Neuroinflammation is the brain’s defense mechanism. When it detects a threat, like toxins, infections, or injuries, it reacts to protect itself. But this reaction can backfire.
If left unchecked, neuroinflammation may damage healthy brain cells. It’s closely tied to conditions like memory loss, brain fog, and serious diseases.
This blog explains what neuroinflammation is, what causes it, how it shows up, and the most effective ways to treat and manage it.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Neuroinflammation?
Neuroinflammation is the brain’s immune response to any kind of harm. This could happen due to injury, infections, toxins, or even chronic stress. This response is natural, but when it lasts too long, it can harm healthy brain cells.
Neuroinflammation refers to how the brain and spinal cord react when they sense danger. Specialized brain cells, like microglia and astrocytes, jump into action. These cells release chemicals to fight the threat. But if this defense goes on too long, it may start hurting brain tissue instead of protecting it.
Neuroinflammation Symptoms
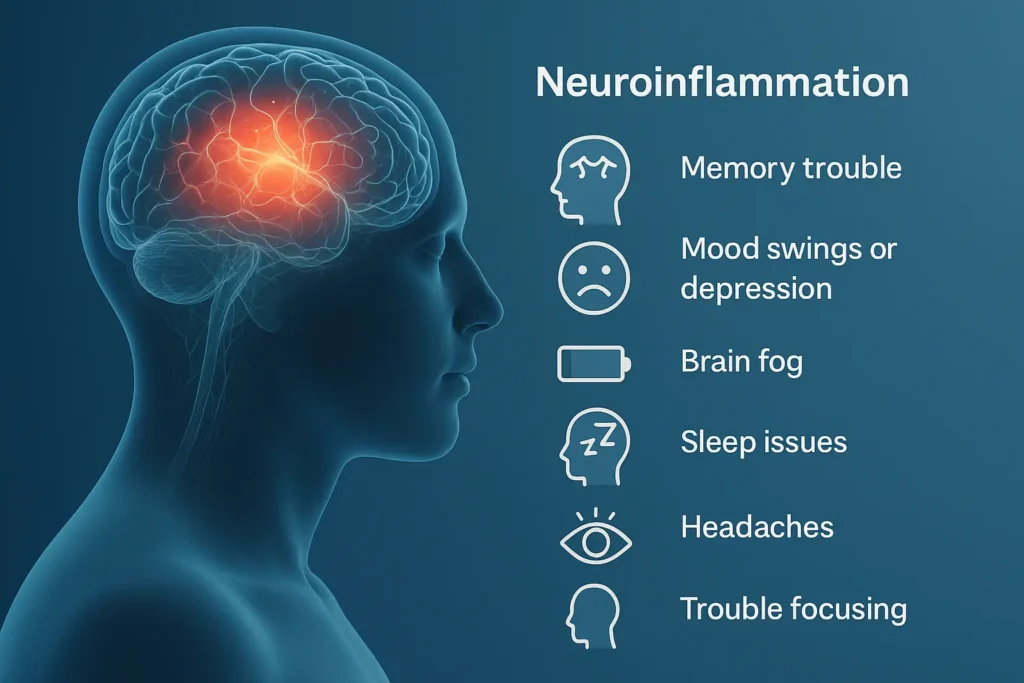 When neuroinflammation happens, the signs can be confusing. It doesn’t always show up like a typical illness. Some common neuroinflammation symptoms include:
When neuroinflammation happens, the signs can be confusing. It doesn’t always show up like a typical illness. Some common neuroinflammation symptoms include:
- Memory trouble
- Mood swings or depression
- Brain fog
- Fatigue
- Sleep issues
- Headaches
- Trouble focusing
These symptoms can feel mild at first but may grow over time. People often mistake them for stress or aging. That’s why many live with neuroinflammation for years without knowing.
The Spectrum of Neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation isn’t the same in everyone. It can range from short-lived to long-lasting. Some people deal with quick inflammation from an injury. Others may have smoldering neuroinflammation, which slowly damages the brain over time.
This is more common in chronic conditions like neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease or neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease.
This ongoing brain inflammation can make other problems worse. It’s linked to mood disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and even cognitive decline.
Key Players in Neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation involves several important brain cells.
- Microglia sense threats and release chemicals to protect the brain.
- Astrocytes help regulate brain signals and keep the environment stable. When overactive, both can worsen neuroinflammation signs.
- Oligodendrocytes, which help with signal transmission, can also get damaged during neuroinflammation.
These cells interact with immune cells, leading to either protection or destruction. Disruption in any part can trigger worsening neuroinflammation symptoms and lead to chronic disease.
This is the case in conditions like smoldering neuroinflammation, where low-grade inflammation continues silently.
What Triggers Neuroinflammation?
There are many neuroinflammation causes, and they aren’t always obvious. Here are some of the most common:
- Infections (viruses, bacteria, fungi)
- Head injuries
- Chronic stress
- Autoimmune diseases
- Environmental toxins
- Poor gut health
- Hormonal changes
- Lack of sleep
Even emotional stress can spark a chain reaction in the brain. Over time, small triggers can lead to full-blown neuroinflammation.
For example, the UCSF Multiple Sclerosis and Neuroinflammation Center has found links between immune overreactions and MS flare-ups. This proves that brain inflammation is not just about injury, it can be immune-driven too.
How Do We Diagnose Brain Inflammation?
A neuroinflammation test isn’t easy, it usually involves a mix of tools:
- Brain imaging (MRI, PET scans)
- Blood tests for inflammatory markers
- Spinal fluid analysis
- Neurological exams
Doctors may also look at medical history and behavior changes. Since the signs can look like other brain issues, careful testing is needed to make a clear diagnosis.
What are the Treatments for Neuroinflammation?
Neuroinflammation treatment depends on what’s causing it. Sometimes reducing the source, like stress or infection, helps a lot. Other times, medical therapy is needed.
Here are some common approaches:
- Anti-inflammatory medications: These help calm the brain’s immune response.
- Lifestyle changes: Getting good sleep, eating healthy, and exercising can lower inflammation.
- Stress management: Chronic stress is a big trigger. Relaxation techniques and therapy can help.
- Supplements: Some neuroinflammation supplements like omega-3s, curcumin, and resveratrol have shown promise.
- Treating underlying diseases: Conditions like lupus, MS, or depression may need separate care to control neuroinflammation.
Knowing how to treat neuroinflammation means first understanding the root cause. That’s where the healing begins.
Your Action Plan for a Healthier Brain
If you’re dealing with brain inflammation symptoms, you can take action today.
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Eat leafy greens, berries, turmeric, and omega-3-rich fish to reduce neuroinflammation causes.
- Exercise: Daily walks or workouts improve blood flow and lower the signs of brain inflammation.
- Quality sleep: Deep sleep clears brain toxins and eases neuroinflammation.
- Stress control: Meditation and breathing exercises can lower stress-induced neuroinflammation.
- Stay hydrated: Water flushes harmful compounds linked to neuroinflammation causes.
- Limit toxins: Reduce alcohol, processed foods, and pollution exposure.
- Use proven neuroinflammation supplements: Under medical advice, try omega-3, curcumin, and resveratrol.
Learning how to reduce neuroinflammation isn’t about big changes overnight. It’s small steps done every day.
When to Reach Out for Help
If symptoms like confusion, memory loss, or mood swings keep growing, talk to a doctor. Early action can prevent lasting brain damage. A test for brain inflammation may help figure out what’s wrong.
Also, if there’s a family history of brain disorders like dementia or MS, don’t ignore subtle signs. Conditions like neuroinflammation depression may not seem serious at first but they often grow if left untreated.
Conclusion
Neuroinflammation can be silent but dangerous.
Acting early, managing neuroinflammation causes, recognizing its symptoms, and starting the right treatment is the best way to protect your brain.
Your brain deserves the same attention as your heart or lungs. And if something feels off, talk to a neurologist.
FAQs About Neuroinflammation
How do you reduce neuroinflammation?
Eat anti-inflammatory foods, exercise, sleep well, reduce stress, and consider doctor-approved supplements to ease neuroinflammation and support long-term brain health.
What is the role of neuroinflammation?
Neuroinflammation helps defend the brain from injury or infection. When prolonged, it causes tissue damage, leading to mental decline or disease.
What is the difference between inflammation and neuroinflammation?
Regular inflammation happens in the body. Neuroinflammation happens in the brain and spinal cord, often linked to memory, mood, and neurological disorders.
What are the symptoms of neuroinflammation?
Common symptoms of neuroinflammation include brain fog, memory issues, low energy, mood changes, headaches, and poor focus. These signs may grow if not treated.
Can exercise reduce neuroinflammation?
Yes. Exercise increases blood flow, reduces oxidative stress, and lowers chemicals that trigger neuroinflammation, helping improve mood and brain clarity.
How do you detect neuroinflammation?
Doctors use imaging scans, blood work, and spinal fluid checks as a neuroinflammation test to confirm inflammation in the brain.
Is neuroinflammation serious?
Yes. Untreated neuroinflammation can damage neurons, affect thinking, and raise the risk of brain disorders. Early care is key.
Does depression cause neuroinflammation?
Yes. Research shows chronic neuroinflammation depression is linked to higher levels of brain inflammation, worsening both mood and memory.
How does neuroinflammation start?
Neuroinflammation starts when the brain reacts to infections, injuries, toxins, or stress, any of which can damage brain cells over time.
How long does neuroinflammation last?
It depends. Some cases are short-term, but chronic neuroinflammation can last years if the cause is not removed or treated.
Can neuroinflammation be cured?
There’s no one-time cure. But early neuroinflammation treatment can stop its progress, ease symptoms, and restore brain health.
Is neuroinflammation painful?
Neuroinflammation doesn’t always hurt. But it can cause headaches, fogginess, or sensitivity due to the brain’s altered signals.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Board-Certified Neurologist
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.




