Schizophrenia is a chronic Migrain disorder that affects how you think, perceive reality, and respond emotionally. It can cause hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and reduced motivation, often disrupting daily functioning if left untreated.
Schizophrenia treatment is a long-term medical approach designed to control these symptoms, protect brain health, and reduce relapse risk. It works by combining antipsychotic medication with therapy and structured support to stabilize thinking and behavior.
Early, continuous treatment lowers hospitalization rates and slows cognitive decline. Effective care also focuses on preventing relapse, managing side effects, and rebuilding daily skills.
What Is Schizophrenia Treatment?
Schizophrenia treatment is a medical and mental health plan used to control psychosis and protect brain function. Psychosis means losing contact with reality. It can include hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real) and delusions (strong false beliefs). Treatment does not remove the illness, but it reduces symptom intensity and frequency.
Schizophrenia treatment must be continuous, and stopping care often leads to relapse. Each relapse increases the chance of long-term problems with memory, attention, and emotional control. This is why doctors stress early and steady care.
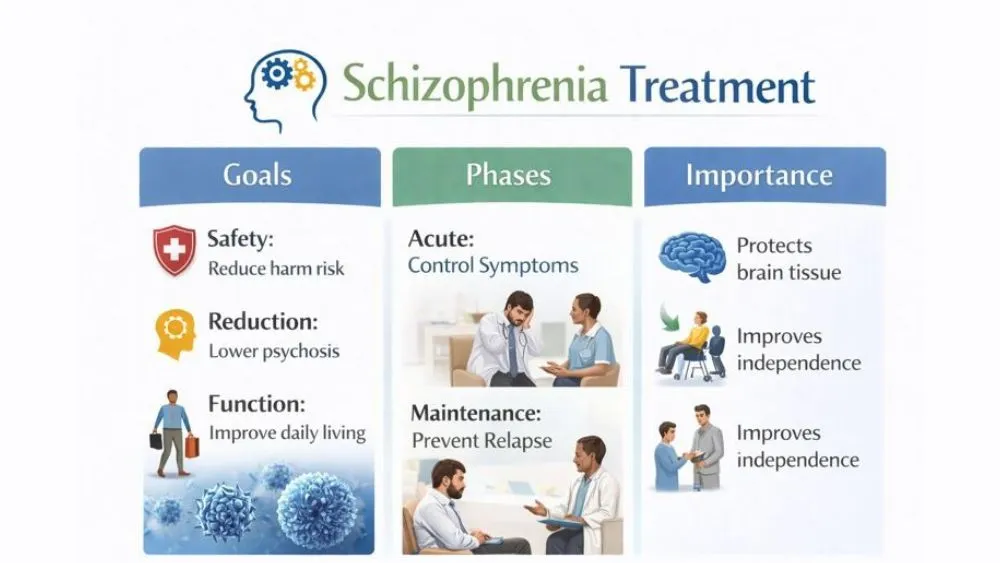
Goals Of Schizophrenia Treatment
- Safety: Severe psychosis raises the risk of harm, confusion, and poor judgment.
- Reduction: Hallucinations should weaken. Delusions should lose control over thinking.
- Function: You should be able to sleep, eat, communicate, and manage daily tasks.
Long-term goals include fewer hospital stays and better thinking skills. Early care with delayed care shows better work ability and social stability when treatment starts early. This evidence comes from multi-year follow-ups, not short trials.
Acute Vs Maintenance Treatment Phases
Schizophrenia treatment works in two phases. The acute phase starts during severe symptoms. Doctors focus on rapid symptom control. Hospital care may be needed if safety is at risk. Medicine doses are often higher during this stage.
Maintenance treatment begins after symptoms settle for relapse prevention. Doctors often lower doses to reduce side effects. Maintenance care lasts for years. For many people, it lasts for life. Relapse rates rise sharply when maintenance care stops.
Importance Of Early Diagnosis And Treatment
Early schizophrenia treatment protects the brain. Untreated psychosis is linked to faster gray matter loss (brain tissue involved in thinking). Early care slows this process. It also improves response to medication.
People treated within the first year of symptoms often need lower doses later. They also show better social recovery. This is why early intervention clinics exist in many countries.
Schizophrenia Treatment Medications
Medicines form the base of schizophrenia treatment . Without them, psychotic symptoms usually return. These drugs act on dopamine, a brain chemical linked to perception and belief formation. Doctors follow strict treatment guidelines for schizophrenia when choosing drugs. The choice depends on symptoms, side effects, age, and past response.
Typical (First-Generation) Antipsychotics
These older drugs include haloperidol and fluphenazine, which strongly block dopamine. They reduce hallucinations and delusions. However, they often cause movement problems called extrapyramidal symptoms (muscle stiffness, shaking, and restlessness).
Because of these risks, typical drugs are now used less often. They may still be chosen when cost is a concern or when newer drugs fail.
Atypical (Second-Generation) Antipsychotics
Atypical drugs include risperidone, olanzapine, and quetiapine. They affect dopamine and serotonin. This balance lowers movement side effects. They also help with mood and anxiety.
Most modern schizophrenia treatment plans start with these drugs. However, they raise the risk of weight gain and high blood sugar. Doctors monitor these risks closely. These drugs are widely accepted as core treatment medications for schizophrenia .
Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics
These injections last weeks or months. They solve missed doses, which are one of the top relapse triggers.
Long-acting injections lower hospital readmission rates. Many specialists recommend them early, not only after repeated relapse. They are an important form of treatment medication for schizophrenia when adherence is difficult.
Clozapine For Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
Clozapine is used when two other drugs fail. It is the most effective drug for severe cases. It also lowers suicide risk, a benefit supported by large population studies.
Clozapine carries serious risks, including low white blood cell counts. Because of this, regular blood tests are required. Despite the risks, clozapine remains a critical option within treatment guidelines for schizophrenia .
Monitoring Side Effects And Safety
Safe schizophrenia treatment requires monitoring. Doctors track weight, blood sugar, cholesterol, and movement changes. Monitoring reduces long-term harm and improves adherence. Ignoring side effects leads many people to stop treatment, which raises relapse risk.
Schizophrenia Therapy Options
Therapy improves insight, coping, and daily functioning when combined with medication. If you receive structured therapy, you have fewer relapses and better social outcomes than with medication-only care.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps you question distorted thoughts. For example, it teaches ways to test whether a belief is real or stress-driven. CBT does not remove hallucinations, but it reduces the distress caused by them. It is one of the most studied therapy options for schizophrenia .
Cognitive Remediation Therapy
This therapy targets thinking skills like memory and attention. Brain training tasks are used for small but steady gains in thinking speed and problem-solving. These gains support work and education.
Family Therapy And Psychoeducation
Family stress increases relapse risk. Family therapy teaches communication and problem-solving. Psychoeducation explains symptoms in simple terms with fewer relapses when families receive structured education. This approach is part of the recommended therapy options for schizophrenia .
Social Skills Training
Social skills training teaches conversation, planning, and conflict handling. These skills do not return on their own after psychosis. Training improves independence and confidence over time.
Supportive Psychotherapy
Supportive therapy focuses on trust and routine. It helps you manage stress and stay engaged in care. It does not challenge beliefs directly but supports emotional stability.
Non-Drug Treatments For Schizophrenia
Non-drug care targets real-world problems like stress, isolation, and poor routines. Psychosocial support reduces emergency visits even when symptoms are medically stable.
Psychosocial Interventions
These include structured therapy, housing support, and job coaching. They address real-life problems, not just symptoms. Psychosocial care lowers hospitalization rates.
Assertive Community Treatment (ACT)
ACT teams provide care in the community. They visit homes and manage crises early, which reduces emergency admissions. It is strongly supported by treatment guidelines for schizophrenia .
Lifestyle And Behavioral Strategies
Sleep loss worsens psychosis, whereas substance use increases relapse risk. Stable routines protect mental health. These steps support long-term treatment for schizophrenia even though they are not medicines.
Schizophrenia Rehabilitation Programs
Rehabilitation focuses on rebuilding daily function after symptoms stabilize. Schizophrenia treatment is incomplete without rehabilitation because symptom control alone does not restore life skills. People who enter structured rehab earlier regain independence faster and stay out of hospitals longer.
Psychiatric Rehabilitation Goals
Practical functioning includes managing money, keeping appointments, personal hygiene, and problem-solving. Psychiatric rehabilitation also targets confidence and decision-making. Many people lose these skills during repeated psychotic episodes. Rehab helps relearn them step by step, without pressure.
Programs are personalized. Some focus on daily living, while others focus on work or education. Combining rehab with medication improves long-term outcomes more than medication alone.
Vocational Rehabilitation Programs
Work improves structure, income, and self-worth. Vocational rehab helps you prepare for jobs through skill training, resume help, and job placement support. Some programs use supported employment models, where you start working quickly and receive coaching on the job.
Research comparing sheltered work to supported employment shows higher job retention with supported models. This makes vocational care a core part of rehabilitation programs for schizophrenia .
Community-Based Rehabilitation Services
Community services help you stay connected outside hospitals. These include day programs, peer support groups, and case management. Case managers help coordinate appointments, housing, and benefits. Community-based care reduces isolation, which is a known relapse trigger.
Residential And Supported Housing Programs
Stable housing is critical because housing instability raises relapse risk and medication non-adherence. Supported housing provides supervision when needed but still allows independence. You will have fewer hospitalizations when housing support is included in schizophrenia treatment .
Schizophrenia Long-Term Treatment
Long-term care prevents relapse and protects thinking ability over the years. Stopping treatment, even after stability, sharply increases relapse risk within months.
Maintenance Therapy Strategies
Maintenance therapy uses the lowest effective medication dose. This reduces side effects while preventing relapse. Doctors adjust doses slowly. Abrupt changes raise relapse risk. Therapy often continues during maintenance to support coping and stress control. Stopping medication entirely leads to relapse in most cases, even after years of stability.
Preventing Relapse
Relapse prevention is a major goal of schizophrenia treatment . Early warning signs include sleep problems, social withdrawal, and rising suspicion. Families often notice these signs first.
Relapse prevention plans include regular follow-ups, medication reminders, and stress management. Long-acting injectable medicines also reduce relapse by preventing missed doses.
Managing Negative Symptoms
Negative symptoms include low motivation, flat emotions, and reduced speech. These symptoms respond poorly to medication. Psychosocial care and rehab work better. Structured routines, goal-setting, and activity scheduling show modest but meaningful improvement.
Improving Long-Term Functioning
Function improves when care addresses real-life needs. Work, relationships, and purpose matter. You will observe better outcomes when long-term treatment for schizophrenia includes rehab, therapy, and community support.
Managing Side Effects Of Schizophrenia Treatment
Side effects affect adherence more than symptom severity. Monitoring weight, movement, and blood markers reduces long-term medical harm and improves treatment continuation.
Metabolic Side Effects
Some antipsychotics cause weight gain, high blood sugar, and high cholesterol. Doctors monitor these risks with regular tests. Lifestyle changes, such as walking and diet adjustments, help reduce harm. Early management prevents long-term health problems.
Movement Disorders And EPS
Movement side effects include stiffness, tremors, and restlessness. These are more common with older drugs, but can occur with newer ones. Dose adjustments or medication changes often help. Early reporting is important.
Blood Tests And Long-Term Monitoring
Clozapine requires regular blood tests due to infection risk. Other medications need metabolic monitoring. Safe schizophrenia treatment depends on routine checks.
Emergency And Acute Schizophrenia Treatment
Acute care stabilizes severe psychosis and restores safety during crises. Early crisis intervention reduces the need for long hospital stays and limits functional decline.
When Hospitalization Is Required
Hospitalization is needed when there is danger to self or others, severe confusion, or inability to care for basic needs. Hospital care provides close monitoring and rapid medication adjustment.
Managing Severe Psychosis
Severe psychosis requires calm settings and medical supervision. Doctors may use short-term higher doses or sedating medicines. The goal is stabilization, not long-term dosing.
Crisis Intervention Methods
Crisis teams respond quickly to worsening symptoms. They often prevent hospitalization by acting early. Crisis services reduce emergency admissions when used correctly.
Living With Schizophrenia
Daily stability depends on routines, support, and stress control. Long-term studies link structured daily life with fewer relapses and better emotional regulation.
Daily Life And Independence
Simple routines help maintain stability. Regular sleep, meals, and activities reduce stress on the brain. Independence grows gradually with support.
Role Of Caregivers And Family
Families help monitor symptoms and support treatment adherence. Education reduces blame and conflict. Research shows lower relapse rates when families are involved in care.
Coping Strategies And Support Systems
Peer support groups provide shared understanding. Therapy helps manage stress and setbacks. Strong support systems improve quality of life over time.
Prognosis And Recovery
Recovery means symptom control and improved function, not cure. Outcomes improve with early treatment, consistent care, and strong social support systems.
What Recovery Means In Schizophrenia
Recovery means symptom control and functional improvement. It does not always mean complete symptom absence. Many people work, study, and live independently with ongoing schizophrenia treatment .
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Early care, medication adherence, and social support improve outcomes. Substance use and repeated relapses worsen prognosis.
Can Schizophrenia Be Cured?
There is no cure. However, long-term stability is common with proper long-term treatment for schizophrenia .
When To See A Doctor
Early medical review prevents relapse escalation and hospitalization. Subtle changes like sleep disruption often appear weeks before full symptom return.
Early Warning Signs
Sleep changes, paranoia, and withdrawal signal relapse. Early treatment reduces severity.
Medication Side Effects
Side effects that affect daily life need medical review. Adjustments improve adherence.
Signs Of Relapse
Confusion, fear, and unusual beliefs signal relapse. Early care prevents hospitalization.
FAQs
What Is The Best Schizophrenia Treatment?
The best schizophrenia treatment combines medication, therapy, and rehabilitation. This approach reduces relapse and improves long-term functioning more than any single method alone.
How Long Does Schizophrenia Treatment Last?
Treatment usually lasts for many years. For most people, long-term treatment for schizophrenia is ongoing because stopping care greatly increases relapse risk, even after long periods of stability.
Can Schizophrenia Be Treated Without Medication?
Medication is the foundation of schizophrenia treatment . Therapy alone does not control psychosis in most cases.
What Therapies Work Best For Schizophrenia?
CBT, family therapy, and skills training are effective therapy options for schizophrenia . They reduce distress, improve communication, and support daily functioning when combined with medication.
Is Schizophrenia Treatment Lifelong?
For many people, yes. Lifelong care reduces relapse and protects brain function. Some need lower doses over time but still require monitoring.
What Happens If Schizophrenia Is Untreated?
Untreated illness leads to frequent relapses, brain stress, and loss of daily skills. Long-term outcomes are significantly worse without schizophrenia treatment .
Can People With Schizophrenia Live Independently?
Many people live independently with proper care. Rehabilitation programs for schizophrenia play a key role in building life and work skills.
How Effective Are Rehabilitation Programs?
Rehabilitation improves work ability, social skills, and independence. Fewer hospitalizations occur when rehabilitation programs for schizophrenia are included.
What Is Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia?
This condition occurs when symptoms persist despite two medications. Clozapine is often effective in these cases and follows strict treatment guidelines for schizophrenia .
How Can Families Support Schizophrenia Treatment?
Families support care by encouraging adherence, reducing stress, and learning early relapse signs. Family involvement improves outcomes in long-term studies.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.