Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Childhood Trauma?
Childhood trauma refers to distressing incidents that compromise a child’s sense of safety and trust. Trauma in children does not always mean visible wounds; it can be emotional, psychological, or social.
A child may face trauma from sudden events like an accident or long-lasting experiences such as neglect. The impact is often deep because the child is still developing ways to understand the world.
Trauma in children can change the way the brain develops. Stress chemicals remain high, making it hard for them to regulate emotions, build healthy relationships, and feel secure. Recognizing these early changes is key.
Types of Traumatic Events in Childhood

There are many types of childhood trauma, and each can affect the child differently. Some common forms include abuse, neglect, violence, accidents, or sudden loss.
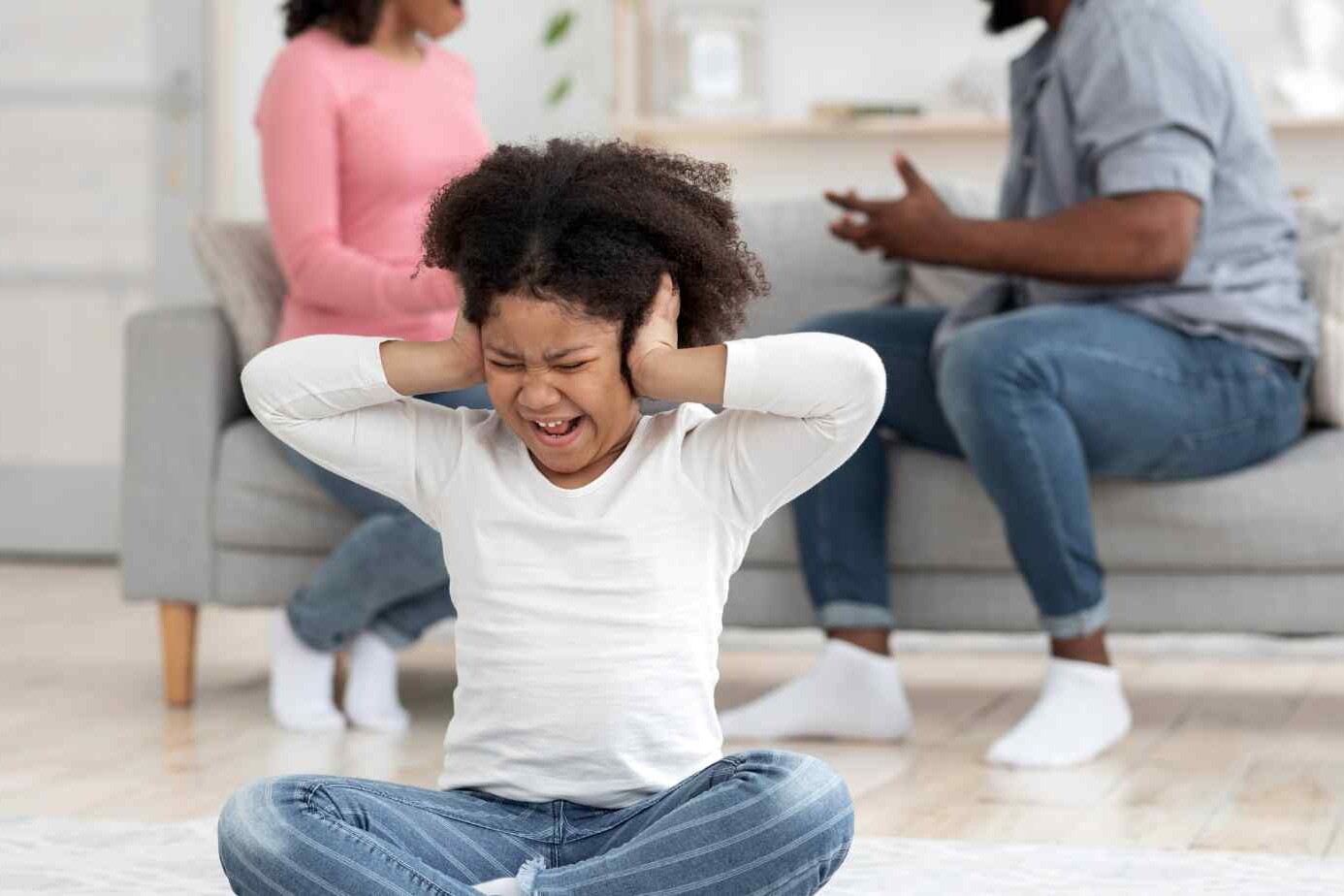
For instance, a child who witnesses domestic violence may grow up fearful and withdrawn, while a child who experiences bullying may struggle with self-confidence. A car crash or natural disaster can leave a child anxious and hyper-alert.
It is important to note that trauma does not only come from extreme events. Ongoing stress, such as living with a parent who struggles with addiction, can be just as damaging.
Factors Affecting a Child’s Trauma Response
Not every child reacts the same way to trauma. Several factors shape the response. These include the child’s age, the severity of the event, the length of exposure, and the presence of supportive caregivers.
A toddler may show trauma through crying, nightmares, or refusal to separate from parents. School-age children might show falling grades or sudden aggression. Teens may withdraw from friends or engage in risky behaviors.
Support from parents or trusted adults is often the strongest protective factor. A safe environment can help the child process pain. Without this, trauma may develop into long-term struggles.
Behavioral Signs of Childhood Trauma
The signs of childhood trauma can be seen in everyday behavior. Some are easy to miss because they look like ordinary misbehavior. Frequent signs include irritability, intense fear, clinginess, or a return to earlier behaviors like thumb-sucking.
Teachers may notice that children stop focusing in class, while parents may notice tantrums or trouble sleeping. Some children become overly responsible, trying to take care of younger siblings as a way of feeling in control.
If these behaviors persist, they are more than just a phase. They may point to deep distress caused by trauma.
Examples of Childhood Trauma
Physical, Emotional, and Sexual Abuse
A prominent example of childhood trauma is abuse. Physical abuse involves hitting, slapping, or shaking that causes injury. Emotional abuse includes insults, humiliation, or rejection. Sexual abuse refers to non-consensual or inappropriate sexual interactions.
Children who face abuse often carry invisible scars. They may feel guilty, blame themselves, or live in fear of others. Abuse also affects trust and makes it difficult to form healthy attachments later in life.
Childhood Neglect and Trauma
Childhood neglect and trauma happen when children do not receive food, clothing, shelter, medical care, or emotional support. Neglect can be physical or emotional, but both leave children feeling abandoned.
The effects of emotional neglect are often long-lasting. Children may grow up doubting their worth, unable to regulate emotions, or struggling with social skills. This form of trauma is often overlooked, but it can be just as harmful as direct abuse.
Witnessing Violence and Disasters
Children who witness violence in the home, community, or media can also suffer trauma. They may live in constant fear, expecting danger even in safe places. This type of trauma creates a sense of helplessness.
Natural disasters, accidents, or sudden losses also traumatize children. A child who survives a flood may fear rain for years. A child who witnesses a school shooting may experience flashbacks or panic at loud noises.
Impact of Unresolved Childhood Trauma
Attachment Styles in Adulthood
When trauma is not addressed, it shapes adult relationships. This phenomenon is recognized as childhood trauma and its impact on relationships. Survivors often develop insecure attachment styles.
Some avoid closeness to protect themselves. Others cling tightly to relationships, fearing abandonment. Some swing between love and fear. These patterns often trace back to unhealed childhood wounds.
Such attachment issues make it hard to build trust, create stable families, or feel emotionally secure.
Consequences of Childhood Trauma in Adulthood
Mental Health Issues Related to Trauma
The childhood trauma mental health impact is wide-reaching. Common psychological outcomes include depression, anxiety, PTSD, and various personality disorders. Trauma rewires the brain’s stress system, making adults more sensitive to future stress.
Many adults also turn to alcohol, drugs, or food to numb the pain. The risk of addiction is higher in those who faced severe trauma as children.
Physical Health Problems from Childhood Trauma
The psychological effects of childhood trauma are linked to physical health problems too. Chronic stress weakens the immune system and increases the risk of illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, and digestive issues.
Adults with childhood trauma history may experience chronic pain, migraines, and fatigue. Doctors sometimes treat these symptoms without realizing the root lies in past trauma.
Recognizing Childhood Trauma and Its Signs
Recognizing Trauma by Age Group
Recognizing childhood trauma depends on the child’s age. Young children may show clinginess, separation anxiety, or sleep problems. School-age children may act out, perform poorly in school, or withdraw socially.
Teens may show self-harm, aggression, substance use, or risky behavior. Learning how to recognize childhood trauma in kids allows parents and teachers to provide early support.
Early detection also prevents the early signs of PTSD in children from becoming lifelong struggles.
How Families Can Help Children Experiencing Trauma
Families are central to healing. Children need consistent routines, safe spaces, and unconditional love. Listening without judgment gives children the courage to express emotions.
Parents should avoid forcing the child to “move on” quickly. Instead, they can encourage healthy coping like drawing, journaling, or sports. Family therapy may help everyone learn how to support the child better.
A nurturing environment can counteract the damage of trauma and build resilience.
Treatment for Childhood Trauma
Evidence-Based Therapies for Recognizing Trauma
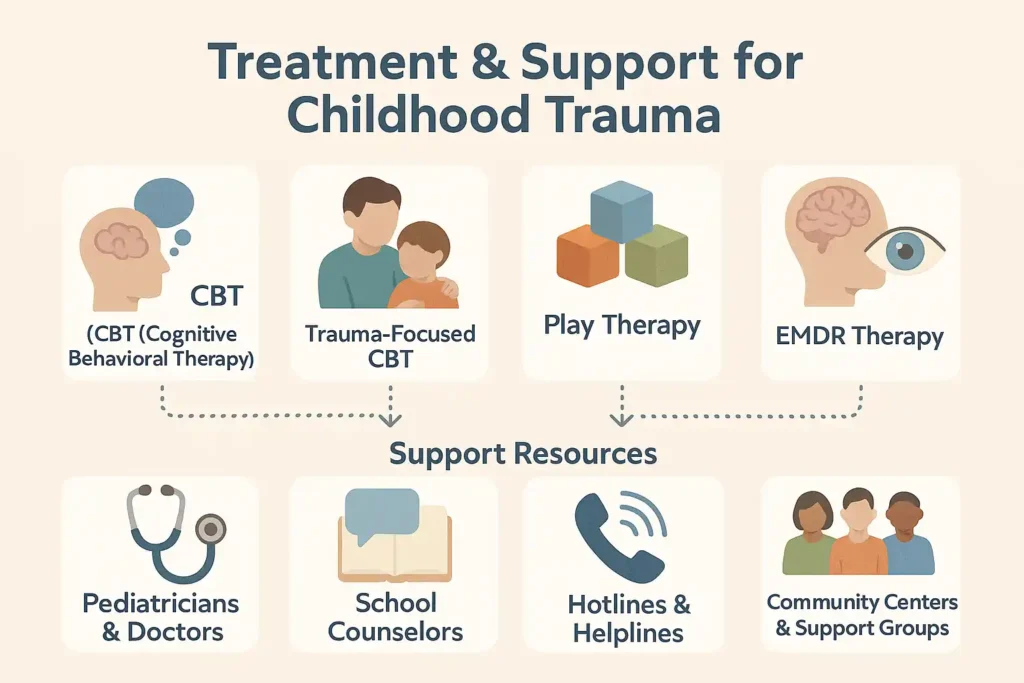
Therapy is crucial in healing. Common approaches include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, which teaches children to replace negative thoughts, and Trauma-Focused CBT, which involves both child and caregiver.
Play Therapy helps younger children express emotions without words. EMDR therapy assists in reducing the emotional charge of traumatic memories. These therapies make recognizing trauma easier and give children tools to cope.
Resources for Childhood Trauma Support
Help is available. Parents can reach out to pediatricians, school counselors, or child protection services. National hotlines, local support groups, and community centers provide both immediate and long-term support.
Knowing where to find help makes it easier for families to take the first step.
The Bottom Line
The impact of childhood trauma lasts a lifetime if ignored. But children can recover when surrounded by care, therapy, and support. Recognizing the signs of childhood trauma early is the key to preventing long-term suffering.
Every adult who steps in to protect and guide a child helps rewrite their story of pain into one of resilience.
FAQs
What are some examples of childhood trauma?
Examples include abuse, neglect, bullying, witnessing violence, losing a parent, or surviving disasters. Each of these experiences can leave deep emotional and psychological scars in children.
How to recognize signs and symptoms of trauma?
Signs include nightmares, sudden aggression, regression, clinginess, withdrawal, or poor school performance. These behaviors may reflect hidden pain rather than simple misbehavior or temporary mood changes.
How to recognize your childhood trauma?
You may notice recurring struggles in relationships, persistent fear, anxiety, depression, or triggers that connect to past experiences. Recognizing patterns helps you identify unhealed trauma from your childhood.
What are signs of unhealed childhood trauma?
Adults may face anxiety, depression, addiction, unstable relationships, or chronic health problems. They may also struggle with trust, emotional regulation, or recurring flashbacks tied to unresolved traumatic events.
What are the 4 types of childhood trauma?
The main types are physical abuse, emotional abuse, sexual abuse, and neglect. Each affects children differently, but all can shape development, relationships, and long-term health in significant ways.
What are the physical symptoms of childhood trauma in adults?
Symptoms include headaches, digestive issues, chronic fatigue, heart problems, or pain without clear cause. These health problems may develop when stress hormones remain high for years.
What is the fight response in childhood trauma?
The fight response is when a child reacts with aggression or anger to danger. It is a survival instinct, but if unhealed, it can carry into adult behavior.
About The Author

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.
→ Book a consultation to discover which remedies suit your needs best.