Edema means fluid builds up in a part of the body where it should not be. When this buildup happens inside the brain, it becomes cerebral edema , one of the most dangerous forms of swelling because the brain is trapped inside a hard skull with no room to expand.
As fluid rises, pressure builds, blood flow drops, and brain cells start to lose oxygen. This can affect how you think, speak, move, or even breathe. Doctors treat cerebral edema as an emergency because even small pressure increases can harm vital areas that keep you alive.
Understanding what triggers it, how symptoms appear, and why quick treatment matters helps you act fast if warning signs show up.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Cerebral Edema?
Cerebral edema means that extra fluid builds up inside your brain, raising the pressure in your skull. The skull is a rigid bone, so it cannot stretch to make room. When pressure rises, blood flow drops, brain cells lose oxygen, and important areas for breathing and thinking can fail.
Doctors see cerebral edema as a sign of serious illness, not as a small side issue. Fast treatment of cerebral edema improves survival, although the exact outcome depends on the cause and how early care starts. Different types of cerebral edema react in different ways to treatment, so doctors first try to determine which pattern is present.
How Brain Swelling Develops (Fluid Buildup, Pressure Changes)
Inside your skull, you have brain tissue, blood, and clear fluid called cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). When cerebral edema adds water to the tissue, the other parts must move. At first, veins and CSF spaces drain more to hold pressure steady. Once this “reserve” is used, even a small extra amount of fluid can cause a sharp rise in pressure, called intracranial pressure.
Difference Between Swelling Vs Edema
Swelling is any increase in size. Edema means that the extra size comes mainly from trapped fluid. In cerebral edema , fluid collects inside brain cells, around them, or both. It may come from leaky blood vessels or from cells that have lost control of their salt pumps.
When doctors use the phrase brain swelling cerebral edema , they mean that fluid is the main reason for the swelling, not a clot or a tumor. That detail guides which drugs, such as steroids or osmotic agents, are likely to work and which might be harmful.
Why Cerebral Edema Is A Medical Emergency
Your brain needs steady blood flow and stable pressure. Cerebral edema upsets that balance. As pressure climbs, less blood reaches key areas. If the swelling pushes the brain downward, a dangerous shift called herniation can stop breathing or blood pressure control within minutes.
Because of this, new severe headache, repeated vomiting, sudden confusion, weakness, or seizures needs urgent medical review. Waiting at home with possible cerebral edema can cost you vital time.
Causes Of Cerebral Edema
The causes of cerebral edema include direct brain problems and whole-body illnesses. Often more than one factor is present, for example, a head injury plus low blood oxygen.
Traumatic Brain Injury (Falls, Accidents, Blows)
A strong hit to the head is one of the leading triggers of cerebral edema worldwide. A fall, road crash, or sports blow can bruise brain tissue and tear small vessels so that blood and fluid leak into nearby areas. Swelling often worsens over the first one to three days, which is why doctors repeat scans and watch closely even if you seemed “fine” at first.
Stroke (Ischemic & Hemorrhagic)
A stroke happens when part of your brain suddenly loses its blood supply. In an ischemic stroke, a clot blocks a vessel. In a hemorrhagic stroke, a vessel bursts and bleeds into tissue.
Both patterns can cause cerebral edema because cells without oxygen pull in water and swell, and blood around a bleed can also draw fluid into the white matter. Swelling often peaks a few days after the stroke, so doctors keep patients in stroke units during that risk window.
Infections (Meningitis, Encephalitis)
Meningitis infects the coverings of the brain, while encephalitis infects the tissue itself. In both settings, immune cells and fluid rush into the area, and vessels become more leaky. This can produce cerebral edema , especially when treatment is delayed or the germ is very aggressive.
Quick use of antibiotics or antivirals lowers the risk of lasting damage, but some people still have problems, so experts stress that evidence is not perfect.
Brain Tumors & Mass Effect
A brain tumor takes up space inside a closed skull. Many tumors also damage the blood-brain barrier so that plasma fluid leaks into nearby white matter and causes cerebral edema called vasogenic edema.
The combined pressure from tumor and edema, known as mass effect, can lead to headaches, personality changes, or seizures. Steroid drugs often shrink this type of swelling, but they do not help every cause and can have strong side effects, so doctors balance risks and benefits carefully.
Hypoxia (Drowning, Suffocation, Cardiac Arrest)
When your brain does not get enough oxygen during near-drowning, severe asthma, or cardiac arrest, energy levels fall fast. Cell pumps that control salt and water stop working, and water enters the cells, creating a diffuse form of cerebral edema that often affects much of the brain.
Cooling treatments and careful control of oxygen and blood pressure may help in some patients, but results vary, and current research is still growing, so doctors explain that predictions are never exact.
Toxic/Metabolic Causes (Liver Failure, Poisoning, DKA)
Severe liver failure lets toxins like ammonia build up in your blood. Diabetic ketoacidosis and very low blood sodium disturb fluid balance. These metabolic problems can pull water into brain tissue and cause cerebral edema even when the head was never hit.
In such cases, you need both brain support and slow, careful correction of salts, sugar, and toxins. Rapid extreme shifts can worsen swelling, so doctors adjust treatment step by step.
Brain Swelling & Cerebral Edema Connection
Intracranial Pressure Rise & Brain Tissue Shifts
As cerebral edema increases, intracranial pressure usually rises. At first, cerebrospinal fluid and venous blood drain more to keep pressure near normal. Once that reserve is gone, pressure can climb quickly and push brain tissue sideways or downward, pinching nerves and vital blood vessels.
How Swelling Damages Neurons
Neurons are the main working cells in your brain. Swelling from cerebral edema squeezes their blood supply and fills the space around them with waste chemicals. Some neurons swell until their outer wall breaks, and the released substances then injure nearby cells, so damage spreads beyond the original problem area.
Stages Of Worsening Edema
Early symptoms of cerebral edema can seem mild, such as strong headache, nausea, or feeling unusually sleepy or confused. As pressure rises, speech may become unclear, vision may blur, or one side of your body may feel weak. In late stages, seizures, deep coma, and abnormal breathing can appear. At that point, emergency care is essential to protect life and reduce long-term disability.
Symptoms Of Cerebral Edema
When cerebral edema grows, the brain struggles to work normally. The symptoms of cerebral edema depend on how fast the pressure rises and which area is affected.
Mild Symptoms: Headache, Nausea, Confusion
Early signs often look simple. You may feel a heavy headache that does not improve much with rest. Nausea or sudden vomiting can appear. Confusion may develop, especially when you try to focus or answer questions.
Doctors explain that these early signs matter because even slow cerebral edema can shift into dangerous pressure levels. Evidence from stroke and trauma studies shows that minor confusion often appears hours before more serious symptoms.
Moderate Symptoms: Speech Issues, Irregular Breathing, Seizures
As swelling increases, symptoms of cerebral edema become easier to notice. Speech can turn slow or unclear. You may use the wrong words or struggle to put simple thoughts together. Breathing may change. It can become too fast, too slow, or uneven.
Seizures sometimes develop because swelling irritates brain cells. A seizure may look like shaking, stiffening, or brief staring spells. Once seizures appear, doctors suspect moderate or advanced cerebral edema , and they often move the patient to intensive care.
Severe Symptoms: Coma, Abnormal Posturing
Severe cerebral edema can push brain structures downward. This can lead to coma. The person does not wake up or react to pain or voices. The arms or legs may twist into stiff positions called abnormal posturing. Pupils may stop reacting to light. At this point, pressure is dangerously high and needs emergency treatment.
Symptoms In Infants Vs Adults
Infants show symptoms of cerebral edema differently because their skull bones are not fully joined. A bulging soft spot, nonstop crying, poor feeding, or repeated vomiting may appear. They may seem floppy or too sleepy.
Adults show symptoms like headaches, behavior changes, weakness, or speech trouble. Doctors treat both groups aggressively because swelling can worsen quickly.
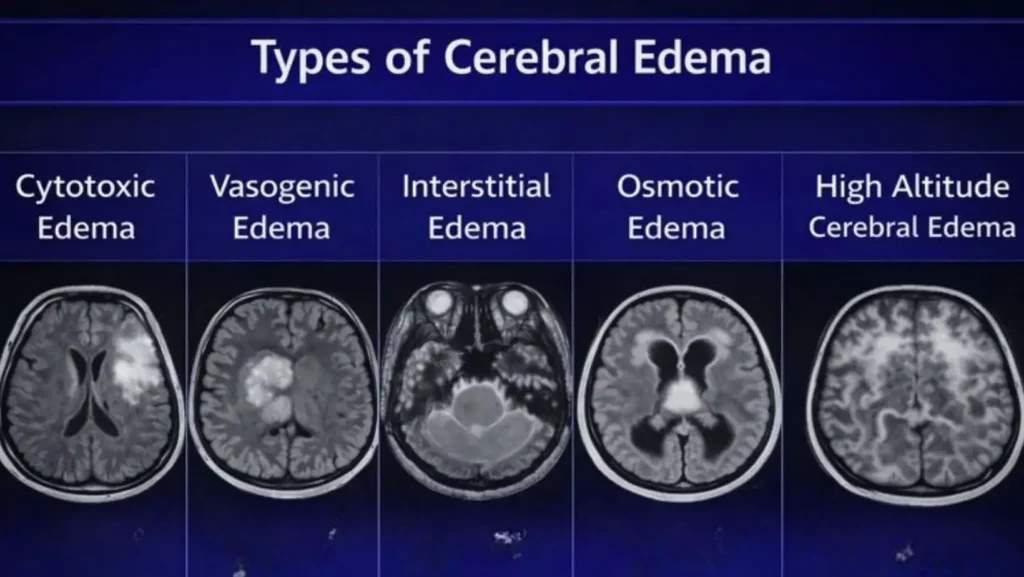
Types Of Cerebral Edema
Doctors sort types of cerebral edema by how the fluid builds up. This helps them choose safe treatments.
Cytotoxic Edema
This type happens when brain cells lose their normal salt control, so water rushes into the cells. Stroke and low oxygen states often cause it. Because the fluid sits inside the cells, drugs like steroids do not help. Instead, doctors support oxygen levels and blood flow to reduce further damage.
Vasogenic Edema
Vasogenic edema appears when vessels leak fluid into the spaces around brain cells. Tumors, infection, or trauma are common causes. This type of cerebral edema often responds to steroid medicines because they reduce vessel leak. It is one of the types of cerebral edema that doctors can often shrink before surgery.
Interstitial Edema
This form develops when cerebrospinal fluid escapes from the brain’s internal chambers into nearby tissue. It often occurs with hydrocephalus. Doctors sometimes drain fluid through a small tube to lower pressure.
Osmotic Edema
Osmotic edema develops when blood salts drop too fast or when blood becomes much less salty than brain tissue. Water moves into the brain to balance the difference. Correcting sodium too quickly can worsen this condition, so doctors adjust levels very slowly.
High Altitude Cerebral Edema
High-altitude cerebral edema is a dangerous reaction to low oxygen at high mountain levels. Fluid leaks into the brain and causes confusion, unsteady walking, and severe headache. Quick descent and oxygen are the strongest treatments.
Diagnosis Of Cerebral Edema
Doctors use tests to confirm cerebral edema and rule out other emergencies.
CT Scan Findings
A CT scan is fast and shows swelling clearly. When cerebral edema is present, the brain grooves look narrow and fluid spaces look compressed. Blood or tumors, which can cause brain swelling cerebral edema , appear on the scan as well. CT scans help guide early treatment decisions.
MRI Findings
MRI gives more detail than CT. It shows exactly where fluid sits and helps doctors tell which of the types of cerebral edema is present. MRI also helps detect infections, small strokes, and early tissue injury. It takes longer but offers better clarity.
Neurological Assessment
Doctors check alertness, movement, speech, and reflexes. This exam helps them see how much pressure the swelling is causing. It also gives early signs if cerebral edema begins to worsen.
ICP Monitoring
In severe cases, doctors place a small device through the skull to monitor intracranial pressure. This tool gives real-time readings. If pressure climbs, doctors adjust medicines or may consider surgical treatment.
Treatment For Cerebral Edema
Treatment aims to lower pressure and fix the cause of swelling. No single method works for every person because causes of cerebral edema differ.
Emergency Stabilization
Doctors first secure breathing and blood flow. They raise the head slightly to help drainage. They give oxygen and control blood pressure to protect the brain. This step slows brain swelling cerebral edema, while other treatments start.
Medications: Mannitol, Hypertonic Saline, Steroids
Mannitol helps pull water out of brain tissue. Hypertonic saline works similarly. Doctors adjust dose based on age, kidney health, and lab values. Steroids help reduce swelling from tumors or severe inflammation. They do not help cytotoxic edema, so doctors choose them carefully.
Surgical Options: Craniectomy, Shunt, Ventriculostomy
If medicines do not reduce cerebral edema , surgeons may remove part of the skull so the brain can expand safely. A ventriculostomy drains excess fluid. A shunt gives long-term drainage of cerebrospinal fluid. These tools control pressure and prevent herniation.
Treating The Underlying Cause
True recovery depends on fixing the source. Stroke may need clot removal. Infection needs strong antibiotics or antivirals. Tumors may need surgery or radiation. Metabolic causes need careful correction of salts and toxins. By treating the root problem, doctors prevent new waves of cerebral edema .
Recovery, Long-Term Effects And Prognosis
Recovery varies widely. Mild cases of cerebral edema may resolve in days. More serious cases may take weeks or months. Some people develop lasting memory or focus problems, especially after strokes or lack of oxygen. Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy help rebuild strength and skills. Studies show that early rehab improves independence, although results depend on age and brain injury size.
When To Seek Emergency Care
Sudden Severe Headache Or Vomiting
A sudden, powerful headache with vomiting can be a warning sign of cerebral edema or bleeding. If this appears suddenly, you need urgent care.
Loss Of Consciousness Or Seizures
Passing out or having a seizure may signal dangerous pressure changes. Because this can come from brain swelling cerebral edema , doctors need to examine you immediately.
Weakness, Confusion, Trouble Speaking
If you suddenly feel weak on one side, lose your balance, or cannot speak clearly, seek help at once. These signs appear in strokes, one of the most serious causes of cerebral edema .
FAQs
Is Cerebral Edema Reversible?
Some cases of cerebral edema improve fully when treated early, but severe or long-lasting pressure can cause lasting cell injury, so results depend on the cause and treatment timing.
How Long Does Cerebral Edema Take To Develop?
Cerebral edema may build up over minutes after injury or may grow slowly for days after infections or tumors. The speed varies with the underlying cause.
Can Cerebral Edema Cause Permanent Brain Damage?
If cerebral edema blocks blood flow or compresses vital brain areas, permanent injury may occur. Many people improve, but some effects can remain.
What Is The Survival Rate For Cerebral Edema?
Survival depends on age, cause, and how quickly treatment starts. Mild cerebral edema often improves, while severe cases need intensive care.
Can Dehydration Cause Cerebral Edema?
Severe dehydration followed by rapid fluid replacement can shift sodium levels and trigger cerebral edema , so doctors correct fluids slowly.
Is Cerebral Edema The Same As Hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus is extra fluid in brain chambers. Cerebral edema is fluid inside or around brain cells. Both raise pressure but are different problems.
Can Cerebral Edema Occur After A Stroke?
Yes. Stroke is one of the major causes of cerebral edema , especially during the first few days. Doctors monitor closely to catch swelling early.
Can You Recover Fully From Cerebral Edema?
Some people fully recover from cerebral edema when treated quickly. Others may have lasting changes, depending on the severity and brain areas affected.
About The Author

Medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, MD, DM (Neurology)
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained, board-certified neurologist with expertise in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders, including migraines, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and movement disorders. His clinical focus includes evidence-based neurological care and patient education.
All content is reviewed for medical accuracy and aligned with current neurological guidelines.