Long-term stress can raise blood pressure, disturb sleep, change hormones, and increase inflammation. All of these increase your chance of stroke over time. Stress is also linked to unhealthy habits like smoking, poor diet, and lack of movement, which add even more risk.
Doctors from major groups such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the American Heart Association, Mayo Clinic, and large research studies agree that mental stress and poor emotional health are important stroke risk factors. They also agree that stress does not act alone. It works together with other risks like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
Table of Contents
ToggleCan Anxiety Cause A Stroke
Anxiety itself is a strong worry or fear that can feel hard to control. During an anxiety spike, your body goes into “fight or flight.” Heart rate increases. Blood pressure rises. Stress hormones surge. This reaction is normal in short bursts. The problem starts when it happens many times each week for months or years.
Large studies show mixed but important results:
- A big European study called the Rotterdam Study found that people with strong anxiety symptoms had a higher short-term risk of stroke.
- A meta-analysis that pooled several studies found that anxiety disorders linked with about a 24% higher stroke risk.
- The World Stroke Organization reports that poor mental well-being, including stress and depression, nearly doubles the risk of stroke and mini stroke.
Anxiety does not guarantee a stroke, but high and long-lasting anxiety clearly adds to overall risk, especially when other medical problems are present.
Anxiety-Triggered Blood Pressure Spikes Increasing Stroke Risk
During an anxiety episode, your body releases adrenaline and similar hormones. These chemicals:
- Make your heart beat faster.
- Tighten your blood vessels.
- Raise your blood pressure for a short time.
If your arteries are healthy, they usually handle these short spikes. The concern comes when you live with frequent spikes on top of mild or hidden high blood pressure. Repeated peaks strain the artery walls. Small tears can form in the inner lining. Over time, plaque (fat and cholesterol deposits) grows in those areas.
Panic Attacks Elevating Vascular Strain
A panic attack is a sudden wave of intense fear. You may feel:
- Chest tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Shaking
- Dizziness
- A feeling that you might die
During these attacks, your blood pressure can jump quite high for a brief period. Most healthy young people will not have a stroke from one attack. But if you already have weak brain vessels, severe high blood pressure, or an unrecognized heart rhythm problem, that sudden surge can add real strain.
Doctors do not say panic “causes” stroke on its own. They see it as a trigger that can push an already stressed system over the edge. So if you live with panic, you should treat it as a medical issue and not just a personality trait.
Inflammatory Response During Anxiety Episodes
Stress and anxiety not only change your pulse. They also change your immune system. When your mind stays on high alert, your immune cells release chemicals that cause low-grade inflammation in the body.
Research links this type of chronic inflammation with:
- Faster plaque build up in arteries.
- Higher chance that plaque will break.
- Greater tendency for the blood to clot.
This creates a long-term path where stress can cause a stroke through chronic inflammation and not just through short-term blood pressure spikes.
When Anxiety Masks Early Stroke Symptoms
Anxiety and early stroke can share symptoms. Both can cause:
- Dizziness
- Chest tightness
- Feeling “out of it”
- Trouble speaking clearly
The anxiety itself might not be causing the stroke, but it can stop you from seeking help when an actual stroke starts.
Early stroke symptoms that you should never blame only on stress include:
- Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of your face, arm, or leg.
- Sudden confusion or trouble speaking or understanding others.
- Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Sudden strong headache with no clear cause.
If these signs appear, especially all at once, you treat them as stroke first, not as anxiety. At that point, you call emergency services.
High Stress Blood Pressure Stroke
High blood pressure is the top modifiable stroke risk factor across the world.
The term “high-stress blood pressure stroke” means a stroke that occurs in someone whose pressure stays high or swings sharply due to stress. Stress alone does not set the numbers for your blood pressure, but it strongly shapes habits and body reactions that push those numbers up.
Acute Blood Pressure Surges Weakening Blood Vessels
Short bursts of stress come from things like:
- A heavy argument
- A sudden shock or bad news
- A tight work deadline
In these moments, your blood pressure may shoot up much higher than your usual level. For most people, the pressure comes back down. But repeated surges can weaken tiny brain vessels over the years.
In older adults or people with long-term high blood pressure, this thinning can end in a small vessel bursting. That leads to bleeding inside the brain, which is one type of stroke called hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding stroke).
Chronic Stress-Driven Hypertension Progression
Chronic stress also changes how you live each day. Many people under pressure:
- Move less.
- Choose quick, salty, or sugary foods.
- Drink more alcohol.
- Smoke or vape more.
- Sleep poorly.
These habits raise blood pressure and keep it high. Over time, someone with borderline readings can slide into full hypertension without even noticing.
Stress Hormones Damaging Arterial Walls
Stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline are useful in short danger. When they stay high for long periods, they do harm.
Too much cortisol over time can:
- Raise blood sugar.
- Increase fat around your waist.
- Worsen cholesterol levels.
- Make blood vessels stiffer and less flexible.
These changes all speed up atherosclerosis, which is plaque buildup inside arteries. Narrow and stiff arteries make it easier for a clot to block blood flow to your brain. Thus, stress hormones form another link in how stress can cause a stroke without any direct blow to the head or visible injury.
Plaque Instability From Prolonged Stress
Plaque in your arteries is not always smooth and safe. Inflammation and stress hormones can make plaque more fragile. That means a piece can crack. When that happens, platelets rush in and a clot forms on that damaged spot.
If part of that clot breaks off and travels to a brain artery, it can block blood flow and cause an ischemic stroke (clot stroke). Years of stress-driven blood pressure problems, vessel damage, and plaque buildup end in one bad moment where the plaque finally breaks.
Stress-Induced Stroke Symptoms
The term stress-induced stroke symptoms can cause symptoms that feel like a stroke, and a stroke can appear during a time of stress. You need to know the difference as well as you can, but you also need to know when not to guess.
Stroke-Like Neurological Symptoms Triggered By Stress
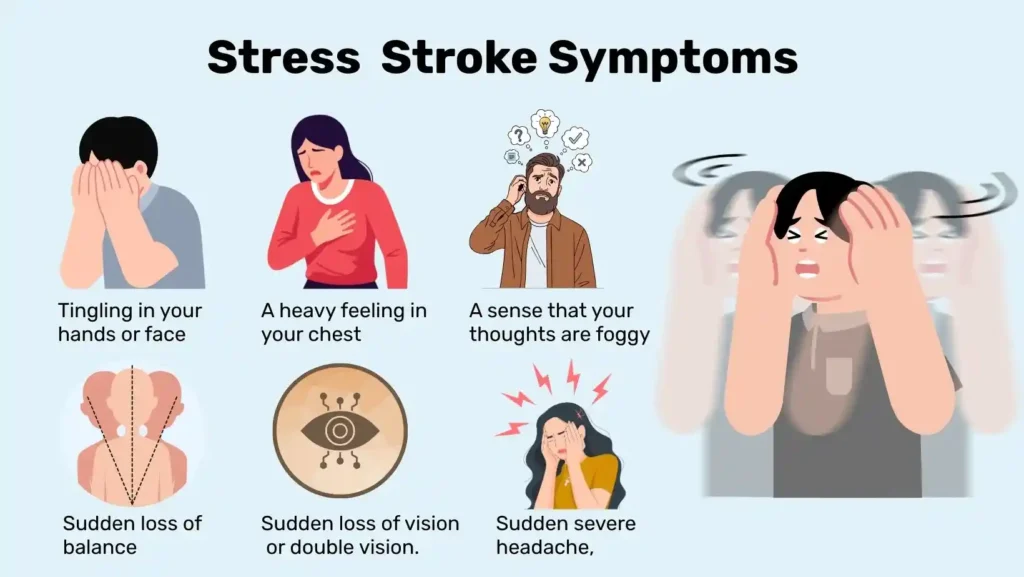
When you feel very stressed, you might notice:
- Tingling in your hands or face
- A heavy feeling in your chest
- A sense that your thoughts are foggy
Hyperventilation (fast breathing) during panic can change carbon dioxide levels in your blood. That may lead to dizziness, tingling, or visual spots. These are not strokes, but they feel scary.
At the same time, real strokes can happen in stressful moments. That is why doctors prefer to treat any sudden, one-sided, or clear speech change as possible stroke first. You should never treat s tress-induced stroke symptoms at home.
FAST Warning Signs Worsened By Stress
The FAST rule helps you spot stroke:
- Face drooping
- Arm weakness
- Speech trouble
- Time to call emergency help
Some groups add B and E and use BE FAST: Balance problems and Eye changes.
Stress affects these signs in two ways. First, strong emotion can make your face feel tight or your hands shake, so you may dismiss real weakness as “just stress.” Second, people around you may delay action because they think you are having a panic attack. This delay is critical. For clot-busting drugs, doctors often have only a few hours to act.
Numbness, Confusion, And Speech Changes During Stress Spikes
It helps to think about patterns:
- Stress or panic often cause tingling on both sides, racing heart, and fast breathing.
- Stroke more often causes numbness or weakness on one side, slow or slurred speech, or trouble understanding simple words.
Red-Flag Symptoms Requiring Emergency Care
Call emergency services right away if you notice any of these signs, even during a stressful event:
- Sudden weakness or numbness in your face, arm, or leg on one side.
- Sudden trouble speaking, saying the wrong words, or not understanding others.
- Sudden loss of vision or double vision.
- Sudden severe headache, different from your usual headaches.
- Sudden loss of balance, trouble walking, or strong dizziness.
These are not typical stress-induced stroke symptoms . They are classic medical red flags. At that moment, you get medical help and let trained staff separate stress from stroke with proper tests.
Can Stress Trigger A Mini Stroke
A mini stroke is also called a TIA (transient ischemic attack). It is a brief block of blood flow to the brain that causes stroke-like signs, then clears within minutes or hours. There is no lasting brain damage, but the warning is serious.
So stress can trigger a mini stroke . Studies show that people who live with high stress and poor mental health have a higher chance of both stroke and mini stroke. Stress changes blood pressure, blood clotting, and heart rhythm.
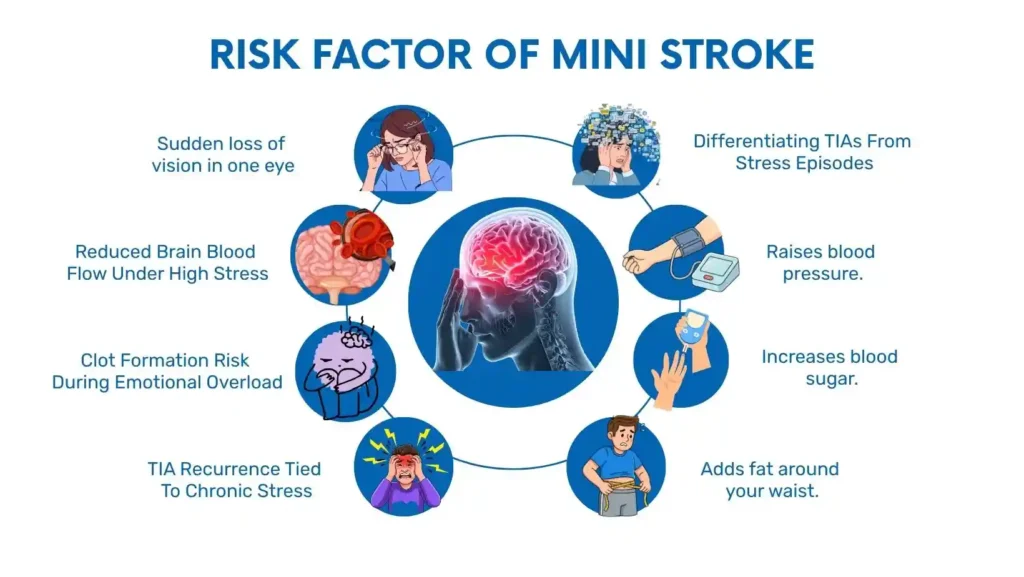
Reduced Brain Blood Flow Under High Stress
Under strong mental stress, your body sends blood to muscles and the heart. Some brain areas may get a little less blood for a short time. If your neck or brain arteries are already narrowed by plaque, this change can drop flow below the level your brain cells need.
That is one way stress can cause a stroke in a “mini” form first. Symptoms can be:
- Sudden trouble speaking
- Sudden weakness in one arm or leg
- Sudden loss of vision in one eye
Even if everything clears in 10 minutes, doctors treat it as a TIA and move fast, because a full stroke may follow within hours or days.
Clot Formation Risk During Emotional Overload
During emotional overload, your body releases a wave of stress chemicals. These make platelets stickier and increase clotting factors. That means your blood is more likely to form small clots.
If a tiny clot forms on a rough patch inside a neck artery and then breaks free, it can drift to the brain. If it blocks a small artery for a few minutes and then dissolves, you get a TIA.
TIA Recurrence Tied To Chronic Stress
People who already had a TIA must be extra careful. Ongoing stress makes it harder to control blood pressure, sugar, and cholesterol. It also makes it harder to take pills on time and keep a healthy routine.
Studies show that mental health problems after TIA and stroke, like anxiety and depression, are common and linked with worse outcomes. If you ignore your stress, your chance of another TIA or a full stroke stays high. This is a core part of chronic stress stroke risk after a first warning event.
Differentiating TIAs From Stress Episodes
You cannot see inside your arteries at home, so you have to judge based on signs. In simple terms:
- TIAs cause sudden, clear loss of function, such as weakness, vision loss, or language trouble.
- Stress episodes more often cause racing thoughts, chest tightness, fast breathing, and fear, without clear one sided loss.
That is why experts say that any sudden stroke like sign, even if you feel stressed, must be checked in an emergency unit.
Chronic Stress Stroke Risk
chronic stress stroke risk is not about one bad day. It is about the total load on your body over months and years. A recent meta-analysis found that people with long-term psychological stress had about a 46 percent higher risk of stroke compared with those with low stress.
This does not mean that everyone under stress will have a stroke. It means the odds move in the wrong direction when stress stays high and you do not manage it. This is one of the strongest ways stress can cause a stroke across a whole population.
Long-Term Cortisol Exposure Damaging Arteries
Cortisol is a main stress hormone. In short bursts, it helps you respond to danger. In long exposure it:
- Raises blood pressure.
- Increases blood sugar.
- Adds fat around your waist.
- Worsens cholesterol.
All of these create a higher chronic stress stroke risk by speeding up artery damage. When you see belly fat and high pressure building over the years, you are also seeing how stress can cause a stroke later in life if nothing changes.
Sleep Deprivation Raising Overall Stroke Risk
Stress often ruins sleep. You may lie awake with your mind racing or wake up many times. Poor sleep links with higher blood pressure, weight gain, and diabetes, which all raise stroke risk.
When sleep loss continues for years, it becomes part of the chronic stress stroke risk . Fixing sleep is one of the fastest ways to start lowering your stroke .
Chronic Inflammation Increasing Clot Formation
Long-term stress can keep your immune system in a low flame state. This chronic inflammation damages the inner lining of arteries and makes blood more likely to clot.
High-Risk Populations With Elevated Stress Levels
Groups that face money issues, unstable jobs, discrimination, or heavy caregiving loads often show higher stress levels and higher stroke rates. Recent data suggest that young and middle-aged women with high stress may have a sharply higher risk of ischemic stroke.
This shows that chronic stress stroke risk is not only a personal issue. It is also a social one. But at your personal level, you still have the power to change daily habits and seek support. That will lower how strongly stress can cause a stroke in your own life.
How Stress Affects The Brain And Arteries
To understand why stress can cause a stroke at all, it helps to see what happens in your body step by step.
Sympathetic Nervous System Causing Vasoconstriction
When you feel stressed, the sympathetic nervous system fires. It speeds your heart and tightens many blood vessels, a change called vasoconstriction. Blood pressure goes up. Over time, repeated tightening makes vessels stiffer and less able to relax. This makes it easier for high pressure and clots to damage the brain.
Platelet Activation Increasing Clot Tendency
Stress does not just move blood faster. It changes blood behavior. Platelets, the small cell parts that help stop bleeding, become more active and sticky during stress. That means your blood is more ready to clot.
If plaque in an artery cracks, sticky platelets rush in and a clot forms. This is one of the key ways stress can cause a stroke by turning a stable, narrowed artery into a blocked one.
Oxidative Stress Impairing Vascular Function
Chronic stress raises oxidative stress, which is damage from harmful oxygen-related particles in the body. These particles harm the inner lining of your blood vessels. Damaged lining cannot widen well. It also attracts more fat and inflammatory cells.
As this damage builds, your chronic stress stroke risk goes up because vessels become narrow and rough inside, where clots can catch.
How Stress Weakens The Blood-Brain Barrier
The blood-brain barrier is a thin layer of cells that protects your brain by filtering what moves from the blood into brain tissue. Some research suggests that long-term stress and high cortisol may make this barrier more leaky.
A weaker barrier may not cause a stroke by itself. But it may make brain tissue more sensitive to damage when blood flow drops, which again shows how stress can cause a stroke in more than one way.
Diagnosing Stroke Vs Stress Symptoms
When symptoms hit, doctors do not guess. They follow a clear path to tell stress from stroke.
Neurological Exam And Vital Checks
In the emergency room, a doctor will:
- Check your face, arms, legs, and speech.
- Ask you to follow simple commands.
- Check balance and vision.
- Measure blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen level.
If the exam shows one-sided weakness or clear speech trouble, they treat you as possible stroke, no matter how stressed you feel.
Using CT/MRI To Rule Out Stroke
A CT scan or MRI of the brain shows if there is bleeding or signs of tissue damage from low blood flow. A TIA often has no damage on the scan, but doctors still treat it as a serious warning.
Blood Pressure And Cardiac Rhythm Evaluation
You will likely have blood tests and heart monitoring. Doctors look for:
- Very high blood pressure.
- Abnormal heart rhythm such as atrial fibrillation.
- High sugar or cholesterol.
Identifying Subtle TIAs Mistaken For Anxiety
Some TIAs are subtle. You might have:
- Brief trouble finding words.
- Short loss of vision in one eye.
- A few minutes where one hand feels weak or useless.
These can look like anxiety, low sugar, or “just feeling off.” Yet TIA guides from NIH and AHA state that all such events need urgent imaging and risk review, because stroke risk is highest in the first 48 hours.
Treatment For Stress-Related Stroke Risk
Emergency Care For Suspected Stroke
If doctors think a clot is blocking a brain artery and you come in fast enough, they may give clot-busting medicine or use a special tube to remove the clot. These choices depend on timing, scan results, and your overall health.
Blood Pressure Stabilization Protocols
After the first hours, the team works to keep your blood pressure in a safe range. They may use IV drugs at first, then switch to pills. They will talk with you about home monitoring, salt intake, and a long-term plan. Good control lowers the chance of another high-stress blood pressure stroke in the future.
Rehabilitation For Stress-Exacerbated Cases
Many people feel fear, sadness, or anger after a stroke or TIA. This stress can slow physical recovery and raise blood pressure again. Rehab teams now include mental health checks, support groups, and sometimes medicine for mood or anxiety.
This care is not extra. It is a direct way to cut chronic stress stroke risk after a major life event.
Treating Underlying Anxiety Or Chronic Stress
If your story shows that anxiety can cause a stroke and stress may have added to your event, doctors may suggest:
- Talk therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy.
- Relaxation and breathing training.
- Changes in work or home routine to reduce strain.
- Medicine for anxiety or depression when needed.
Dosage and drug choice vary with age, other illnesses, and symptoms. Your doctor will tailor them to you. Treating anxiety is one of the most practical ways to lower the chance that stress can cause a stroke again.
Prevention: Reducing Stress To Lower Stroke Risk
You cannot erase all stress, but you can shrink its power over your brain and heart.
Stress-Management Lifestyle Changes
Simple daily habits that work against stress and stroke include:
- Brisk walking or other movement on most days.
- A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Limited salt, sugar, and deep-fried food.
- No smoking and limited alcohol.
These steps make it less likely that stress can cause a stroke in your future because they lower blood pressure, improve vessel health, and support better mood.
Therapy Methods That Reduce Stroke-Related Stress
Therapy and stress programs are not only for people with severe mental illness. They can help anyone whose stress feels too high.
Methods such as cognitive behavioral therapy, problem-solving therapy, and simple breathing and body relaxation exercises can reduce anxiety and blood pressure in many people.
Avoiding Known Stress Triggers
You cannot avoid every stress trigger, but you can often reduce some clear ones. For example:
- Set limits with people who always push you into conflict.
- Take breaks from news or social media that leaves you tense.
- Plan money and work tasks in small steps to avoid last-minute panic
These changes make life calmer and reduce the number of times your body goes into full “alarm” mode. That in turn reduces the number of times stress can cause a stroke ..
When Medication For Stress Or BP Is Needed
Sometimes lifestyle and therapy are not enough on their own. Doctors may suggest:
- Blood pressure pills if readings stay high.
- Cholesterol drugs if levels are high or you already had stroke or TIA.
- Medicine for anxiety or depression if symptoms are strong.
Doctors usually choose doses based on your age, kidney and liver function, and other medicines you take. They also check for side effects.
FAQ
Can Extreme Stress Be Fatal And Cause A Stroke?
Yes, very strong stress can be part of a fatal stroke, especially if you already have high blood pressure or artery disease. It can push pressure up, trigger clots, and worsen vessel damage that already exists.
Can Stress Alone Form A Blood Clot?
Stress alone rarely forms a clot from nothing. It can make platelets stickier and blood more ready to clot though, especially when plaque or heart problems already exist, which means stress can make a stroke more likely.
Can Emotional Shock Trigger A Stroke?
A sudden shock can cause a big rise in blood pressure and stress hormones. In someone with weak or narrowed vessels, this may trigger bleeding or a clot stroke, so emotional shock can sometimes act as the final push in that process.
Can Panic Attacks Mimic A Stroke?
Yes, panic attacks can mimic stress-induced stroke symptoms , with chest tightness, dizziness, and tingling. They usually lack one-sided weakness or loss of speech, but you should still seek urgent care if you are unsure.
Does Long-Term Anxiety Permanently Increase Stroke Risk?
Long-term anxiety can increase stroke risk because it keeps blood pressure, heart rate, and inflammation higher and often harms sleep. Good treatment for anxiety can lower this added risk over time and improve quality of life.
Can Young Adults Have A Stress-Related Stroke?
Yes, young adults can have strokes, especially if they smoke, have untreated high blood pressure, use drugs, or carry other risks. Strong stress can then act as a trigger, which is why healthy habits matter early.
Can Stress Cause A Hemorrhagic Stroke?
In people with very high blood pressure or weak brain vessels, intense stress can drive pressure high enough to make a small artery burst. This bleeding in the brain is a hemorrhagic stroke and it is often severe and life-threatening.
What’s The Difference Between Stress Symptoms And A Mini Stroke?
Stress symptoms often include fast breathing, chest tightness, and fear. A mini stroke is more likely to cause sudden one-sided weakness, loss of speech, or vision changes and needs emergency brain imaging and stroke prevention treatment.
How Fast Can Stress Elevate Stroke Risk?
Short bursts of stress can trigger a stroke in someone already at very high risk, but for most people, danger grows over months or years. The longer you stay stressed and uncontrolled, the more chronic stroke develops.
What Is The Quickest Way To Reduce Stroke Risk From Stress?
The quickest steps are to check and control your blood pressure, get medical help for anxiety, stop smoking, move your body daily, and seek support. These reduce how strongly stress can cause a stroke for you right now and in the future.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.