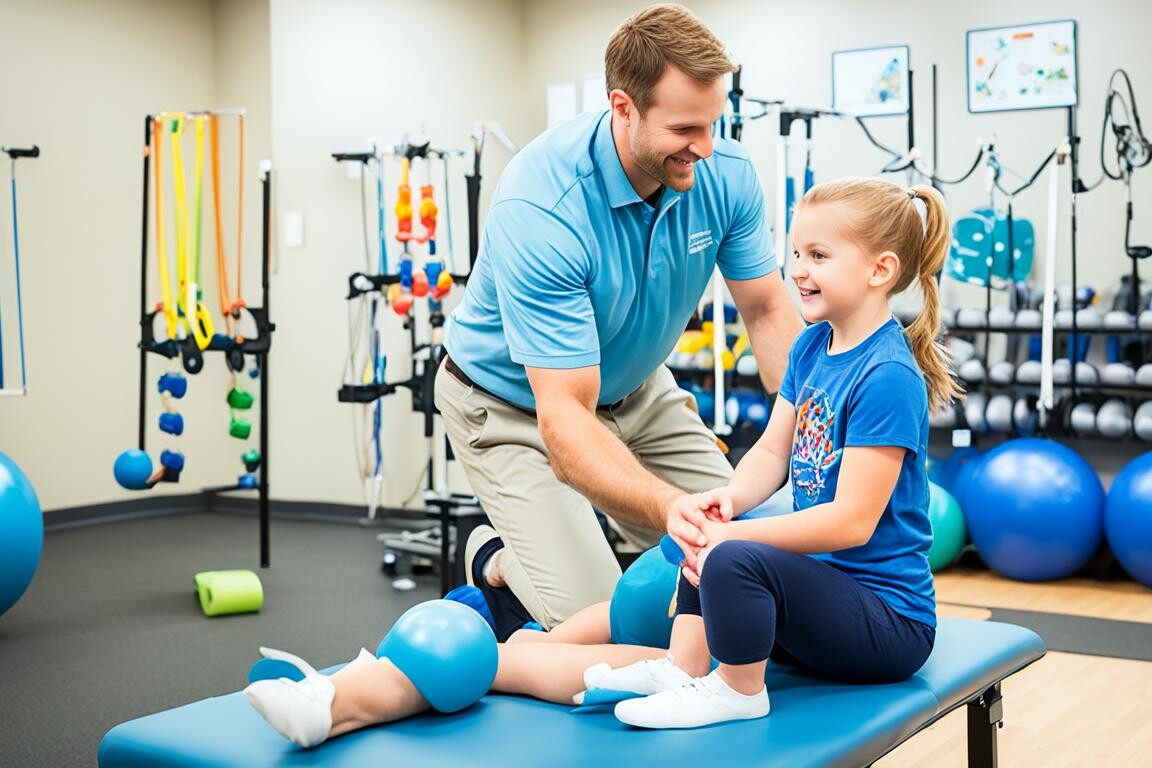
When treating spastic quadriplegia, it is crucial to consider an individualized approach that addresses the specific needs of each child. Treatment options can vary based on the severity of symptoms and may involve a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, medications, assistive devices, and in some cases, surgery.
Treatment Options:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is often the first-line treatment for children with spastic quadriplegia. It focuses on improving muscle strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Through targeted exercises and activities, physical therapists help enhance motor skills and promote independent movement.
- Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy plays a vital role in developing daily living skills for children with spastic quadriplegia. Occupational therapists work with individuals to improve self-care, fine motor skills, and adaptive techniques, allowing them to participate in daily activities more effectively.
- Speech Therapy: Speech therapy is essential for individuals with spastic quadriplegia who experience speech and language difficulties. Speech therapists develop personalized plans to address articulation, oral coordination, and language skills, helping children improve their communication abilities.
- Medications: Medications may be prescribed to manage spasticity and associated conditions like epilepsy, which can occur in children with spastic quadriplegia. Muscle relaxants and anti-seizure medications are commonly used to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Assistive Devices: Assistive devices such as braces, splints, or orthotics can provide support and help correct limb deformities. These devices assist individuals with activities of daily living, enhance mobility, and promote independence.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be considered to correct severe limb and joint problems caused by spastic quadriplegia. Procedures such as tendon lengthening or orthopedic surgeries can help improve range of motion, alleviate pain, and enhance functionality.
By implementing a comprehensive treatment plan that combines these various strategies, children with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy can experience improvements in mobility, communication, and overall quality of life.
Prognosis and Outlook for Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy
The prognosis for a child with spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy is more challenging compared to other forms of cerebral palsy. This severe type of cerebral palsy carries a higher risk of complications and associated conditions, which can have a significant impact on a child’s lifespan and independence. However, with the right treatments and support, there is hope for improved quality of life and increased functionality.
Treatments and support options play a crucial role in managing the symptoms and enhancing the well-being of children with spastic quadriplegia. This involves a multidisciplinary approach that may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and even surgery, depending on the specific needs of the child.
The goal of these interventions is to improve mobility, communication skills, and overall quality of life. Physical therapy helps promote muscle flexibility, coordination, and strength, while occupational therapy focuses on developing independence in daily activities. Speech therapy assists in communication and language skills to enable effective interaction with others.

| Treatment and Support | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Improves muscle tone, flexibility, and mobility. |
| Occupational Therapy | Enhances independence in daily activities and promotes functional skills. |
| Speech Therapy | Aids in improving communication and language skills. |
| Surgery | Corrects muscle and joint problems to enhance mobility and reduce discomfort. |
The prognosis and outlook for each individual with spastic quadriplegia may vary depending on the severity of their condition, the effectiveness of the treatments, and the level of support they receive. It is important to recognize that there is no cure for spastic quadriplegia, but with ongoing interventions, children can experience improvements in their functionality, independence, and overall well-being.
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to remain informed, seek medical guidance, and provide the necessary support to ensure the best possible outcomes for individuals with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy.
Causes and Risk Factors of Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy
The underlying causes of spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy, like other forms of cerebral palsy, involve brain damage or abnormal brain development. This damage can occur before, during, or shortly after birth.
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of a child developing spastic quadriplegia. These risk factors include:
- Prematurity: Babies born prematurely have a higher risk of developing cerebral palsy, including spastic quadriplegia. The earlier the baby is born, the greater the risk.
- Fetal infections or stroke: Infections in the fetal stage or an interruption of blood supply to the developing brain can cause brain damage leading to spastic quadriplegia.
- Maternal infections or medical conditions: Maternal infections during pregnancy, such as rubella or cytomegalovirus, as well as medical conditions like high blood pressure or gestational diabetes, can increase the risk of cerebral palsy.
- Exposure to toxins: Certain toxins, such as lead or mercury, can harm the developing brain and contribute to the development of spastic quadriplegia.
- Genetics: While the majority of cases are not directly linked to genetic factors, recent research suggests that genetics may play a role in a subset of individuals with cerebral palsy.
It’s important to note that in some cases, the exact cause of cerebral palsy, including spastic quadriplegia, may remain unknown.

Conclusion
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy is a challenging condition that affects all four limbs, resulting in mobility difficulties and other associated complications. While there is no cure for spastic quadriplegia, there are several treatment options available to manage its symptoms and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy are crucial components of treatment, helping to improve muscle function, mobility, and communication skills. Medications can assist in managing spasticity and associated conditions, while surgery may be considered to address muscle and joint problems.
Early intervention and ongoing support are essential for children with spastic quadriplegia. With appropriate treatments and assistive devices, many individuals can lead fulfilling lives, achieving independence and personal growth. It is important for parents and caregivers to seek medical guidance and support to understand the available treatment options and provide the necessary care and assistance for their loved ones.
While living with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy can present challenges, a proactive approach to treatment and support can significantly improve the prognosis and maximize an individual’s potential. By understanding the condition and exploring the available treatment options, individuals with spastic quadriplegia can lead fulfilling lives and achieve their goals with the necessary support and care.
FAQ
What is spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy is a severe form of cerebral palsy that affects both the arms and legs, as well as the trunk and face in many children. It is characterized by increased muscle tone, which makes the muscles stiff and movements jerky and awkward.
What are the symptoms and early signs of spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
The symptoms of spastic quadriplegia are more severe than other types of cerebral palsy and can include rapidly contracting and releasing muscles, joints that cannot stretch or move, muscle tightness and spasticity, muscle tremors, difficulty walking, limb scissoring, speech impediments or language disorders, seizures, and cognitive disabilities. The early signs of spastic quadriplegia are usually obvious and easy to spot, with a baby showing immediate signs of stiff muscles, such as rigid or crossed legs and arms, spastic limbs, tense muscles, and tremors.
What complications can arise from spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy can lead to various complications, including limb deformities, scoliosis (a curvature of the spine), ankle deformities, joint contractures (permanent shortening of the muscles around a joint), malnutrition, seizures, constipation, and incontinence.
What are the treatment options for spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
Treatment options for spastic quadriplegia vary depending on the severity of symptoms and may involve physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, medications (muscle relaxants and medications for associated conditions like epilepsy), assistive devices, and surgery.
What is the prognosis for individuals with spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
The prognosis for a child with spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy is worse than for other forms of cerebral palsy. This type of cerebral palsy has an increased risk of more complications and associated conditions that can shorten lifespan and compromise a child’s ability to live independently.
What are the causes and risk factors of spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
The underlying causes of spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy are the same as any other type of cerebral palsy, which include brain damage or abnormal brain development. This can occur due to various factors such as prematurity, fetal infections or stroke, maternal infections or medical conditions, exposure to toxins, or genetics. In some cases, the exact cause may be unknown.
What is the conclusion about spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
While there is no cure for spastic quadriplegia, treatments and support options can significantly improve a child’s quality of life and give them the opportunity to lead more productive lives. Treatment interventions, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and surgery, can help manage symptoms and improve mobility, communication, and overall well-being.
Source Links
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.