What happens when a child’s body doesn’t move the way it should? When the simple act of sitting, speaking, or even holding a toy becomes hard? This is the painful reality for families affected by spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy. It’s not just about muscle control, it’s about daily life, growth, and emotional challenges. As a neurologist, I’ve seen the toll this condition takes — not just on children, but on entire families.
In this blog, we will explore spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy in detail. We’ll talk about what it is, what causes it, how to spot the signs early, and what you can do to help your child live a better, fuller life.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Spastic Quadriplegic Cerebral Palsy?
Spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy is a severe type of cerebral palsy that affects all four limbs — both arms and both legs. It causes tight, stiff muscles, making movement difficult. It often comes with other problems like seizures, speech issues, and trouble with learning or thinking.
A Simple Explanation of the Condition
To understand spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy, let’s break down the term:
- Spastic – This means the muscles are tight and stiff.
- Quadriplegia – All four limbs (arms and legs) are affected.
- Cerebral Palsy – A brain condition caused by damage or abnormal development of the brain before, during, or shortly after birth.
This type of motor function disorder affects both movement and posture. In most cases, children also experience developmental delays in walking, talking, and learning.
How Common is Spastic Quadriplegia?
According to the CDC:
- Cerebral palsy in children occurs in 2 to 3 out of every 1,000 live births.
- About 77% of these are classified as spastic types.
- Of those, a large percentage are diagnosed as spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy, the most severe form.
This shows just how important early recognition and treatment are.
Impact on Daily Life
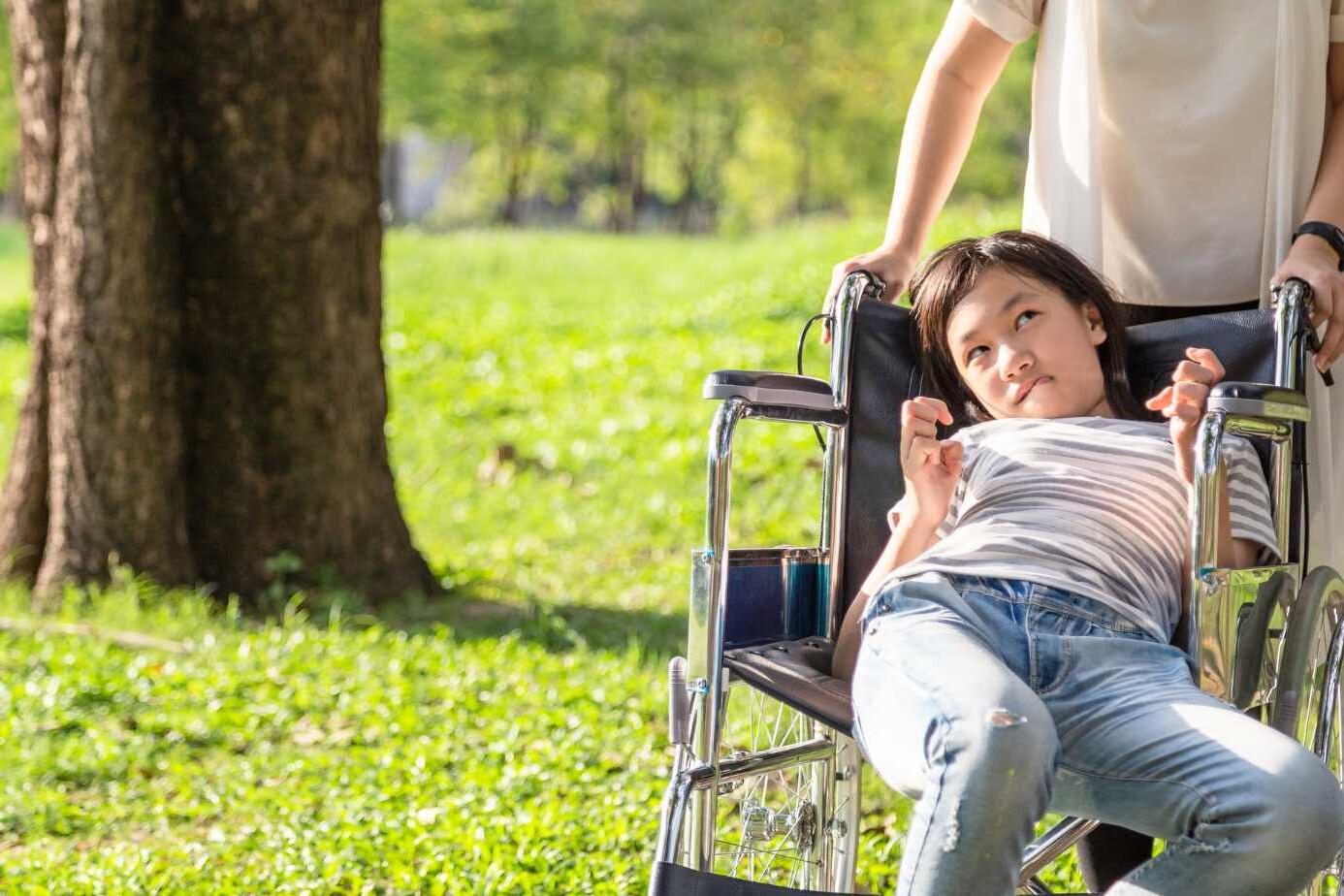
Spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily life. The muscle stiffness and limited range of motion make it difficult to perform tasks independently, such as getting dressed, eating, or even speaking. Additionally, the involvement of the face can lead to challenges in facial expressions and communication.
The severity of spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy varies among individuals, with some being able to walk with assistance, while others may require a wheelchair for mobility. The level of functional impairment determines the support and interventions needed to improve quality of life.
Read: Understanding Gut-Brain Axis and Its Impact on Health
Management and Treatment
Although there is no cure for spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy, various interventions and treatments can help manage the condition and improve quality of life. The management approach typically involves a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, tailored to address the individual’s specific needs and challenges.
Treatment options for spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy may include:
- Physical therapy to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Occupational therapy to enhance daily living skills, such as self-care and fine motor control.
- Speech therapy to address communication difficulties and improve speech clarity.
- Medications to manage spasticity and alleviate associated symptoms.
- Assistive devices, such as braces or splints, to support mobility and improve posture.
A comprehensive treatment plan takes into account the individual’s needs, goals, and overall health. Ongoing monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to ensure the best possible outcomes.
| Treatment Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Focuses on improving muscle strength, flexibility, and mobility through exercises and specialized techniques. |
| Occupational Therapy | Helps individuals develop independence in daily activities and enhances fine motor skills. |
| Speech Therapy | Targets communication difficulties and improves speech clarity through specialized exercises and techniques. |
| Medications | Prescribed to manage spasticity and alleviate associated symptoms. |
| Assistive Devices | Braces, splints, or mobility aids to support mobility and improve posture. |
How Severe is Spastic Quadriplegia Cerebral Palsy?
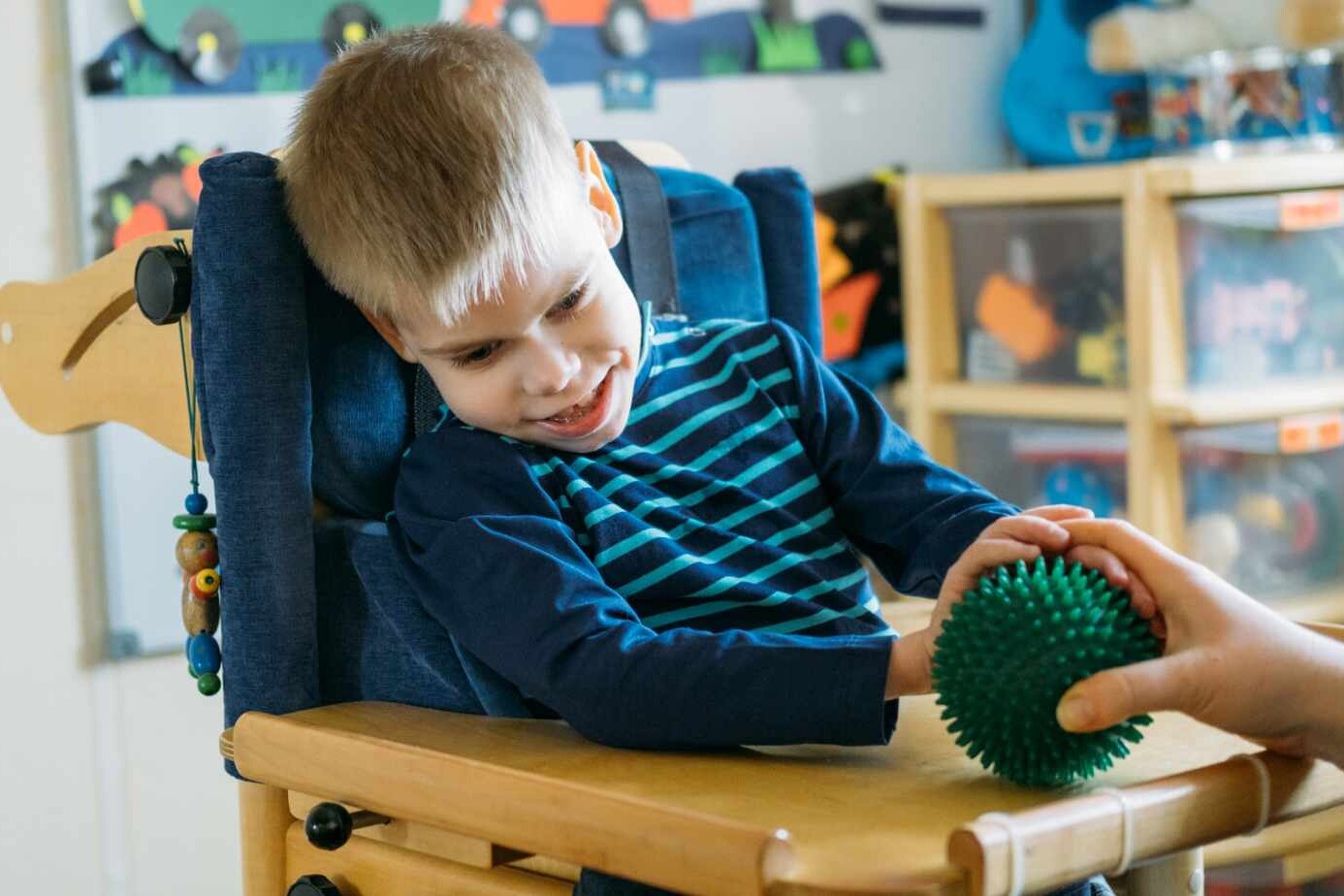
Spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy is considered the most severe form of cerebral palsy due to its impact on multiple areas of the body. Children with this condition often experience significant motor impairments, making walking impossible. They may also have associated conditions such as speech difficulties or seizures. The severity of spastic quadriplegia CP requires lifelong support and care to manage developmental disabilities and associated complications.
The Impact of Spastic Quadriplegia Cerebral Palsy
Spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy affects both arms, legs, and often the torso and face. The increased muscle tone and stiffness lead to jerky and awkward movements, making daily activities challenging for individuals with this condition. The severity of spastic quadriplegia CP can vary, but it significantly impacts mobility, independence, and overall quality of life.
Children with spastic quadriplegia CP are unable to walk and may require the use of assistive devices, such as wheelchairs or walkers, to move around. The limitations in mobility can affect their participation in various activities, hindering their social and emotional development.
| Severity of Spastic Quadriplegia Cerebral Palsy | Impact |
|---|---|
| Motor impairments | Movements are jerky, uncoordinated, and characterized by increased muscle tone and stiffness. |
| Speech difficulties | Communication can be challenging, with speech impediments or language disorders often present. |
| Seizures | Individuals with spastic quadriplegia CP may experience seizures, which can further complicate their condition. |
| Developmental disabilities | Children with spastic quadriplegia CP often have accompanying developmental disabilities, requiring ongoing support and management. |
Managing the severity of spastic quadriplegia CP involves a multidisciplinary approach. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving motor function, flexibility, and range of motion. Occupational therapy focuses on enhancing independence in daily activities, while speech therapy helps individuals communicate effectively. Medications may be prescribed to manage spasticity and associated conditions. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address muscle tightness or joint deformities.
While there is no cure for spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy, ongoing support and care can help individuals with this condition lead fulfilling lives. It is essential for individuals with spastic quadriplegia CP and their families to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans and ensure access to necessary resources and therapies.
What Causes Cerebral Palsy?
Cerebral palsy, including spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy, is primarily caused by brain damage or abnormal brain development. Several factors contribute to the development of this condition, which affects individuals from different backgrounds, including:
- Prematurity: Babies born prematurely are at a higher risk of developing cerebral palsy due to their underdeveloped brains.
- Fetal Infections or Stroke: Infections during pregnancy or strokes that occur in utero can lead to brain damage, resulting in cerebral palsy.
- Maternal Infections or Medical Conditions: Maternal infections, such as rubella or cytomegalovirus, as well as medical conditions like thyroid disorders or epilepsy, can increase the risk of cerebral palsy in the baby.
- Exposure to Toxins: Certain toxins, such as lead or mercury, can interfere with the normal development of the brain, potentially causing cerebral palsy.
- Medical Negligence: In some cases, medical negligence during childbirth, such as oxygen deprivation or improper handling of a baby, can result in brain damage leading to cerebral palsy.
Brain damage during specific periods of development, such as between 26 and 34 weeks of gestation, can lead to white matter lesions or holes in the brain. These abnormalities affect the transmission of signals to the body, resulting in motor impairments seen in cerebral palsy.
Maternal high blood pressure during pregnancy can also increase the risk of fetal stroke and subsequent cerebral palsy.
Understanding the causes of cerebral palsy is crucial for prevention, early interventions, and providing support to individuals and families affected by this condition.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Prematurity | Babies born prematurely are at a higher risk of developing cerebral palsy due to their underdeveloped brains. |
| Fetal Infections or Stroke | Infections during pregnancy or strokes that occur in utero can lead to brain damage, resulting in cerebral palsy. |
| Maternal Infections or Medical Conditions | Maternal infections or medical conditions can increase the risk of cerebral palsy in the baby. |
| Exposure to Toxins | Certain toxins can interfere with the normal development of the brain, potentially causing cerebral palsy. |
| Medical Negligence | Medical negligence during childbirth can result in brain damage leading to cerebral palsy. |
Symptoms of Spastic Quadriplegia
The symptoms of spastic quadriplegia are more severe compared to other types of cerebral palsy. Individuals with this condition may experience:
- Rapid muscle contractions and muscle tightness
- Difficulty with limb movement and coordination
- Limb “scissoring” – when the legs cross, making walking difficult
- Speech impediments or language disorders
- Seizures
- Cognitive disabilities
- Other associated complications
The severity of symptoms can vary among individuals, and early identification is crucial for appropriate interventions and support.
Common Symptoms of Spastic Quadriplegia
| Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Rapid muscle contractions | Uncontrolled and involuntary muscle movements |
| Muscle tightness | Increased muscle tone and stiffness |
| Difficulty with limb movement and coordination | Challenges with performing smooth and coordinated movements |
| Limb “scissoring” | Crossing of the legs, making walking difficult |
| Speech impediments or language disorders | Difficulties with speaking or understanding language |
| Seizures | Episodes of abnormal electrical activity in the brain |
| Cognitive disabilities | Challenges with learning, thinking, and problem-solving |
| Other associated complications | Additional medical conditions or impairments that may coexist |
Diagnosing and Treating Spastic Quadriplegia
Diagnosing spastic quadriplegia typically occurs during infancy when significant delays in development are observed. A comprehensive evaluation process is conducted to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions. This includes a thorough physical examination, review of medical history, and brain imaging tests such as CT scans and MRIs.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, a multidisciplinary approach is adopted for the treatment of spastic quadriplegia. This approach combines various therapies and interventions to address the individual needs and challenges faced by those with this condition.
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in improving motor function, flexibility, and range of motion. Through tailored exercises and techniques, physical therapists help individuals with spastic quadriplegia strengthen their muscles, improve coordination, and enhance overall physical abilities. Regular physical therapy sessions can significantly enhance mobility and independence.
Occupational therapy focuses on developing independence in daily activities. Occupational therapists work with individuals to improve fine motor skills, adapt to daily challenges, and maximize functionality in areas such as self-care, school, work, and leisure activities. They may introduce tools and assistive devices to facilitate independent living and enhance overall quality of life.
Speech therapy is essential for individuals with spastic quadriplegia to improve communication skills. Speech-language pathologists assess speech and language abilities and develop personalized therapy plans to address specific challenges such as articulation, fluency, or language disorders. By enhancing communication skills, individuals can better express themselves and engage effectively with others in various social contexts.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage spasticity, alleviate associated conditions, or control seizures. Assistive devices and technology, such as orthotics or mobility aids, can also be beneficial in enhancing mobility and independence.
In severe cases where muscle tightness or joint deformities persist despite therapy and medication, surgery may be considered. The goal of surgery is to correct physical abnormalities and improve function. Orthopedic procedures can help release tight muscles, correct bony deformities, or improve joint alignment, allowing for better movement and reduced discomfort.
Overall, the management of spastic quadriplegia involves a comprehensive and individualized treatment plan that addresses physical, functional, and communication needs. Through a collaborative effort among healthcare professionals, individuals with spastic quadriplegia can improve their abilities, achieve greater independence, and lead fulfilling lives.
| Treatment Options for Spastic Quadriplegia | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Therapy | Improves motor function, flexibility, and range of motion through tailored exercises and techniques. |
| Occupational Therapy | Fosters independence in daily activities, enhances fine motor skills, and introduces assistive devices for better functionality. |
| Speech Therapy | Enhances communication skills, addresses speech or language disorders, and improves overall social interaction. |
| Medication | Manages spasticity, associated conditions, and controls seizures. |
| Surgery | Corrects physical abnormalities, improves function, and resolves persistent muscle tightness or joint deformities. |
Conclusion
Spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy can have a profound impact on the lives of individuals, often necessitating lifelong support and care. While there is no cure for this condition, there are various treatment options and interventions available to help improve mobility, foster independence, and enhance overall quality of life.
It is crucial for individuals with spastic quadriplegia and their families to collaborate closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans. Through a multidisciplinary approach, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and medication, individuals with spastic quadriplegia can make significant strides in managing symptoms and improving functionality.
Despite the challenges posed by spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy, with the right support and treatment options, many individuals can lead fulfilling lives. It is important to remember that every person’s journey is unique, and a comprehensive treatment approach tailored to individual needs is essential to maximize their potential and well-being.
FAQ
What is spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy?
Spastic quadriplegic cerebral palsy is a severe form of cerebral palsy that affects both arms, legs, and often the torso and face. It is characterized by increased muscle tone and stiffness, making movements jerky and awkward. Children with this condition usually have developmental disabilities and are unable to walk.
How severe is spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy?
Spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy is considered the most severe form of cerebral palsy due to its impact on multiple areas of the body. Children with this condition experience significant motor impairments, making walking impossible. They may also have associated conditions such as speech difficulties or seizures.
What causes cerebral palsy, including spastic quadriplegia?
Cerebral palsy, including spastic quadriplegia, is caused by brain damage or abnormal brain development. Various factors can contribute to the development of this condition, including prematurity, fetal infections or stroke, maternal infections or medical conditions, exposure to toxins, or medical negligence.
What are the symptoms of spastic quadriplegia?
Symptoms of spastic quadriplegia include rapid muscle contractions, muscle tightness, difficulty with limb movement and coordination, limb “scissoring,” speech impediments or language disorders, seizures, cognitive disabilities, and other associated complications. The severity of symptoms can vary among individuals.
How is spastic quadriplegia diagnosed and treated?
Spastic quadriplegia is generally diagnosed during infancy when significant delays in development are observed. A thorough physical examination, medical history review, and brain imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis. Treatment for spastic quadriplegia includes a multidisciplinary approach, focusing on physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, medication, assistive devices and technology, and, in some cases, surgery.
Can spastic quadriplegia be cured?
There is no cure for spastic quadriplegia cerebral palsy. However, early interventions and comprehensive treatment approaches can help improve mobility, independence, and overall quality of life for individuals with this condition. Lifelong support and care are often necessary.
Source Links
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.