What is brain surgery?
Brain surgery is a medical procedure where a neurosurgeon operates on the brain to treat conditions like tumors, aneurysms, or seizures. Since the brain controls every body function, this procedure requires extreme precision.
Doctors use different neurosurgical techniques depending on the problem. While some surgeries are done through open skull procedures, others use cameras or robotic tools for better accuracy. Brain surgery recovery depends on the method and the patient’s health.
Who performs brain surgery?
Brain surgery is performed by highly trained doctors called neurosurgeons. They specialize in the brain, spine, and nervous system. A neurosurgeon works with anesthesiologists, oncologists, radiologists, and critical care specialists to ensure safe treatment.
Neurosurgeons use tools like microscopes, navigation systems, and intracranial pressure monitoring to plan surgery. Their training takes over 10 years, combining medical school, surgical training, and hands-on practice. Only skilled neurosurgeons can safely perform complex cases like brain aneurysm surgery or deep brain stimulation surgery.
What are the types of brain surgery?
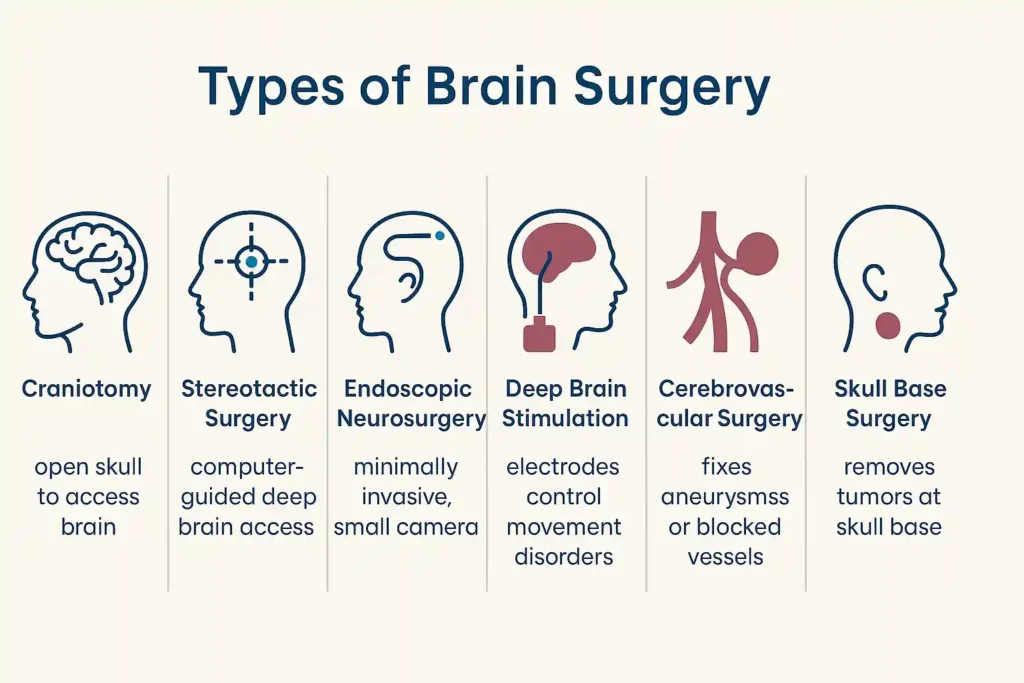
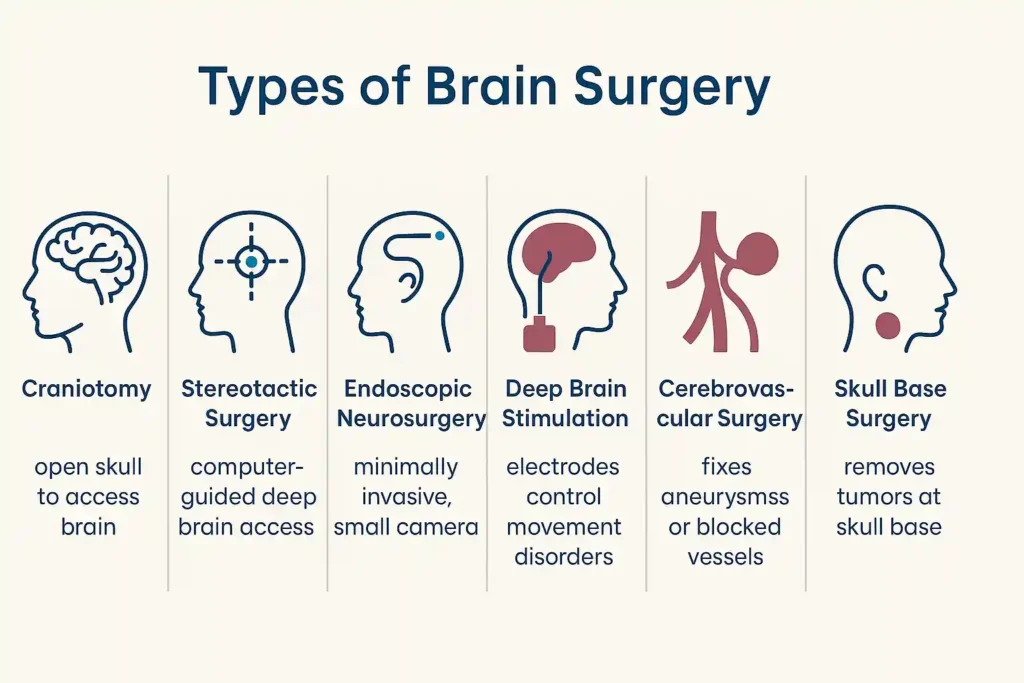
Brain surgery can be performed in many ways. The type is influenced by the patient’s medical condition and the specific location of the issue.
- Craniotomy: The most common, where a part of the skull is removed to access the brain.
- Stereotactic surgery: Computer-guided surgery that helps reach deep areas without damaging healthy tissue.
- Endoscopic neurosurgery: This method utilizes a miniature camera for less invasive surgical interventions.
- Deep brain stimulation surgery: Electrodes are placed in the brain to control movement disorders.
- Cerebrovascular surgery: Treats blood vessel problems, like aneurysms or blockages.
- Skull base surgery: This operation is designed to remove tumors situated at the base of the skull.
Each type is chosen after careful diagnosis, imaging tests, and risk evaluation.
What does brain surgery treat or manage?
Brain surgery is performed to treat a variety of life-threatening and disabling conditions, including:
- Surgery for brain tumors that aims to remove both cancerous and benign growths.
- Brain aneurysm surgery to repair blood vessel bulges that could rupture.
- Brain surgery for seizures when epilepsy does not respond to medicines.
- Brain mass surgery to remove abnormal tissue.
- Brain aneurysm repair to prevent bleeding in the brain.
- Treatments for infections, head injuries, or high intracranial pressure monitoring results.
In addition, some patients undergo neurorehabilitation after surgery to regain strength, speech, or movement.
Table of Contents
ToggleTreatment Details
How should I prepare for brain surgery?
Brain surgery requires careful preparation. Doctors order MRI scans, blood tests, and neurological exams. Patients may need to stop blood-thinning medicines and fast before surgery.
Doctors explain the type of surgery, whether brain tumor removal, deep brain stimulation, or cerebrovascular surgery. Mental preparation is also vital. Anxiety is common, and counseling may help patients face the procedure with confidence.
What happens during brain surgery?
Brain surgery begins with anesthesia. Once asleep, the neurosurgeon makes a cut in the scalp. For open surgery, a piece of the skull is removed. Then, the surgeon carefully treats the problem.
Some operations, like endoscopic neurosurgery, only need a small incision. Others, such as skull base surgery, are more complex. Advanced tools and neurosurgical techniques help reduce damage to healthy brain tissue.
Will I be awake for brain surgery?
Brain surgery may sometimes be done while the patient is awake. Awake craniotomy allows doctors to check speech and movement during the procedure. This is especially important in brain tumor surgery near speech areas.
Where will a surgeon make an incision during brain surgery?
Brain surgery incisions vary depending on the condition. For brain tumor removal, the cut is usually made near the affected area. For deep conditions, stereotactic surgery guides precise entry points.
How long does brain surgery take?
Brain surgery can take anywhere from 3 to 12 hours. Simple cases may be shorter, but complex ones like brain aneurysm surgery or brain mass surgery may require longer operating times.
What happens after brain surgery?
Brain surgery recovery begins in the neurocritical care unit. Patients are closely monitored for swelling, bleeding, or seizures. Some may need breathing tubes at first.
After stabilization, patients move to a regular ward. Therapy starts early to help them regain strength. Speech and movement therapy are common. Many require neurorehabilitation before returning home.
Risks / Benefits
What are the benefits of brain surgery?
Brain surgery offers life-saving benefits. It removes dangerous tumors, repairs blood vessels, and controls epilepsy. For conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, deep brain stimulation can improve the quality of life.
How successful is brain surgery?
Brain surgery success depends on the condition. For example, brain aneurysm surgery success is 80–95%. Brain tumor surgery outcomes vary by tumor type but improve greatly when detected early.
What are the risks or complications of brain surgery?
Brain surgery carries risks. Complications include:
- Infection or bleeding.
- Seizures after surgery.
- Weakness, vision, or speech problems.
- Memory loss or confusion.
- Clots in blood vessels.
Doctors reduce these risks with advanced neurosurgical techniques and close monitoring.
Recovery and Outlook
What is the recovery time for brain surgery?
Brain surgery recovery depends on surgery type and patient health. Minor cases take 4 to 6 weeks. Major operations may take months. Rehabilitation is often needed to regain speech, balance, or strength.
Patients who undergo neurorehabilitation recover faster. They may receive therapy for memory, movement, or behavior. Follow-up visits are essential to track healing.
When To Call the Doctor
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Brain surgery patients should contact their doctor if they have severe headaches, seizures, fever, confusion, or fluid leaking from the incision. Quick care prevents complications and ensures proper healing.
The Bottom Line
Brain surgery is one of the most advanced forms of neurosurgery. While it carries risks, it often saves lives and improves quality of life. Patients who follow recovery steps and undergo neurorehabilitation often live long, fulfilling lives.
FAQs
Is brain surgery successful?
Brain surgery is usually successful. Success rates vary with condition. Brain aneurysm surgery, brain tumor surgery, and deep brain stimulation surgery all show high success when done early under expert neurosurgeons.
How long does it take to recover from brain surgery?
Brain surgery recovery varies. Minor operations heal in 4–6 weeks. Major surgeries may need months with rehabilitation. Recovery also depends on the patient’s age, health, and post-surgery therapy.
What is brain surgery called?
Brain surgery is also called neurosurgery. It includes different types like craniotomy, endoscopic neurosurgery, and stereotactic surgery, depending on the condition being treated and the technique used.
Will I ever be the same after brain surgery?
Many people return to normal life after brain surgery. Some may need rehabilitation to regain speech or movement, but long-term outcomes are often good with proper medical support.
Can you live a long life after brain surgery?
Yes, many patients live long lives after brain surgery. Success depends on the condition, follow-up care, and recovery. Early treatment improves chances of long-term survival and good quality of life.
What causes brain tumors?
Brain tumors may be caused by genetic changes, family history, radiation, or uncontrolled cell growth. Some are cancerous, others are benign. Brain tumor surgery is often the main treatment.
Can you talk after brain surgery?
Yes, most people can talk after brain surgery. If the speech area is affected, therapy helps restore communication. Awake craniotomy ensures speech is protected during brain tumor removal.
What to avoid after brain surgery?
Patients should avoid heavy lifting, alcohol, smoking, driving too early, and missing medications after brain surgery. Following doctor’s advice supports safe recovery and prevents long-term complications.
Can you be awake during brain surgery?
Yes. Awake brain surgery is used for tumors near speech or movement centers. Patients stay awake so doctors can test speech and movement while performing delicate neurosurgical techniques.
About The Author

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.
→ Book a consultation to discover which remedies suit your needs best.




