Benign Essential Blepharospasm is a neurological movement disorder that causes repeated, uncontrolled eyelid closure. You are not losing vision, and your eye muscles are not weak. The problem starts in the brain areas that control movement. Over time, the spasms can block vision by force, not by damage. This condition is classified as a focal dystonia [a disorder that causes muscles to contract when they should not].
You may first notice blinking that feels excessive. Later, blinking turns into squeezing. Daily tasks like reading or driving can become unsafe. Early recognition matters because treatment works best when symptoms are identified correctly.
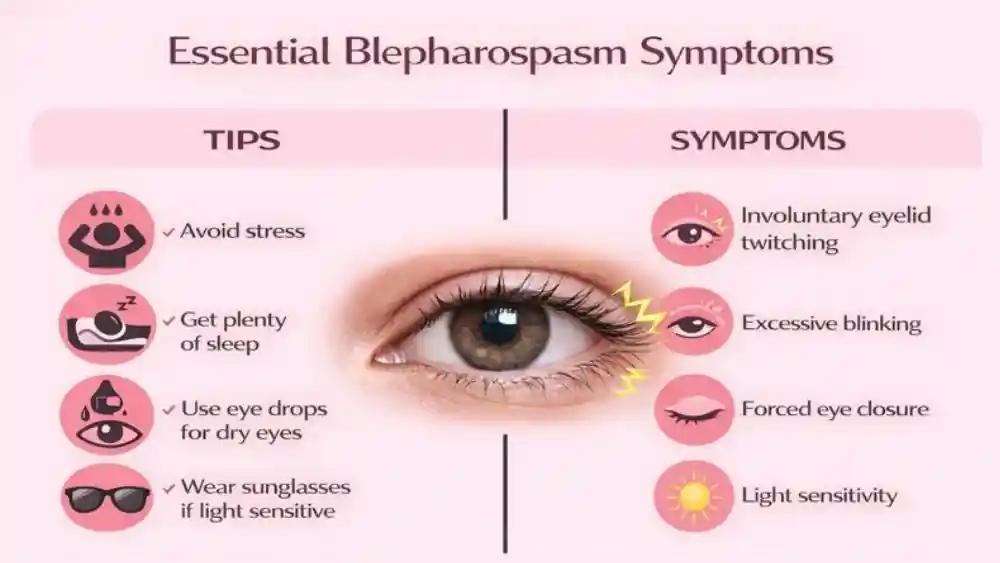
Essential Blepharospasm Symptoms
Involuntary Eyelid Twitching Disorder Explained
Benign Essential Blepharospasm often begins as a mild eyelid twitching disorder that does not stop. Unlike common eyelid twitches caused by stress or caffeine, this twitching becomes patterned and repetitive. You cannot control it by effort, and rest does not stop it.
The twitching comes from faulty nerve signals. These signals tell the eyelid muscles to contract even when they should relax. This is why doctors classify the condition as dystonia. Early essential blepharospasm symptoms may appear only during stress or bright light exposure.
Excessive Blinking And Forced Eye Closure
Blinking becomes stronger and faster. Over time, blinking turns into forceful closure. Your eyelids may shut tightly for seconds or longer. This can happen many times a day.
This stage marks established benign essential blepharospasm. Vision loss during spasms is functional, not structural. Your eyes still see normally when the lids open. Many patients describe feeling trapped behind closed eyelids.
Light Sensitivity, Eye Irritation, And Visual Difficulty
Light sensitivity is common. Sunlight, screens, and fluorescent lights often worsen spasms. Wind and dry air increase irritation. These triggers overstimulate already sensitive blink reflex pathways.
You may feel burning, dryness, or grit in the eyes. Dry eye often coexists but does not cause the disorder. These remain key essential blepharospasm symptoms that affect daily safety.
How Symptoms Progress Over Time
Symptoms usually start mild and become more frequent. Progression varies widely. Some people worsen over two to five years. Others stabilize early. Research shows no brain damage progression, but symptom burden can increase.
Untreated benign essential blepharospasm may spread to nearby facial muscles in some patients. Evidence here is limited, and not everyone experiences spread.
Causes Of Benign Essential Blepharospasm
Abnormal Brain Signaling And Facial Dystonia
Benign Essential Blepharospasm develops due to abnormal communication between the brain and eyelid muscles. The brain sends excessive signals that trigger repeated muscle contraction. This places the condition under facial dystonia blepharospasm .
Functional imaging studies show altered activity in motor control circuits. These findings come from small patient groups, so conclusions remain cautious.
Role Of Basal Ganglia Dysfunction
The basal ganglia [deep brain structures that regulate movement] help smooth muscle actions. In blepharospasm, these structures fail to filter muscle signals correctly.
Neurology research from movement disorder centers shows irregular firing patterns in these pathways. This explains why the causes of benign essential blepharospasm are neurological rather than muscular or eye-based.
Genetic And Idiopathic Causes
Some patients report family members with dystonia or tremor disorders. This suggests a genetic role. No single gene explains all cases. Most cases remain idiopathic [no clear cause]. This is common in movement disorders. Genetics may increase risk but does not guarantee disease.
Trigger Factors That Worsen Eyelid Spasms
Triggers do not cause the disorder but worsen symptoms. Common triggers include stress, fatigue, bright light, illness, and emotional strain. Avoiding triggers helps symptom control but does not reverse benign essential blepharospasm. Trigger sensitivity differs from person to person.
Facial Dystonia Blepharospasm
Difference Between Blepharospasm And Hemifacial Spasm
Blepharospasm affects both eyes. Hemifacial spasm affects one side of the face. Hemifacial spasm usually comes from nerve compression, not brain signaling problems. This distinction matters because treatments differ. Facial dystonia blepharospasm requires neurological management rather than nerve surgery.
Meige Syndrome And Other Dystonia Overlaps
Some patients develop spasms in the jaw or neck. This combination is called Meige syndrome. It confirms the dystonia origin of the disorder. Overlap does not mean worsening prognosis. Many patients still respond well to treatment for benign essential blepharospasm .
Conditions That Mimic Blepharospasm
Dry eye disease causes blinking but not forced closure. Tics cause brief movements and stop during sleep. Eye infections cause pain and redness. Doctors rule out these conditions before diagnosing benign essential blepharospasm. Correct diagnosis prevents unnecessary treatments.
Eyelid Twitching Disorder
Normal Eyelid Twitch Vs Pathological Blepharospasm
A normal twitch lasts days and resolves. It does not block vision. Pathological twitching persists for months and worsens. A chronic eyelid twitching disorder with forced closure strongly suggests blepharospasm and needs evaluation.
Red Flags That Require Medical Evaluation
Red flags include frequent eye closure, difficulty driving, facial spasms, and symptoms lasting over three months. Early evaluation improves symptom control in Benign Essential Blepharospasm and prevents safety risks.
Diagnosis Of Benign Essential Blepharospasm
Clinical Examination And Symptom History
There is no lab test for benign essential blepharospasm. Diagnosis relies on symptom pattern, triggers, and direct observation of eyelid movement. Doctors assess blink rate, spasm strength, symmetry, and response to light or stress.
Neurological Assessment
A neurologist evaluates muscle control and checks for other dystonia signs. This helps confirm the diagnosis and exclude nerve damage or stroke. This step is important when symptoms appear suddenly or spread beyond the eyelids.
Tests Used To Rule Out Secondary Causes
Imaging tests may be ordered if symptoms affect one side or start abruptly. These tests rule out tumors, vascular issues, or brain injury. They do not diagnose blepharospasm directly. Diagnosis remains clinical for benign essential blepharospasm.
Botox Treatment For Blepharospasm
When eyelid spasms interfere with vision and safety, injections become the main treatment choice. This approach targets the muscle overactivity that defines benign essential blepharospasm rather than masking symptoms.
How Botulinum Toxin Injections Work
Botox treatment for blepharospasm works by blocking nerve signals that cause eyelid muscles to contract. The toxin prevents the release of acetylcholine [a chemical that triggers muscle movement]. When the signal stops, the muscle relaxes. This reduces both blinking strength and forced eye closure.
Botulinum toxin does not affect vision or brain function. It acts only at the injection site, which makes it a targeted therapy for benign essential blepharospasm.
Effectiveness And Duration Of Relief
Most patients notice improvement within three to seven days. Peak benefit usually appears by two weeks. Relief often lasts three to four months, though timing varies. Botox treatment for blepharospasm remains the most effective symptom-control option available.
Injection Frequency And Dosing
Doctors usually repeat injections every twelve weeks. Injection sites and dose depend on muscle strength and symptom pattern. No fixed dose fits everyone.
Specialist experience matters. Poor placement can reduce the benefit or increase the side effects in benign essential blepharospasm.
Common Side Effects And Risks
Temporary eyelid drooping may occur if nearby muscles weaken. Dry eyes or blurred vision can also appear for a short time. These effects usually resolve within weeks. Serious complications are rare when injections are done correctly. Overall safety remains high with Botox treatment for blepharospasm .
Other Treatment Options For Blepharospasm
Oral Medications And Their Limitations
Doctors sometimes try oral drugs that affect nerve signaling. These include anticholinergics and muscle relaxants. Results are often modest.
Side effects such as drowsiness and dry mouth limit long-term use. Oral drugs rarely replace injections in benign essential blepharospasm.
FL-41 Tinted Lenses And Light Management
FL-41 lenses filter blue light, which often triggers spasms. Many patients report reduced blinking and less discomfort. Light management does not treat the brain cause. It helps control triggers that worsen facial dystonia and blepharospasm symptoms.
Surgical Treatment (Myectomy)
Myectomy removes selected eyelid muscles that cause closure. Surgeons reserve it for severe cases that fail injections. Surgery improves symptoms for some patients, but results vary. It does not correct the underlying brain signaling problem.
Role Of Supportive And Behavioral Therapies
Good sleep, stress control, and dry eye treatment support symptom control. Behavioral strategies help reduce spasm frequency. These approaches do not cure benign essential blepharospasm, but they improve daily comfort and function.
Living With Benign Essential Blepharospasm
Daily life changes when eyelids close without warning. Understanding how the condition affects routine tasks helps you adapt without giving up independence or safety.
Daily Coping Strategies
You may plan tasks around symptom peaks. Sunglasses and tinted lenses help outdoors. Short breaks reduce visual strain. Consistent treatment schedules help maintain function. Living well with benign essential blepharospasm requires adjustment, not withdrawal.
Impact On Driving, Reading, And Work
Driving becomes unsafe when spasms block vision. Some people restrict driving during symptom flares. Reading may require more breaks.
Work performance can suffer without treatment. Proper management allows many people with benign essential blepharospasm to remain employed.
Mental Health Considerations
Chronic symptoms can lead to frustration and anxiety. Social embarrassment is common. These reactions are understandable. Mental health support improves coping. Addressing emotional strain is part of complete care for benign essential blepharospasm.
Prognosis And Long-Term Outlook
Many people worry about whether symptoms will keep worsening. Knowing how benign essential blepharospasm typically behaves over time helps set realistic expectations.
Does Benign Essential Blepharospasm Get Worse?
Symptoms often worsen slowly during the first few years. Many patients then reach a stable phase. Rapid decline is uncommon. Treatment controls symptoms well, even if the disorder persists long-term.
Can Symptoms Go Into Remission?
Complete remission is rare but reported. Partial improvement is more common. Most patients need ongoing management. There is limited research on why remission occurs in some cases of benign essential blepharospasm.
Can Benign Essential Blepharospasm Be Prevented?
Prevention focuses on control rather than cure because the exact cause remains unclear. Small adjustments can still reduce symptom intensity and improve stability.
Trigger Avoidance And Lifestyle Adjustments
Avoiding bright light, managing stress, and reducing fatigue help control symptoms. These steps reduce spasm frequency. Prevention of disease onset is not currently possible due to unknown causes.
Eye Care And Environmental Modifications
Treating dry eyes reduces irritation. Humid air helps in dry climates. Screen brightness adjustments also help. These changes support comfort in people with benign essential blepharospasm.
When To See A Doctor
Some changes signal the need for medical review rather than routine follow-up. Early attention prevents avoidable risks and keeps treatment effective.
Symptoms Requiring Urgent Evaluation
Sudden vision loss, severe pain, or one-sided facial weakness needs urgent care. These may indicate other conditions. Blepharospasm itself does not cause pain or permanent vision loss.
When Treatment Needs Adjustment
Shorter relief duration or reduced response signals the need for dose or site changes. Doctors can modify treatment plans. Regular follow-up keeps benign essential blepharospasm well controlled.
FAQs
Is Benign Essential Blepharospasm Permanent?
Benign Essential Blepharospasm is usually long-term. Symptoms often persist for years, but treatment controls them well. Some people experience partial improvement over time, though complete remission remains uncommon.
Is Blepharospasm A Form Of Dystonia?
Yes. Blepharospasm is classified as focal dystonia, meaning it affects one muscle group. It results from abnormal brain signals rather than eye disease or muscle weakness.
How Effective Is Botox Long Term?
Long-term studies show sustained benefit for most patients. Effectiveness does not usually decline when injections are timed correctly. Botox treatment for blepharospasm remains the standard therapy.
Can Stress Worsen Eyelid Spasms?
Yes. Stress increases muscle excitability and worsens symptoms. Stress does not cause the disorder, but it strongly influences symptom severity in benign essential blepharospasm.
Is Blepharospasm Related To Parkinson’s Disease?
Both involve motor control pathways, but they are separate conditions. Most people with blepharospasm never develop Parkinson’s disease.
How Do Blepharospasm Symptoms Progress Over Time?
Symptoms usually start mild, worsen gradually, and then stabilize. Progression speed varies widely. Early treatment improves long-term control.
What Causes Benign Essential Blepharospasm?
The disorder comes from abnormal brain signaling that overstimulates eyelid muscles. The exact cause remains unknown in many cases.
How Does Abnormal Brain Signaling Lead To Eyelid Spasms?
The brain sends repeated contraction signals instead of allowing muscles to relax. This causes involuntary blinking and closure seen in benign essential blepharospasm.
What Role Does Basal Ganglia Dysfunction Play in Blepharospasm?
The basal ganglia fail to filter unwanted movements. This allows excessive eyelid contractions to occur without voluntary control.
Is Benign Essential Blepharospasm Genetic or Idiopathic?
It can be both. Some cases show family history, while many remain idiopathic with no clear cause identified.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.