Understanding Family Systems Therapy: A Comprehensive Guide
From the start, family plays a key role in your life. It shapes your emotional health and personal growth. The family systems approach shows how each person affects the whole family.
This guide will cover family systems theory. It will explain its key ideas, how it helps, and how to start with a therapist.
Family systems therapy sees how closely connected family members are. It looks at the family, not just one person, to understand everyone's role. This method helps create better family relationships for everyone's benefit.
What is Family Systems Therapy?
Family systems therapy looks at how each family member's actions and relationships fit together. It helps us see how everyone in the family affects each other. This method focuses on changing family interactions for the better.
This therapy believes that people can't be understood alone. They are deeply connected to their family's relationships and patterns. Therapists use this idea to help families see and change the forces that shape their lives.
Family systems therapy shows how each person's feelings and actions make up a family's unique system. By understanding these connections, families can tackle problems, solve conflicts, and create a supportive environment. This helps everyone in the family grow and be happy.
If you want to make your family stronger, deal with tough times, or fix old issues, family systems therapy can help. It's a deep way to improve family life. By looking at family dynamics closely, families can reach their full potential and build a better future together.
Core Principles of Family Systems Therapy
Family systems theory is the base of family systems therapy. It sees the family as a connected whole. This therapy has core principles that shape its view.
Triangles
Triangles are a big part of family systems therapy. They are three-person relationships within the family. These triangles help reduce tension between two people by adding a third.
Therapists use these dynamics to help families understand their complex relationships. They work on finding better ways for families to talk and support each other.
Differentiation of the Self
Differentiation of the self is another key idea. It means being able to keep your own identity and emotions in the family. People who are well-differentiated think and act on their own but still connect with their families.
This skill makes family systems therapy help people become more aware and strong against family issues. It's about understanding how families work together and changing for the better.
Using these main ideas, therapists help families grow in understanding and change for the long term. They see how family members depend on each other and the patterns that affect them. This approach offers a complete and changing way forward.
Family systems therapy Techniques and Exercises
Family systems therapy uses many techniques and exercises to help families understand and improve their relationships. These methods involve everyone in the family. They aim to change negative behaviors and ways of talking into positive ones.
One key technique is the genogram, a chart that shows a family's history and relationships. It helps families see patterns and where they come from. This can help them understand how these patterns affect their interactions now.
Family sculpting is another exercise where family members arrange themselves to show their roles and connections. This can reveal a lot about how they see themselves and each other.
Reframing lets families see their problems in a new, more positive way. Circular questioning helps them understand each other's views and experiences better. Joining means the therapist works with the family to build trust and openness.
Boundary making, detriangulation, and enactments are also key in family systems therapy. These help families set clear boundaries, deal with complex relationships, and practice scenarios to improve talking and solving conflicts.
These techniques and exercises help families see patterns, express their feelings, talk better, and build stronger, more supportive relationships.

Family systems therapy is not the same for every family. The right techniques and exercises depend on the family's unique needs and dynamics. Working with a skilled family therapist is important. They can guide you and help you see the benefits of family systems therapy.
Benefits of Family Systems Therapy
Family systems therapy helps families build stronger bonds and solve conflicts better. It creates a supportive space for everyone to grow and feel good. This type of therapy makes talking openly easier, helping family members understand each other better.
It also teaches skills for solving conflicts. This leads to more empathy and deeper connections within the family. Feeling safe and supported, families grow together, facing life's ups and downs as a team.
Family systems therapy is great for improving how families talk to each other. It helps solve problems and make the family atmosphere more peaceful. This makes everyone feel closer and more emotionally secure.
This therapy does more than help individuals; it strengthens the whole family. It helps families deal with challenges better and creates a caring place for everyone. By using this approach, families can reach their full potential and support each other in thriving.
When to Use Family Systems Therapy
Family Systems Therapy is great for big life changes or crises in a family. This includes things like a divorce, the loss of a loved one, or big shifts that upset the family balance. It's also useful when fights keep happening and talking things out is hard.
This therapy is super helpful when a family member, like a kid or teen, is struggling with behavior or mental health issues. It looks at how the family's dynamics affect the person's health. Then, it works to make the family environment healthier.
If you or your family are going through big changes, crises, or ongoing fights, or if someone is dealing with mental health problems, consider Family Systems Therapy.
This therapy looks at the whole family. It helps people and families deal with tough times, get better at talking, and build a stronger, more supportive family bond.
Research on Effectiveness
Studies show that family systems therapy is very effective. It helps with a wide range of issues. Families often see lasting positive changes in how they interact with each other.
This therapy is great for many problems. It helps with addiction, anger, anxiety, and more. Families can feel better and communicate better after therapy.
It also helps with depression, eating disorders, and parenting issues. People feel less anxious and depressed. They also get better at solving problems and understanding each other.
Conditions Addressed
Family systems therapy is good for many mental health issues. It's useful for fixing communication and helping with substance abuse. It's a key tool for families facing tough times.
- Addiction and substance abuse
- Anger management problems
- Anxiety
- Bipolar disorder
- Depression
- Dysfunctional relationships
- Eating disorders
- Infidelity and divorce
- Parenting issues

This therapy looks at the whole family to help with different issues. It shows how important family support is for mental health.
Getting Started with Family Systems Therapy
Starting your family's healing journey with family systems therapy means finding the right therapist. You can make this easier with tools like Grow Therapy's search feature. This tool helps you find therapists by looking at their qualifications, certifications, insurance, and availability. It makes sure you find someone who fits your family's needs.
But it's not just about finding a therapist. It's also important to feel good about working with them. Grow Therapy's provider finder helps you find therapists who are a good match for your family. This makes starting your therapy journey smoother and more rewarding.
Success in family systems therapy comes from finding a therapist who fits your family's style and needs. By doing your homework and connecting with the right therapist, you can start a journey that strengthens your family. It also helps you face life's challenges better and with more understanding.
How Family Systems Therapy Works
Family systems therapy is a team effort aimed at making family relationships healthier and improving how you talk to each other. In your first family systems therapy sessions, the therapist will learn about your family's interactions, goals, and past. They use this info to create a plan just for your family's needs.
For about 12 sessions, the therapist leads open talks in your family. Everyone gets to share their thoughts and feelings. This creates a safe space for family members to understand and support each other better.
The therapist uses tools like genograms, family sculpting, reframing, and enactments to understand your family's habits and interactions. These tools help the therapist help your family change for the better and move towards a more positive family systems therapy process.
By tackling deep-seated issues and enhancing communication, family systems therapy can help your family face challenges and build stronger bonds. The therapist helps your family change, leading to more harmony and well-being.
Considerations and Challenges
Family systems therapy can be tough because it needs everyone in the family to work together. One big challenge is when family members don't want to go to therapy. They might be scared of change, want things to stay the same, or don't trust the therapist.
Therapists in family systems therapy must stay neutral. This helps them keep things fair and open. But, family members might see this as not supporting them or even okaying bad behavior. This can be hard when families want clear advice or help from the therapist.
Therapists also have to deal with the complex ways families interact and the power differences between members. They need to make sure everyone gets a chance to speak and be heard. It's tricky to balance the needs and views of each person while helping the family work better together.
To overcome these hurdles, therapists use different methods, such as:
- Encouraging open and honest talk among family members
- Helping family members see and understand each other's sides
- Getting family members to own up to their actions
- Creating ways to deal with resistance and build trust
With skill and care, family systems therapists can help families get past these issues and make lasting changes.
Conclusion
Family systems therapy offers a unique way to tackle family challenges. It sees your family as a connected system. This means every action and relationship affects everyone else.
This approach helps you understand and improve your family's dynamics. It leads to better communication and conflict resolution. It also builds deeper emotional support and strengthens family ties.
Family systems therapy can change lives. It's not just for dealing with crises. It's for making your family's life better overall. The methods and ideas of this therapy can lead to lasting changes for everyone.
This therapy shows how to handle family life's complexities. It empowers you to make your family more supportive and happy. By using family systems therapy, you can grow personally and make your family stronger. You'll create a place where everyone can thrive.
FAQ
What is family systems therapy?
Family systems therapy looks at how each family member affects the others. It sees the family as a system where everyone's actions connect. This approach helps fix family problems by focusing on these connections.
What are the core principles of family systems therapy?
This therapy is built on two main ideas. First, it sees relationships as triangles, not just between two people. Second, it teaches people to balance their own needs with the family's needs.
What techniques and exercises are used in family systems therapy?
Therapists use many tools like genograms and family sculpting. They also use reframing and circular questioning. These help families understand and improve their interactions.
What are the benefits of family systems therapy?
This therapy helps families talk better and solve conflicts. It also strengthens family ties and helps them face challenges together.
When is family systems therapy most effective?
It works best during big changes or when there are ongoing fights. It's also good when one family member has mental health issues. It looks at how family dynamics affect these issues.
What does the research say about the effectiveness of family systems therapy?
Studies show it helps with many issues like addiction and depression. It also helps with eating disorders and parenting problems.
How can I find the right family systems therapist for my family?
Use tools like Grow Therapy's search to find a therapist. Look for qualifications, insurance, and how well they fit with your family.
What can I expect during a family systems therapy session?
In the first session, the therapist will learn about your family and goals. They will guide discussions and use techniques to help everyone share and understand each other better.
What are some of the challenges in family systems therapy?
Some challenges include family members not wanting to change. Therapists must stay neutral but avoid seeming to take sides. It's hard to deal with the complex family dynamics.
Source Links
- Family Systems Therapy and Why It Is Helpful
- What Is Family Systems Therapy?
- A Comprehensive Guide to Family Systems Therapy - Grow Therapy
Postpartum Depression Bipolar Disorder: What’s the Connection? | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Being a new mom is both joyful and tough. The birth of a child is a big change. It can also lead to mental health issues like postpartum depression and bipolar disorder. It's key to understand these connections to help women during this time.
Dr. Chandril Chugh, an expert in maternal mental health, talks about the link between postpartum depression and bipolar disorder. He covers symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. This will help you understand this important part of postpartum health better.
If you're a new mom or supporting someone, this guide is for you. It will help you spot signs, find help, and cope. We'll explore the complex world of postpartum mental health together. And make sure you get the care and support you need.
Understanding Postpartum Depression and Bipolar Disorder
Becoming a new parent is exciting but also tough. Some women face postpartum depression or bipolar disorder. Knowing the signs and risks is key.
Symptoms and Risk Factors of Postpartum Depression
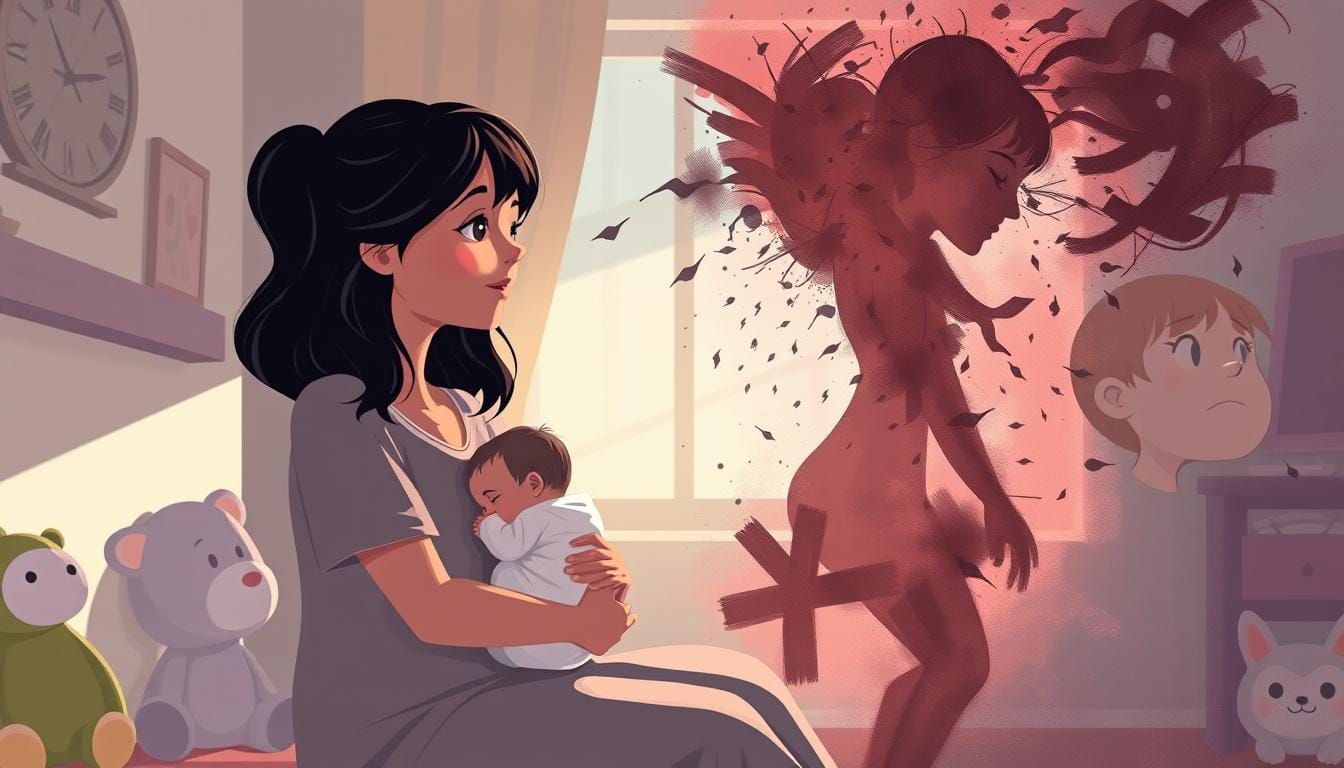
Postpartum depression hits up to 1 in 7 women after having a baby. It brings sadness, feeling not good enough, and trouble bonding with the baby. It can even lead to thoughts of harming oneself or the baby.
Things that might make a woman more likely to get postpartum depression include past depression, big hormonal changes, not enough support, and stressful times.
Bipolar Disorder: Definition and Types
Bipolar disorder makes people feel very up and down. They might feel super happy and full of energy, then very sad and tired. There are different kinds of bipolar disorder, like Bipolar I, Bipolar II, and cyclothymic disorder.
Up to 20% of women who seem depressed after having a baby might actually have bipolar disorder. Doctors use tools like the Mood Disorders Questionnaire (MDQ) to find out.

It's important to understand both postpartum depression and bipolar disorder. This helps keep new moms safe and healthy. Knowing the signs and risks helps doctors help women during this important time.
The Connection Between Postpartum Depression and Bipolar Disorder
There is a strong link between postpartum depression and bipolar. Studies show women with bipolar are more likely to get postpartum depression. Sometimes, postpartum depression can be the first sign of bipolar disorder.
The hormonal changes and stress of childbirth can trigger mood swings in women with bipolar. This can lead to manic or depressive episodes.
The comorbidity of postpartum depression and bipolar disorder is a big worry for doctors. Bipolar disorder affects one to three percent of women. Women with bipolar are more likely to have symptoms after childbirth.
Some women may first show bipolar symptoms in the first year after giving birth. This is especially true if there's a family history of bipolar.
It's important for mothers and their partners to watch for early signs of bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder causes big mood swings. This can include feeling very low or very high.
Severe bipolar can lead to thinking too highly of oneself, hallucinations, and paranoia. Getting help early for postpartum bipolar is key. It's important for the mother's safety and effective treatment.

Understanding the link between postpartum depression and bipolar disorder is key. It helps in diagnosing and managing these conditions together. By recognizing this connection and getting support early, women can better handle the postpartum period. They can also focus on their mental health.
Postpartum Psychosis: A Severe Manifestation
Postpartum psychosis is a rare but serious mental health issue. It can happen in the weeks after a baby is born. Unlike postpartum depression, which is common, postpartum psychosis is a medical emergency. It needs immediate help.
Recognizing the Signs of Postpartum Psychosis
It's important to spot the early signs of postpartum psychosis. This helps get medical help fast. Look out for:
- Sudden and severe mood swings
- Hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized thinking
- Confusion, disorientation, and trouble concentrating
- Paranoia or suspiciousness
- Inability to sleep or too much sleepiness
- Thoughts of harming oneself or the baby
If you or someone you know has these postpartum psychosis symptoms, get help right away. This condition is dangerous for both the mother and the baby. Quick action is key to keeping everyone safe.

Research has found what might cause postpartum psychosis. Stress, immune problems, and family history are factors. Also, big life events, like losing a loved one, can raise the risk.
By spotting the signs of postpartum psychosis and getting medical help fast, mothers can get the care they need. This helps keep them and their babies safe and healthy.
Navigating the Decision to Have Another Child
Women who have had postpartum depression or bipolar disorder face a tough choice. They worry about the chance of it happening again. They also think about how it will affect their family and if they can handle it during another pregnancy and after.
Considerations and Challenges
Thinking about having another child is a big deal. Women must think about the good and bad sides. Studies show that bipolar disorder can come back during the postpartum period in about 45.7% of cases.
Stress, not enough support, and not following medication can make things worse. It's key for these women to work with their doctors. They need a plan to manage their condition and lower risks during pregnancy and after.
Deciding to have another child is a big choice. Women need to think about their mental health, support, and how it will affect their family. It's not something to rush into.
Medication Management During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Women with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder need to manage their meds carefully when pregnant or breastfeeding. Doctors must weigh the risks and benefits of each medication. They consider the mother's mental health, the stage of pregnancy or breastfeeding, and how it might affect the baby.
Weighing the Risks and Benefits
Finding the right balance with medication is key during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Important things to think about include:
- The mother's mental health and how it affects pregnancy or breastfeeding
- The risks of the medication to the baby
- Other options like therapy or lifestyle changes
- The benefits of keeping or changing the medication for the mother's health
It's vital for the patient and their healthcare team to talk openly. This helps find the best balance for the mother and the child.

The National Comorbidity Survey found that bipolar spectrum disorder is common. Studies also talk about postpartum depression. Deciding to keep or change medication during pregnancy and breastfeeding is complex. It requires a careful look at the risks and benefits for both the mother and the baby.
Postpartum depression bipolar disorder: Seeking Professional Help
Getting help is key if you're dealing with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder. These issues can really affect your mental health and how you care for your baby. By asking for help, you can get the right care and treatment to feel better.
Talking to a mental health expert, like a psychiatrist or a perinatal mental health therapist, is a big step. They can help you understand what's going on and find ways to cope. They can also talk about therapy and medicine options.
Support groups and community resources are also great. They let you connect with others who know what you're going through. This can give you emotional support and practical advice.
Remember, you're not alone. By seeking help, you're taking care of your mental health. This is a big step towards a better postpartum experience. Don't be afraid to ask for help.
If you or someone you know is struggling, there are resources to help:
- Postpartum Support International (PSI) - Offers support and resources for women with postpartum depression and other mental health issues.
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline - Provides 24/7 free and confidential support for those in distress, including postpartum depression.
- Local mental health providers - Find licensed professionals in your area who specialize in perinatal mental health through your healthcare or insurance provider.
Don't wait to get the help you need. Your mental health and your baby's well-being are very important. With the right support, you can get through this tough time and come out stronger.
Coping Strategies and Support Systems
Dealing with postpartum depression and bipolar disorder is tough. But, there are ways to cope and get support. Self-care and mindfulness are key to managing symptoms and feeling better.
Self-Care and Mindfulness Techniques
Creating a self-care routine is vital for new moms. This might include:
- Getting enough rest and sleep
- Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet
- Engaging in regular exercise, such as gentle yoga or walking
- Practicing stress-management techniques like meditation or deep breathing
Mindfulness helps manage emotions. It keeps you calm and present. This is helpful for new moms.
Having a strong support network is important. Talk to family, friends, and local groups for help. Support groups offer connection and understanding.
Remember, managing these conditions is a journey. Seeking help is a sign of strength. With self-care, mindfulness, and support, new moms can thrive.
Advocacy and Awareness
It's key to raise awareness and push for better support for women with postpartum depression and bipolar disorder. We need better mental health services, more research funding, and policies that help mothers. Sharing our stories and educating others can help break the stigma and ensure all mothers get the care they need.
Postpartum bipolar is rare but can hit any mother. The risk of severe mental illness is higher right after childbirth than at any other time. Women with a family history of bipolar are at higher risk, and it can first appear after childbirth.
Mental health checks during pregnancy are very helpful. Postpartum Support International offers online groups in English and Spanish for mothers with mood disorders. But, we need more education for doctors and caregivers about postpartum bipolar.
About one in seven women gets perinatal depression. Up to 85% of new moms get the "baby blues," which is short and usually doesn't need medical help. Around 10-15% of white women get postpartum depression, with even higher rates for other racial groups like Latina women.
Nearly two-thirds of women with perinatal depression also have anxiety. About 10% of dads get depression in the first year after their child's birth. Latina women are more likely to have faced traumatic events, which increase depression risk. More social support can help protect against depression in diverse groups.
By spreading awareness and pushing for more resources, we can help all new moms thrive. This is crucial for their well-being and that of their families.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between postpartum depression and bipolar disorder is key. It shows how important it is to care for a new mom's mental health. These conditions can really affect a woman's life and her family.
By learning more about these issues, we can help mothers feel less alone. We can work to make sure every new mom gets the help she needs. This way, they can do well after having a baby.
Don't forget, you're not alone. Talk to doctors, join support groups, and share with your family. With the right help, you can beat these challenges and enjoy your new life.
FAQ
What are the symptoms and risk factors of postpartum depression?
Postpartum depression can make you feel sad and not good enough. It's hard to bond with your baby. You might even think about harming yourself or your baby. Risk factors include depression history, hormonal changes, lack of support, and stressful life events.
What is bipolar disorder, and what are the different types?
Bipolar disorder makes you feel very up and down. You might feel too happy and full of energy, then very sad and tired. There are three main types: Bipolar I, Bipolar II, and cyclothymic disorder. Each has its own symptoms and patterns.
What is the connection between postpartum depression and bipolar disorder?
Women with bipolar disorder are more likely to get postpartum depression. Sometimes, postpartum depression is the first sign of bipolar disorder. The changes in hormones and stress from having a baby can trigger mood swings in women with bipolar disorder.
What is postpartum psychosis, and what are the signs to look for?
Postpartum psychosis is a serious condition. It makes you see things that aren't there and think in a way that's not normal. It's dangerous for you and your baby. Look for sudden mood changes, confusion, and paranoia. Get help right away.
What factors should be considered when deciding to have another child after experiencing postpartum depression or bipolar disorder?
Deciding to have another child is hard for women with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder. You might worry about getting depressed again, how it affects your family, and managing your condition during pregnancy and after. Talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits.
How is medication management handled for women with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder who are considering pregnancy or breastfeeding?
Managing medication is key for women with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder who might get pregnant or are breastfeeding. Your doctor will look at the risks and benefits of different medicines. They'll consider your mental health, the stage of pregnancy or breastfeeding, and how it might affect your baby. It's important to talk openly with your healthcare team.
Where can women with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder seek professional help and support?
Women with postpartum depression or bipolar disorder need professional help. See a mental health specialist like a psychiatrist or perinatal mental health therapist. They can help you get a diagnosis and treatment plan. Support groups and community resources can also offer help and support.
What coping strategies and support systems can help women manage postpartum depression and bipolar disorder?
Besides professional help, there are ways to cope with postpartum depression and bipolar disorder. Take care of yourself by resting, eating well, and exercising. Mindfulness, like meditation, can help with stress and mood. Having a strong support network is also important for emotional and practical help.
How can we increase awareness and advocate for better support and resources for women with postpartum depression and bipolar disorder?
We need to raise awareness and push for better support and resources for women with postpartum depression and bipolar disorder. We should fight for more mental health services, research funding, and policies that support maternal mental health. Sharing your story and educating others can help reduce stigma and ensure women get the care they need.
Source Links
- Pregnant and Postpartum Women with Bipolar Disorder: Taking the Care to Where They Are
- Postpartum Depression: Unipolar or Bipolar? - MGH Center for Women's Mental Health
- Postpartum Bipolar Disorder: Symptoms, Treatment, Outlook
- Bipolar Disorder in the Postnatal Period
- Baby Blues and Postpartum Depression: Mood Disorders and Pregnancy
Postpartum Depression Relaxation Techniques: Finding Relief | Dr. Chandril Chugh
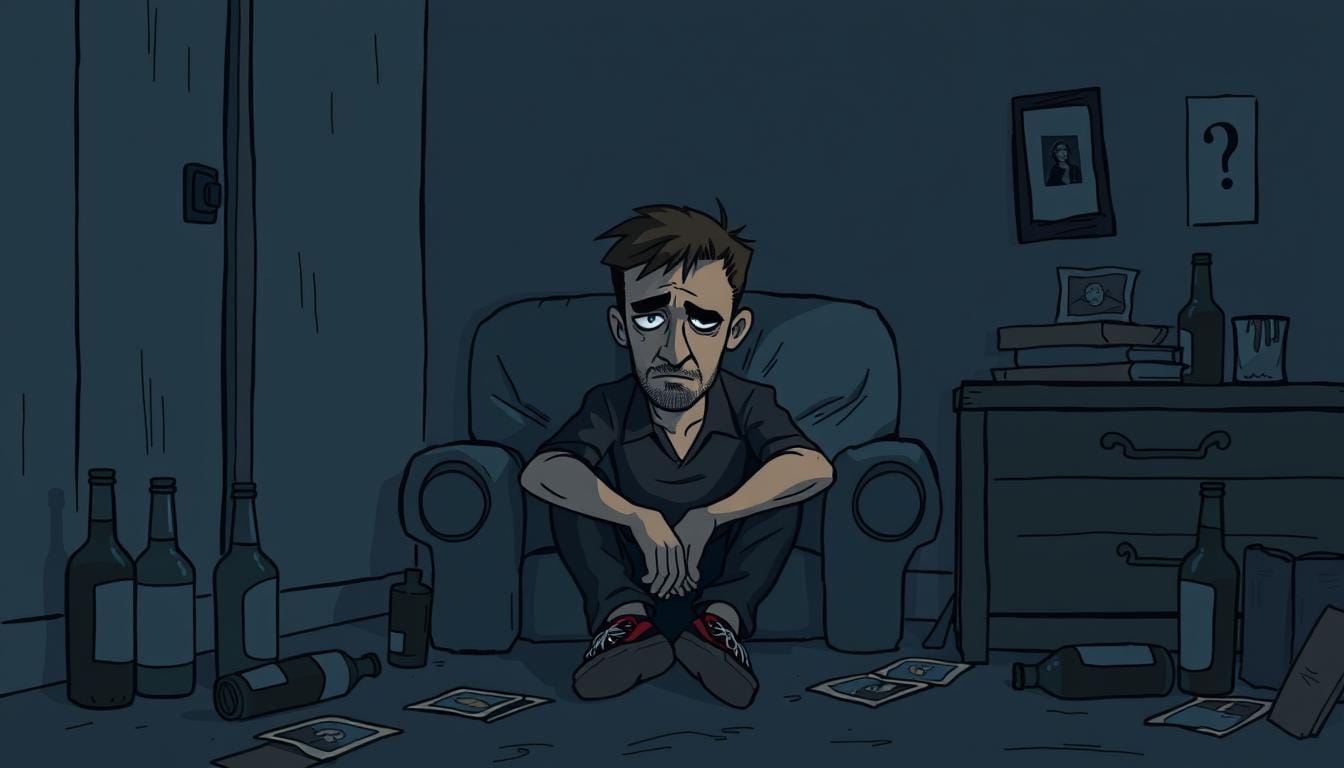
Postpartum depression affects up to 15% of new moms. It brings sadness, anxiety, and tiredness. These feelings make it hard for a mom to take care of herself and her baby.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is an expert in women's mental health. He shares relaxation techniques to help moms feel better. These methods can help moms find joy again after having a baby.
Understanding Postpartum Depression
Postpartum depression is a serious mental health issue that can happen after having a baby. It's key for new moms to know the signs and risks of this condition.
Symptoms and Signs
Signs of postpartum depression include feeling sad all the time, being anxious or irritable, and changes in sleep and eating. It can also make it hard to bond with the baby. Some people might even think about harming themselves.
The "baby blues" are common and usually go away in a few weeks. But postpartum depression is more serious and lasts longer. It can really affect a new mom's daily life.
Risk Factors
Some things can make a mom more likely to get postpartum depression. These include having depression before, big hormonal changes, not having enough support, and feeling very stressed. Women who had it before are more likely to get it again.
Also, having trouble with breastfeeding can lead to postpartum depression. It's crucial for new moms to get help if they're feeling this way. Getting help early can really help them get better.

The Importance of Self-Care for New Mothers
Being a new mom can be overwhelming. It's key to focus on your own care. This way, you can handle the tough parts of motherhood better.
Research shows many women don't take care of themselves after having a baby. Less than 20% of women get back to normal activities at six weeks. This shows how vital self-care is every day.
Self-care is simple. It means getting enough sleep, eating well, and relaxing. Studies say it can lower stress by 25% and boost mental health by 40%.
Your health is as important as your baby's. Self-care helps you manage motherhood and keep your mental health strong. Ask for help and seek professional help if needed.

Motherhood is tough, but with self-care, you can do great. Cherish small moments of self-care. Remember, caring for yourself is essential for your and your family's well-being.
Relaxation Techniques for Postpartum Depression
Being a new mom can be tough, especially with postpartum depression. But, using relaxation techniques can really help. Deep breathing and mindfulness meditation are great options.
Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing can calm your mind and body. Find a quiet spot and get comfy. Take slow, deep breaths in through your nose and out through your mouth.
Feel your belly rise as you breathe in. Let it fall as you breathe out. Do this for a few minutes to relax.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness meditation is also very helpful. It helps you stay in the moment and feel calm. Spend 5-10 minutes each day sitting quietly.
Focus on your breath and let go of worries. It's a simple way to find peace.
But remember, these techniques aren't a replacement for professional help. If you're really struggling, talk to a mental health expert. They can help you find your way back to wellness.

Postpartum Depression Relaxation Techniques
Being a new mom can be tough, especially with postpartum depression. But, there are ways to feel better. Deep breathing and mindfulness are good starts. You can also try other relaxation methods to help your mind and body.
Progressive muscle relaxation is a great technique. It involves tensing and relaxing your muscles. This can help you feel less tense and more calm. Guided imagery, where you imagine peaceful scenes, is also helpful for stress and anxiety.
- Gentle yoga or stretching can help you relax. Try different poses that feel good for you.
- Music therapy is also good for your mood. Soothing music can make you feel better, sleep better, and be less anxious.
- Writing about your feelings can be very helpful. It lets you process your emotions and find relief.
Try different relaxation techniques to see what works for you. Adding these to your daily routine can help you feel better. It can make managing stress and improving your mood easier during the postpartum time.

The Role of Support Systems
Dealing with postpartum depression can feel very lonely. But, it's key to remember you're not alone. Reaching out for support is a big step in getting better.
Looking for professional help is important. A therapist, counselor, or your doctor can offer the right treatment. They can teach you ways to handle your feelings.
Seeking Professional Help
A mental health expert can guide you through tough times. They might suggest therapy like CBT or interpersonal therapy. These methods can really help.
They can also check if you need medicine. This can help make your symptoms better.
Family and Friends' Support
Having a strong support network is crucial. Family and friends can help with everyday tasks. This can reduce stress.
They can also be there to listen and offer comfort. Don't hesitate to ask for help when you need it.
Remember, you don't have to face postpartum depression by yourself. Professional help and your support system are key. With the right support, you can beat this and find happiness again.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Mental Health
Making lifestyle changes can really help with postpartum depression. Eating a healthy diet and staying active are key. Also, getting enough rest and sleep is very important.
Healthy Diet and Exercise
Eating well is very important for new moms. Foods like fish are good for your mood. Drinking lots of water is also good.
Walking with your baby for 20-30 minutes a day can make you feel better. It helps with postpartum depression.
Prioritizing Rest and Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial. Not sleeping well can make you feel worse. So, make sleep a priority.
Try to sleep at the same time every night. Make your bedroom a cozy place for sleep. This helps your body and mind rest well.
Changing your lifestyle takes time and work. But, it's worth it for your mental health. By eating well, staying active, and sleeping well, you're on the right path.
Overcoming Stigma and Seeking Help
Postpartum depression affects up to 20% of new moms worldwide. But, many women hide their struggles because of shame. It's time to talk openly and support new moms.
Postpartum depression is not a sign of weakness. It's a treatable condition that needs kindness and support. By talking about mental health, we help women feel brave enough to ask for help. Seeking help for postpartum depression shows strength, not weakness.
Ending the postpartum depression stigma starts with learning and sharing. Postpartum mood disorders can hit anyone, no matter their background. When we talk openly, more women will feel safe to seek help and share their stories.
You're not alone in this fight. Talk to your doctor, join a support group, or share with loved ones. With the right support and resources, you can face postpartum depression and find your way back to happiness. Let's make talking about postpartum mental health common, not rare.
Postpartum Depression and Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is key for a new mom's mental health. Studies show it lowers the risk of postpartum depression. But, it can also bring its own challenges that might make mental health issues worse. It's vital for new moms to find help and advice to manage these issues.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
There's a strong link between breastfeeding and postnatal depression. A study in Psychological Medicine found breastfeeding can help lower postpartum depression. The Journal of Psychosomatic Research also looked into how breastfeeding helps with mental health after birth.
Managing Breastfeeding Challenges
Breastfeeding has its benefits, but it can also be tough. Research shows it might be harder for moms with depression to breastfeed. To face these challenges, moms should get help from doctors, support groups, and other moms who've been through it.
By understanding both the good and the hard parts of breastfeeding, moms can get the help they need. With the right support, breastfeeding can be a big help for mental health after having a baby.
Conclusion
Postpartum depression is treatable and affects many new moms. With the right support and strategies, you can find relief and joy again. Try relaxation techniques like deep breathing and mindfulness. Also, prioritize self-care and seek help from professionals and loved ones.
You're not alone in this journey. There are many resources and strategies to help with postpartum depression and anxiety. By focusing on your mental health, you can overcome challenges and thrive as a new mom. With patience, self-compassion, and a willingness to ask for help, you can look forward to a brighter future.
Your mental health after having a baby is just as important as your physical health. Use the support systems around you and try relaxation techniques that work for you. Research shows that relaxation methods can help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression in pregnant women. With the right tools and support, you can make it through this time with strength and resilience.
FAQ
What is postpartum depression?
Postpartum depression is a serious mental health issue. It affects up to 15% of new moms. It makes them feel sad, anxious, and tired, making it hard to care for themselves and their baby.
What are the symptoms of postpartum depression?
Symptoms include feeling sad and anxious all the time. You might also feel irritable, have trouble sleeping or eating, and not bond with your baby. Some people even think about harming themselves.
What are the risk factors for postpartum depression?
If you've had depression before, you're at higher risk. Hormonal changes, lack of support, and stress also play a part.
Why is self-care important for new mothers?
Taking care of a new baby is tough. New moms need to take care of themselves too. This means getting enough sleep, eating well, and doing things that relax them.
What are some effective relaxation techniques for postpartum depression?
Good techniques include deep breathing and meditation. You can also try progressive muscle relaxation, guided imagery, and gentle yoga.
How can support systems help with postpartum depression?
Talking to a therapist or counselor can help. They offer proven ways to cope. Having a strong support network of family and friends also helps a lot.
How can lifestyle changes help manage postpartum depression?
Eating well, staying active, and getting enough sleep are key. These habits can improve your mood and help with depression.
How can breastfeeding affect postpartum depression?
Breastfeeding might lower the risk of depression. But, it can also add stress. This might make mental health issues worse.
Source Links
- Exploring Mental Health In Women: Key Issues And Insights
- 5 Effective Strategies For Sleep Maintenance Insomnia Relief
- There are many different breathing exercises
- What is Post Partum Depression
Young Adult Mental Health: How to Identify & Treat Issues | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Young adulthood is a tough time for mental health. But, with the right help, you can get through it. Around the world, one in seven teens, aged 10 to 19, has a mental disorder. This makes up 13% of all diseases in this age group.
Depression, anxiety, and behavioral issues are big problems for teens. They are the top causes of illness and disability. Suicide is the fourth leading cause of death for those aged 15 to 29.
It's important to protect teens from hard times. We should teach them about feelings and make sure they can get mental health care. We need to focus on the mental health issues young adults face and find ways to help them stay well.
Introduction to Mental Health Challenges in Young Adulthood
Young adulthood is from ages 16 to 24. It's a time of big changes in physical, emotional, and social lives. This stage is both exciting and stressful, making young adults more likely to face mental health issues.
Unique Developmental Period of Transition
Going to college, starting a career, and making close friends are big steps. These experiences are thrilling but also bring a lot of uncertainty and pressure. It's a key time when mental health problems often start or get worse.
High Prevalence of Mental Health Conditions
About one in five young adults have symptoms of depression or anxiety. Mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and eating disorders are common. The peak age for mental illness is during adolescence and early adulthood.
Things like social environment and tough life experiences also play a big role. It's important to understand and tackle these issues to help young adults stay well.
Mental Health Determinants and Risk Factors
Your mental health is shaped by many things. The place you live and the people around you matter a lot. Having a supportive family and friends helps a lot. But, facing economic problems or violence can harm your mental health.
Hard times, like abuse or losing someone close, can really affect you. These events can cause anxiety, depression, and PTSD. Some groups, like those in crisis areas, face extra challenges in staying mentally healthy.
Socio-Environmental Influences
The community and environment you live in matter a lot. Things like money, resources, and friends can help or hurt your mental health. For example, bad housing can hurt your mental health, and not having enough food can make you feel sad.
Adverse Life Experiences and Trauma
Hard life events can really hurt your mental health. Childhood abuse or violence can lead to mental health problems later. Losing someone or going through a disaster can also cause anxiety, depression, and PTSD.
It's important to know how life events affect mental health. By understanding these factors, we can help young adults stay healthy. We can support them by addressing the tough times they face.

Common Mental Health Issues in Young Adults
Young adults often face many mental health challenges as they move into adulthood. Issues like anxiety, depression, and eating disorders can affect their school, social, and emotional lives.
Anxiety and depression are big problems for this age group. About 3.6% of 10-14-year-olds and 4.6% of 15-19-year-olds have anxiety. Meanwhile, 1.1% of 10-14-year-olds and 2.8% of 15-19-year-olds deal with depression. These issues make it hard for them to go to school, keep friends, and do everyday things.
Young adults also have a higher chance of getting behavioral and eating disorders. This includes ADHD, conduct disorders, and eating disorders. These problems add to the challenges they face during this important time.
We need to understand how common mental health problems are in young adults. We must make sure they get the help and support they need. Early help and a strong focus on mental health can help them get through this tough time. It can also help them build strength for the future.
Anxiety and Depressive Disorders
Anxiety and depression are big problems for young adults today. Studies show that 3.6% of kids aged 10-14 and 4.6% of teens aged 15-19 have anxiety. This can make it hard for them to go to school, make friends, and do everyday things.
Depression is also a big worry, affecting about 1.1% of kids aged 10-14 and 2.8% of teens aged 15-19. It can cause them to pull away from friends, struggle in school, and even think about harming themselves. The number of young adults with anxiety and depression is growing fast. We need to help them early to keep them healthy and successful.

Many things can cause mental health problems in young adults. These include bad life experiences, the world around them, and the challenges of growing up. We must find and help them early, and make sure they can get the help they need.
Behavioral and Eating Disorders
Young adulthood is a time of big mental health challenges. Issues like ADHD and conduct disorders can hurt school work and friendships. They can even lead to legal problems.
Eating disorders, like anorexia and bulimia, are very serious. They can harm both body and mind.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
ADHD makes it hard to focus, be still, and act impulsively. It affects about 3.1% of kids aged 10-14 and 2.4% of teens aged 15-19. It can make it tough to do well in school or work.
It also raises the chance of taking risks.
Conduct Disorders and Challenging Behaviors
Conduct disorders involve acting out and being aggressive. They are more common in kids aged 10-14, affecting 3.6% of them. By 15-19, this number drops to 2.4%.
These behaviors can cause legal issues and problems with friends.
Eating disorders, like anorexia and bulimia, are very serious. Anorexia has a very high death rate. It's the second leading cause of death for those with it.
Bulimia involves binge eating and purging. Binge-eating disorder, the most common in the U.S., can cause health problems like obesity and diabetes.
It's important to tackle these disorders early. Getting help and using proven treatments can help young adults overcome these challenges.
Psychosis and Emerging Mental Illnesses
Young adults face many mental health challenges as they grow up. Psychosis, with its hallucinations and disorganized thinking, is one of them. It often starts in late teens or early twenties, a time of big changes.
It's important to spot and treat mental illnesses like psychosis early. Stigma can make things worse, leading to isolation. By teaching young adults and their families about signs of psychosis, we can help them get the right treatment.
Recognizing and Addressing Emerging Mental Illnesses
We need to create places where talking about mental health is easy. Young adults and their families should feel free to ask for help. Healthcare providers should give them the care they need.
Getting help from a mental health expert, like Dr. Chandril Chugh, is key. They can help create a treatment plan that fits each person's needs.
Suicide, Self-Harm, and Risk-Taking Behaviors
Suicide is a big worry for young adults. They have the fourth highest suicide rate in the world. Things like drinking too much, being abused as kids, and having easy access to dangerous things can lead to this.
Young adults also take risks with drugs and unsafe sex. This can hurt their health. We need a strong plan to tackle suicide, self-harm, and risky behaviors in young adults. We must look at the main causes, reduce stigma, and make help easier to find.
Studies show that about 23.2% of non-clinical teens have non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI). Things like childhood trauma, mental health issues, and too much internet use can raise the risk of NSSI. Suicidal thoughts and plans are also a big worry, with some studies showing rates as high as 14.4% and 12.9%.
It's important to know that NSSI and mental health issues can lead to more serious problems like suicide attempts. Sadly, many young people who harm themselves don't get help. During the COVID-19 lockdown, only 13% of teens in England got help after self-harming.
Things like parents splitting up, being bullied, and having autism can also make young people more likely to think about suicide. We need to act early and make sure they have access to mental health help.

We can help young adults get through tough times by understanding the causes, reducing stigma, and making help easier to find. We should talk openly, build resilience, and make sure they get the right treatments. This can really help support the mental health and well-being of our youth.
Mental Health Promotion and Early Intervention
We need to help young adults with their mental health. This means building their strength, teaching them how to cope, and making sure they can get help. By doing this, we help them deal with the big challenges they face.
Building Resilience and Coping Skills
Programs that build resilience are very important. They teach young adults how to handle stress and take care of themselves. These skills help them build a strong mental base.
By teaching these skills, we help young adults become more resilient. This way, they can face life's challenges head-on.
Improving Access to Mental Health Services
It's important for young adults to have easy access to mental health services. We need to make sure these services are available in schools, hospitals, and community groups. This way, they can get help when they need it.
By making services more accessible, we encourage young people to seek help early. This helps prevent their mental health issues from getting worse. It also helps them stay well overall.
Mental health promotion and early intervention go hand-in-hand. They help young adults during a very important time in their lives. By teaching them resilience and making sure they can get help, we set them up for success.
Addressing Unique Needs and Challenges
Young adults face big mental health challenges as they start their journey to independence. It's key to understand their special needs to help them. They deal with stress from school, work, and relationships. They also face past traumas or hard life experiences.
It's important to make mental health care part of their overall well-being. This means helping them stick to their medication and seeing how their physical health affects their mind. It also means working with families and caregivers who know them best.
The COVID-19 pandemic has made the mental health crisis among youth even worse. Experts say it's a national emergency. Governments have spent trillions to fight the pandemic. But, we need to do more to help with poverty and lack of healthcare and education.
- Prioritize data collection and real-time infrastructure to rapidly identify and respond to young people's mental health needs
- Increase research on the impact of technology and social media on youth mental health
- Provide young adults with resources and support for building healthy relationships, managing stress, and seeking help when needed
By focusing on the unique challenges young adults face, we can help them thrive. We can build their resilience for a brighter future.

Young adult mental health
Young adulthood is a time of big changes. It's when many people start their careers, go to college, and grow up. But, it's also a time when mental health issues can start.
Many young adults deal with anxiety, depression, and other mental health problems. These issues come from many places, like family, school, and life experiences. It's important to understand these challenges to help young adults grow into healthy adults.
To help young adults, we need to act early and support them in many ways. We can teach them to be strong and help them find mental health services. This way, they can handle the ups and downs of growing up better.
Young adults face special challenges, like school stress and finding a job. They also deal with relationships and figuring out who they are. With the right help, they can stay mentally healthy and set a good path for their lives.
Helping young adults with their mental health is key for their future. By focusing on their mental health, we can help them succeed and build a better world for everyone.
- Mental health conditions typically begin during childhood, adolescence, or young adulthood.
- Suicidal thoughts are common among teens and young adults.
- Residential treatment may be considered for children facing mental health symptoms.
- Social media plays a role in mental health, especially for teenagers and young adults.
- Young adults may face mental health challenges while in college.
Conclusion
Young adult mental health is very important. This group faces special challenges and often struggles with mental health issues. We need to understand their needs and offer the right support.
By helping young adults, we can make sure they are strong and healthy. We can help them find the care they need. This way, they can smoothly move into adulthood.
We can help young adults by taking a wide-ranging approach. This includes making mental health services more available. It also means teaching them about mental health and using their peers to support each other.
Helping young adults with their mental health is key for their happiness. It also helps society as a whole. By focusing on their mental health, we can build better communities and unlock their potential.
FAQ
What are the unique mental health challenges faced by young adults?
Young adulthood is a time of big changes. These changes can make young people more likely to face mental health problems. Issues like anxiety, depression, and behavioral disorders are common.
What are the top mental health conditions affecting young adults?
Anxiety and depression are big problems for young adults. They affect about 3.6-4.6% and 1.1-2.8% of teens, respectively. ADHD and conduct disorders are also common.
How do socio-environmental factors and adverse experiences impact young adult mental health?
The place young adults live and the people they meet can affect their mental health. Economic problems, violence, and tough family situations can play a role. Traumatic events like abuse or loss can also hurt their well-being.
What are the warning signs of emerging mental illnesses in young adults?
Symptoms like hallucinations and disorganized thinking can signal mental illness. These often start in late teens and early twenties. It's important to spot these signs early and get help.
How can suicide and self-harm be addressed in young adults?
Suicide is a big worry for young adults, with them having the fourth highest rate in the world. Substance abuse, childhood trauma, and easy access to dangerous items are factors. We need a strong plan to help, reduce stigma, and find those at risk.
What strategies can promote mental health and provide early intervention for young adults?
Building resilience is key. Programs that teach coping skills and emotional intelligence help. We also need to make mental health services more accessible in schools and communities. Early help and a focus on young adults' needs are crucial.
Source Links
- Mental Health In Young Adults
- Best Neurologist In Patna, Author Dr Chandril Chugh
- Mental health in young adults and adolescents – supporting general physicians to provide holistic care
- Original research: Work functioning among young adults: the role of mental health problems from childhood to young adulthood
- The social determinants of mental health and disorder: evidence, prevention and recommendations
Therapy Treatment for Depression: Exploring Your Options | Dr. Chandril Chugh
If you're fighting depression, you're not alone. Millions worldwide face this mental health battle. It affects your life, relationships, and happiness. But, there are effective treatments to help you manage symptoms and take back your life.
We'll look at different therapy options, including music therapy, with Dr. Chandril Chugh's help. He's a top expert in mental health. We'll cover how therapy can help with appetite changes, hopelessness, and cognitive issues. This info will help you start your healing journey.
We'll explore music therapy's history, benefits, and how it works. It's a unique way to tackle depression's complex challenges. Knowing your therapy options empowers you to choose what's best for you.
What is Music Therapy?
Music therapy uses music to help people reach their goals and feel better. The American Music Therapy Association (AMTA) says it meets specific goals. Music therapists work with clients to make plans just for them.
It helps people express feelings, handle stress, and talk better. Music therapy is great for those with mental health issues like depression or anxiety.
Studies show it can lower anxiety in people with cancer and those in hospitals. It also helps those with depression more than just talking therapy alone.
How Does Music Therapy Work?
Music therapy includes listening, playing, singing, and writing songs. These activities help people feel and express emotions. Music therapists make plans that fit each person's needs.
- It can release hormones like dopamine and endorphins, making people feel better and less in pain.
- Listening to music can lower anxiety right away. It's a quick way to feel better.
- It helps with social skills, creativity, focus, and coordination. It also boosts self-awareness and family bonds, especially for kids.
Music therapy is a fun way to deal with emotions, stress, and improve mental health.

Music Therapy and Mental Health
Music therapy is a strong tool for mental health, especially for depression. It can lower anxiety and boost self-confidence. Making music helps people express feelings and connect with themselves.
The Benefits of Music Therapy for Mental Health
Music therapy can lower stress hormones and help relax. It also releases mood-boosting chemicals. This can improve emotional stability and mental health.
Music therapy helps with depression by reducing stress and improving mood. It lets people express emotions and relax. Different music styles can meet individual needs and preferences.
There are two music therapy types for depression. One involves creating music, the other listening to it. Both can help improve mental health, along with other treatments.

In summary, music therapy is a valuable addition to mental health care. It offers many benefits for those with depression and other mental health issues. Music helps with self-expression, stress relief, and emotional well-being.
How Does Music Therapy Work?
Music therapy is a powerful tool that works with the brain. It uses the limbic system, which handles emotions and social skills. This system releases happy chemicals like dopamine and endorphins. This is why music therapy helps with depression.
The science behind music therapy shows it affects many brain areas. These include rhythm, emotion, and pitch. It makes the brain's reward center active, improving mood and well-being. Music therapy can lessen depression and anxiety symptoms by offering a positive distraction and encouraging self-expression.
Music can also change how our body reacts. It can slow down heart rate, lower blood pressure, and reduce stress hormones. It helps manage the physical signs of mental health issues. Music therapy can be tailored to fit each person's musical tastes and needs.
Music therapy can be through singing, playing an instrument, or just listening. It uses the brain's sound processing ability. Mental health experts use music to help people with depression and anxiety. They aim to improve emotional control, self-expression, and overall well-being.
History of Music Therapy
Music therapy has ancient roots. In Ancient Greece, people believed music could heal the mind and body. But it wasn't until the 20th century that it became a real therapy.
The first talk of music therapy was in 1789. Doctors studied music's healing effects in the 1800s. In the 1940s, music therapy programs started in universities, thanks to E. Thayer Gaston.
After World War II, musicians visited hospitals to play for soldiers. Music helped these soldiers feel better, both mentally and physically. This showed how powerful music could be.
The field of music therapy has grown a lot since then. The American Music Therapy Association (AMTA) was formed in 1998. It brings together music therapists from the U.S. and over 30 countries.
The Certification Board for Music Therapists (CBMT) has over 8,000 certified music therapists. They hold the MT-BC credential. Music therapy is now recognized for treating mental health issues like depression.

Benefits of Music Therapy for Depression
Music therapy is a powerful tool for treating depression. It offers many benefits for those with this mental health issue. A study looked at 1,649 research papers and found that music therapy can reduce anxiety and help with depression.
It helps people relax and connect with their feelings. This can make the bond between the client and their therapist stronger. This bond is key to better treatment.
Other studies show music therapy can also improve how well people function. It can lower anxiety in those with depression. In a study with 23 people with hard-to-treat depression, researchers found brain activity changes in those who got better.
They also found that enjoying the music more made the therapy work better. This shows that knowing the music can make the therapy more effective.
Music therapy isn't just for adults. It also helps reduce depression and anxiety in cancer patients. This is a non-invasive way to help. As music therapy grows, researchers and clinicians are looking into how it can help with depression in different ways.

- Music therapy can effectively reduce anxiety and alleviate symptoms of depression in adults.
- Music therapy can improve overall functioning and lower anxiety levels in those dealing with depression.
- Music therapy has shown promise in reducing depression and anxiety in cancer patients as a non-invasive method.
- Continued research is needed to explore the clinical applications of music therapy in various contexts to enhance treatment outcomes for mental health conditions like depression.
Therapy Treatment for Depression
Research shows that mixing music therapy with standard care helps a lot. Studies say music therapy can make treatment better than just standard therapy. It makes managing depression symptoms easier and more effective.
Music and emotions are closely linked. Music therapy lets people express themselves and manage stress. It's a great way to help with mental health, whether you make music or just listen.
Combining Music Therapy with Standard Care
Recent studies say music therapy can change the game for depression treatment. It works well with medication and psychotherapy. This way, it tackles depression from both emotional and cognitive sides.
People who try music therapy say it helps a lot. They feel less anxious, more confident, and can talk better. Music therapy can be adjusted to fit each person's needs, making it a great addition to standard care.
If you or someone you know has depression, talk about music therapy. It can be a game-changer when combined with standard care. It might help you feel better and manage symptoms more effectively.
Music Therapy for Children and Adolescents
Music therapy is great for kids and teens with depression. It's fun and lets them express feelings and boost self-esteem. Music-making and performance help them focus and understand themselves better.
It also makes families stronger and helps kids and teens be more resilient. A study showed music therapy can make kids feel better by changing their mood and heart rate.
Music therapists work in many places, helping with mood and anxiety disorders, autism, and trauma. They use special tools to help kids express themselves and manage their feelings. This way, they can deal with depression and other mental health issues.
About 1 in 5 kids and teens in the US face mental health challenges. Music therapy is key in helping them. It lets them find their voice and build strength to overcome depression and other issues.
Implementing Music Therapy
Qualified music therapists start by getting to know you well. They look at your needs, strengths, and what music you like. They also check your emotional, physical, and social health, and how you communicate.
After understanding you, they work with you to set goals. They create a music therapy plan just for you. This plan might include making music, singing, or listening to songs that fit your needs.
The music therapy process is careful and thoughtful. It uses music to help you feel better. With a skilled music therapist, you can start a journey to better mental health and a happier life.
FAQ
What is music therapy?
Music therapy uses music to help people. It helps them reach their goals and feel better. Music therapists make plans just for each person.
How can music therapy benefit mental health?
It can lower anxiety and boost confidence. These are key for those with depression. Making music lets people express feelings and connect with themselves.
How does music therapy work?
It works by using music to reach the brain. It activates parts of the brain for rhythm, emotion, and pitch. This makes the brain release happy chemicals, improving mood.
What is the history of music therapy?
Music therapy has roots in ancient times, like Ancient Greece. It was used for healing. In the 20th century, it became more formal, starting in the 1940s.
What are the benefits of music therapy for depression?
It can lessen anxiety and depression symptoms. It also helps adults function better. Music therapy makes standard treatments more effective.
How can music therapy benefit children and adolescents with depression?
It's a fun way for kids to express feelings and build self-esteem. It helps them develop skills like focus and self-understanding. These are key for managing depression.
How is music therapy implemented?
Qualified music therapists use a detailed approach. They start with an assessment to understand the client's needs. Then, they create a plan tailored to the client's goals.
Source Links
- Effects Of Depression In Your Body | Dr. Chandril Chugh
- 6 Uses and Advantages of CBD Oil with Side Effects
- Exploring Types Of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy For Mental Health
- Music therapy: Types and benefits for anxiety, depression, and more
- What Is Music Therapy, and How Can It Help Me?
Signs of Depression in Men: How to Identify Them | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Depression is a serious mental health issue that affects both men and women. But it shows up differently in men. Dr. Chandril Chugh, a top mental health expert, talks about the signs of depression in men that are often missed.
In this detailed article, we'll look at the special signs of depression in men. We'll also cover the risk factors and causes. Knowing the signs of depression in men helps us support them better. It encourages them to get the help they need, improving their health.
Understanding Depression in Men
Depression is a serious mental health issue that affects many people. It shows up differently in men than in women. Knowing how depression looks in men is key to spotting it early and helping them.
Defining Depression and Its Unique Manifestations in Men
Depression makes people feel sad and hopeless for a long time. In men, it can show up as tiredness, headaches, or stomach problems. Men might also act out more, use drugs, or get angry easily.
Dr. Chandril Chugh says over 6 million men in the U.S. deal with depression every year. Sadly, men are more likely to take their own lives, making up 75% to 80% of all suicides in the U.S.
Men are often expected to be strong and not show their feelings. This can make depression harder to see in them. Work stress, retirement, and past traumas also play a big role.
Knowing how depression looks in men helps doctors, family, and friends to spot it. This is important for helping men and lowering the number of suicides among them.
Recognizing the Signs of Depression in Men
It's important to spot depression in men early. Men often show depression in their own way. Knowing these signs helps loved ones and doctors help them.
- Physical symptoms: Changes in sleep, unexplained aches, and low energy are signs of depression in men.
- Emotional changes: Feeling sad, irritable, and unmotivated are common signs of depression in men.
- Behavioral shifts: Taking more risks, using substances, and pulling away from friends can mean depression.
By noticing these signs, you can help your loved one or patient get the right help. Understanding the link between depression and suicide is also key to preventing tragedy.
Depression is treatable, and men can get better with the right support. If you or someone you know is struggling, get help. We can all work together to make sure everyone gets the care they need.
Physical Symptoms of Depression in Men
Depression in men can show up in physical ways that are easy to miss. Dr.Chugh says men with depression might feel tired, have headaches, or have stomach problems. They might also sleep too much or too little.
These signs can be the only clue that a man is depressed. This can lead to a long wait before he gets help. It's important for doctors to know how physical signs and depression are linked in men.
- About 9% of men in the U.S. feel depressed or anxious every day. Thirty-six percent have felt depressed at some point in their lives.
- Depression hits 5.5% of men, but 10.4% of women. Yet, four times as many men die by suicide as women.
- Men with depression might have headaches, tight chests, or pain in their joints or back. They might also have stomach issues, feel very tired, or have trouble sleeping.
Doctors can spot these signs to help men with depression. By focusing on these physical symptoms, they can improve mental health for men.
Emotional and Behavioral Signs
Depression in men shows up in many ways, not just physical signs. It also affects their emotions and behavior. Spotting these changes is key to helping them get better.
Emotional Manifestations of Depression in Men
Men with depression often feel sad, irritable, and unmotivated. They might struggle to share their feelings. This can make their depression worse.
They might also take more risks, like using drugs or doing dangerous things. These actions show their deep emotional pain. They might pull away from friends and lose interest in things they used to love.

It's important to tackle these emotional and behavioral signs of depression in men. By understanding how depression affects them differently, we can offer better support and treatment.
Behavioral Changes in Depressed Men
Depression in men can show up in big ways. They might drink too much, drive recklessly, or gamble too much. They might also pull away from friends and family, losing interest in work and hobbies.
These changes can make depression worse. Men might not talk about their feelings because they're worried about what others think. They might fear it could hurt their job or relationships.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says men are more likely to die by suicide. They often use guns, which are very deadly. Even though women try to kill themselves more, men might turn to booze or drugs instead.
Men with depression might have trouble getting along with others. They might try to escape their problems or have physical issues like headaches. They could also have problems with alcohol or drugs, be controlling or abusive, feel irritable, or take risks.
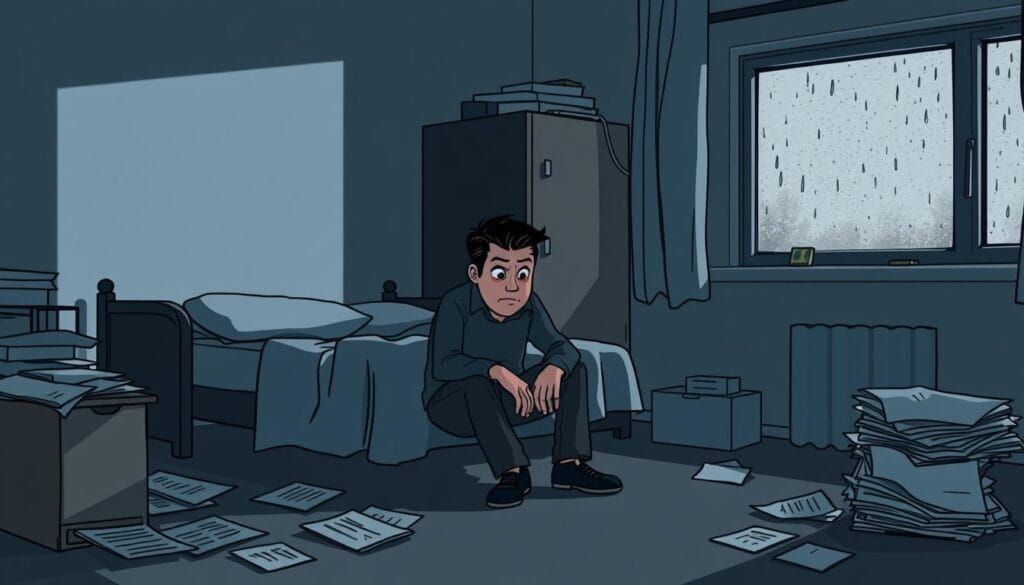
Signs Of Depression In Men
Depression can affect anyone, but it shows differently in men. It's key for men to know the signs they or someone they care about might have.
Men often feel tired, have headaches, or stomach problems. These signs might seem like just physical issues. But, they can really mean something is wrong with their mental health.
Men might also act differently when they're depressed. They might get angry easily, take risks, or pull away from friends. These changes can be hard to spot, but they're important signs.
Knowing these signs is crucial for getting help early. Men might not talk about their feelings as much. So, paying attention to small changes is vital. This way, you can get the help you need and feel better.

- Persistent fatigue or low energy
- Recurrent headaches or digestive issues
- Increased irritability or aggression
- Engaging in risky behaviors
- Withdrawing from social interactions
By spotting these signs, you can take action for your mental health. Remember, asking for help is brave, not weak. Your happiness is important, and with the right support, you can beat depression and find joy again.
Risk Factors and Causes
Depression in men comes from many biological, psychological, and social factors. Hormones, genes, and health issues can raise the risk. Stress, trauma, and negative thoughts also play a part. Social pressures, work demands, and relationship problems add to the mix.
Healthcare providers need to know these factors. They must create detailed plans to help men with depression.
Biological Factors Contributing to Male Depression
Men's biology affects their risk for depression. Hormonal imbalances, like low testosterone, can lead to sadness. Genetic and medical issues, like thyroid problems or chronic pain, also raise the risk.
Psychological and Social Factors Influencing Male Depression
Psychological factors, like trauma and stress, can cause depression in men. Social norms that hide emotions and the need to be tough make it hard for men to talk about their feelings.
Work stress, money worries, and relationship issues also contribute. Knowing how these factors work together is key to helping men with depression.
Diagnosing Depression in Men
Finding depression in men can be tricky. Symptoms often look different from those in women. Doctors need to know the special signs of depression in men. They also must understand why men might not ask for help.
To diagnose depression in men right, doctors do a lot of work. They look at the patient's health history, mental state, and lab results. The National Alliance of Mental Illness says about 1 in 16 men feel depressed, compared to 1 in 8 women.
The mental health assessment for men includes several steps:
- Talking about symptoms, how long they last, how bad they are, and how they affect daily life
- Looking at the patient's health history, including any health problems or medicines
- Checking the patient's emotional state, like mood, thoughts, and actions
- Thinking about risk factors for depression, like family history, stress, or trauma
Doctors might use special tests or questionnaires to help find depression in men. This way, they can make sure they diagnose depression correctly. Then, they can create a treatment plan that fits the man's needs.
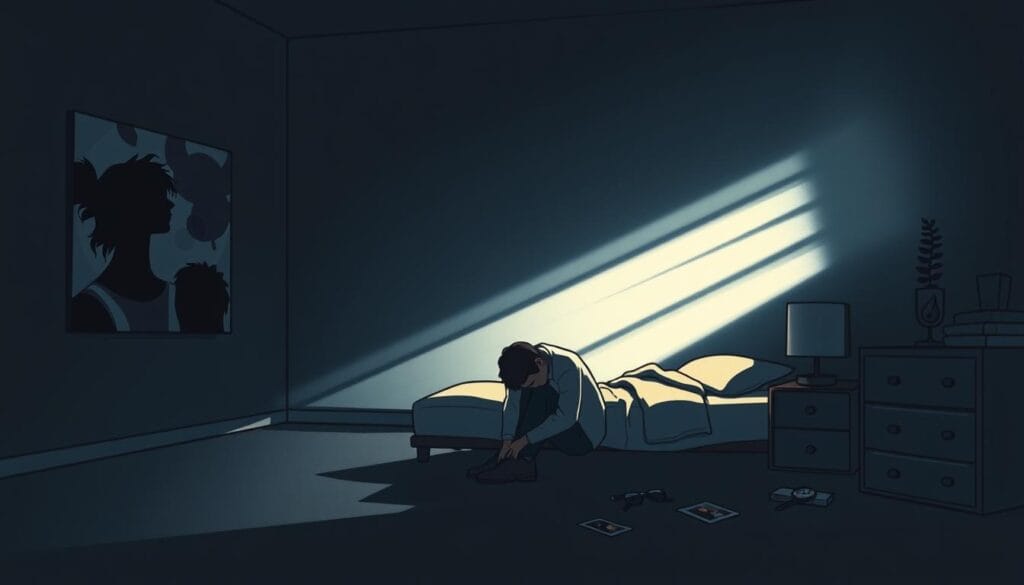

Treatment Options for Depression in Men
If you're a man with depression, know you have many ways to feel better. You can use medicine and talk therapy together. Talking to your doctor can help find the best plan for you.
Medicines like antidepressants can fix the brain's chemical problems. They make you feel better and more like yourself. Talk therapies, like CBT, help you change bad thoughts and feel better emotionally.
Changing your lifestyle also helps. Exercise, managing stress, and having friends can help a lot. Getting help from experts who know about male depression is also key.
Depression is treatable, and you can feel good again. Don't be afraid to ask for help and find resources for better mental health.
Medication Options for Male Depression
- Antidepressants, like SSRIs, help balance brain chemicals and ease depression symptoms.
- Mood stabilizers help with mood swings and emotional ups and downs.
- It's crucial to work with your doctor to find the right medicine and dose for you.
Psychotherapeutic Approaches
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps you change bad thoughts and feel better.
- Interpersonal therapy improves your relationships and communication, great for men with depression.
- Other therapies, like mindfulness, can also help manage depression and emotions.
Everyone's recovery is different, and it might need a mix of treatments. By working with doctors and taking care of yourself, you can beat depression and take back your life.
Overcoming Stigma and Seeking Help
One big problem is the stigma surrounding mental health issues in men. Many men don't want to talk about their feelings because they think it's not manly. But, it's very important for men to talk about their feelings and take care of their mental health.
Dr. Chugh says we need to make a safe place for men to talk about their mental health. By working to reduce the male depression stigma, we can help men feel better and take charge of their mental health.
Getting help for mental health can make life better at work and home. Joining groups like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) can help fight stigma. People can also fight stigma by talking openly about mental health and helping others understand it better.
Remember, asking for help with depression is brave, not weak. By tackling the male depression stigma, we can help more men focus on their mental health and get better.

Conclusion
Depression in men is a big issue that often gets ignored. Chugh says men show depression in different ways than women. They might have physical symptoms, emotional changes, and changes in how they act.
By knowing these signs, doctors, family, and men can get help early. This can lead to better treatment.
We need to break the silence around mental health in men. We want to help them take care of their minds and live happy lives. This guide aims to highlight depression in men and offer support.
Understanding male mental health and helping men with depression is key. We want a world where everyone can talk about their feelings without fear.
FAQ
What is depression, and how does it manifest differently in men?
Depression is a serious mental health issue that affects both men and women. But it shows up differently in men. Men might feel sad, hopeless, and lose interest in things they used to enjoy.
In men, depression can also show up as physical symptoms, emotional changes, and changes in how they act.
What are the unique physical symptoms of depression in men?
Men with depression might feel very tired, have headaches, stomach problems, and sleep issues. These signs can be the only clue that a man is depressed. This can make it hard to get help early.
How do emotional and behavioral changes signal depression in men?
Depression in men can also show up as feeling sad, angry, or unmotivated. Men might take more risks, use drugs, or pull away from friends and family. These actions can make depression worse.
What are the risk factors and causes of depression in men?
Depression in men can come from many places. Hormones, genes, and health problems can play a part. Stress, past traumas, and negative thoughts can also contribute.
Work pressures, social norms, and relationship issues can also affect a man's mental health.
How can depression in men be diagnosed and treated effectively?
Doctors need to look at a man's whole situation to diagnose depression. They'll check his medical history, mental health, and do tests. Treatment might include medicine and talk therapy.
Changing lifestyle habits, like exercising and managing stress, can also help. Having a strong support system is key.
What are the barriers to addressing depression in men, and how can they be overcome?
One big problem is the stigma around mental health. Men might feel weak if they talk about their feelings. But, it's important for men to talk about their mental health.
Creating a safe space for men to open up is crucial. This way, they can get the help they need without feeling judged.
Source Links
- Strategies For Managing Mood Swings Effectively | Dr Chandril Chugh
- Common Women's Mental Health Issues: What To Know
- Memory Loss, Behavioral Changes, and Slurred Speech in a 49-Year-Old Man
- Depression in Men: Symptoms and Physical Effects
- Signs of Depression in Men: 13 Symptoms and What You Can Do
- Behaviors in men that could be signs of depression
Postpartum Depression Rage: Understanding & Managing It | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Being a new mom can bring both joy and challenges. One big issue many face is postpartum depression rage. This condition makes moms feel very angry, irritable, and frustrated. It can really hurt a mom's happiness and her bond with her baby.
Dr. Chandril Chugh, a top expert in maternal mental health, will talk about postpartum depression rage. You'll learn more about how common mental health issues are in women. You'll also see how society's stigma and barriers stop women from getting help. By understanding this crisis better, we can help support moms' mental health more.
The Overlooked Crisis of Women's Mental Health
Women's mental health is often ignored, despite the big challenges they face. Studies show that 1 in 5 women deal with a mental illness, compared to 1 in 8 men. These issues can deeply affect their relationships, work, and life quality.
But, women often face stigma and barriers that stop them from getting the care they need.
Prevalence and Impact of Mental Health Issues in Women
Mental health problems in women are widespread. In the United States, about 400,000 women struggle with mood changes after having a baby. The 'baby blues' affect up to 80% of new moms.
Major depressive disorders cause up to one-third of all deaths by suicide. Women try to take their own lives four times as often as men.
Societal Stigma and Barriers to Accessing Care
Women with mental health issues often face stigma and barriers to care. Stigma is a big problem that stops women from seeking help for mental health issues like postpartum depression.
Money problems, lack of transportation, and not knowing where to find help also block women's access to mental health services.

The crisis of women's mental health needs urgent action. We must tackle the prevalence of mental health issues, reduce stigma, and make care more accessible. This way, we can help women focus on their well-being and overcome their challenges.
Together, we can build a supportive and inclusive space for women to succeed.
Common Mental Health Challenges Faced by Women
Women often face unique mental health struggles. These can greatly affect our daily lives. Anxiety and depression are two big issues. Women are nearly twice as likely to have these problems as men.
Anxiety and Depression: Higher Rates Among Women
Hormonal changes can lead to women's anxiety and women's depression. Social pressures and expectations also play a big role. These can make it hard for women to manage stress and personal life.
Trauma, Stress, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Women are more likely to face traumatic events. This includes gender-based violence and domestic abuse. These experiences can lead to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other stress-related disorders.
Understanding the impact of trauma and PTSD in women is key. It helps us address the unique mental health needs of women. By doing so, we can improve well-being and mental health equality.

Exploring Mental Health Complexities in Women
Women's mental health is complex, influenced by biology, psychology, and society. It's important to understand these factors to help women feel better.
Hormones change a lot in women's lives. These changes can affect their mood and feelings. For example, many women feel sad during pregnancy or after having a baby.
Society also affects women's mental health. They face stress from work and family, and feel pressure to meet expectations. This can make them feel anxious or sad.
Feeling alone can also hurt a woman's mental health. A study in the UK showed new moms often feel lonely. Women from different backgrounds who struggled with depression talked about feeling isolated.
Knowing about women's mental health helps us find better ways to support them. We can address the biological, social, and cultural factors that affect them.

Gender-Specific Risk Factors and Stressors
Women often face unique challenges that can affect their mental health. Conflicts in family, romantic, and social relationships can cause stress and anxiety. The heavy caregiving burden and work-life balance demands can also lead to burnout and mental health issues.
Interpersonal Conflicts and Relationship Dynamics
Women's mental health is influenced by their relationships and social connections. Conflicts in these areas can be a big risk factor and source of stress. These issues can make women feel isolated, inadequate, and emotionally troubled, worsening their mental health.
Caregiving Responsibilities and Work-Life Balance
Women often carry a heavy load of caregiving duties. This can include caring for children, elderly parents, or family members with disabilities. This caregiving burden can be overwhelming and disrupt work-life balance, causing stress, burnout, and mental health problems.
It's important to address these gender-specific risk factors. Supporting women in these challenges is key to promoting their mental health and overall well-being.
Cultural and Ethnic Perspectives on Women's Mental Health
Your mental health is tied to your community's culture. In some places, mental illness is seen as weakness. This makes it hard to get the help you need.
Some ethnic groups show mental health issues as physical symptoms. This is called somatization. It's tough for doctors to find and treat the real mental health problems.
Influence of Cultural Norms and Beliefs
Your culture shapes how you see mental health. Studies show many communities still stigmatize mental illness. This makes people think it's a personal flaw, not a health issue.
This thinking makes it hard to admit and deal with your mental health.
Somatization and Manifestation of Mental Health Issues
In some ethnic groups, mental health shows up as physical symptoms. This is called somatization. It's hard for doctors to find and treat the real mental health problems.
Research shows somatization is a way to show mental distress. Doctors need to know about this to help better.
It's key to understand cultural and ethnic views on women's mental health. This helps get more care and support. Doctors must be aware and work to break down stigma and misunderstandings.

The Impact of Discrimination and Gender-Based Violence
Gender discrimination and violence, like domestic abuse and sexual assault, hurt women's mental health a lot. These issues can cause serious problems, like PTSD, depression, and anxiety. Even postnatal depression is linked to violence by a partner during pregnancy.
A study found a strong connection between domestic violence and mental health problems during pregnancy. The World Health Organization's study showed how common domestic violence is and its bad health effects. It also found that emotional and physical violence during pregnancy can harm both mom and baby even a year later.
Violence by a partner during pregnancy can lead to bad health outcomes in Vietnam. Emotional abuse can make women depressed. Studies have looked at how common and what causes postpartum depression in different cultures, including Vietnam.
We need to tackle the big issues of discrimination and violence against women. By fixing these problems and helping survivors, we can make a better place for women's mental health.
Addressing Mental Health Needs Across the Lifespan
Women's mental health changes as they age. In their teens, girls often deal with anxiety, depression, and body image issues. Pregnancy and the time after having a baby are also key times for their mental health.
Many new moms face postpartum depression and rage. These issues can harm them and their babies if not treated.
Adolescent Mental Health and Body Image Concerns
Adolescence is tough for young women's mental health. They often feel anxious and depressed because of society's high standards and body ideals. It's important to help them early on.
We need to give them tools to handle stress and build a good self-image.
Perinatal Mental Health and Postpartum Depression Rage
The time before and after having a baby is full of big changes for women. Postpartum depression affects 10 to 20 percent of new moms. It can hurt the bond between mom and baby.
Some moms also face postpartum depression rage. This is hard to deal with but needs help from experts.
It's vital to help women with their mental health at every stage of life. We can do this by offering support and resources. This way, we help them face life's challenges and take care of their mental health.
Strategies for Promoting Mental Well-Being in Women
Women face many mental health challenges. But, there are ways to improve mental well-being. It's all about self-care and managing stress. This helps women take charge of their mental health.
Importance of Self-Care and Stress Management
Self-care is key to feeling good. It includes activities like exercise, meditation, and journaling. Taking time for yourself each day can make a big difference.
Managing stress is also vital. Deep breathing, muscle relaxation, or talking to a therapist can help. Finding the source of stress and dealing with it is important.
- Incorporate daily self-care routines, such as yoga, reading, or spending time in nature.
- Explore mindfulness and meditation practices to cultivate inner calm and clarity.
- Seek professional help from a therapist or counselor to manage stress and develop personalized strategies.
- Prioritize getting enough sleep, a key factor in maintaining mental well-being.
- Surround yourself with a supportive network of family, friends, or community groups.
By focusing on women's mental health strategies, self-care, and stress management, women can improve their mental health. This leads to a healthier, more balanced life.
Conclusion
Women's mental health is very important. We need to understand their unique challenges. This way, we can help them feel supported and included.
We should tackle the stigma and barriers to care. We also need strategies for different life stages. The goal is to help women take care of their mental health.
Women face many challenges, like postpartum depression rage. They also deal with anxiety, depression, and trauma. They need the support and resources they deserve.
By focusing on gender-specific risks and cultural factors, we can help. This will lead to a healthier society for everyone.
Your mental health is as important as your physical health. Seek help when you need it. Practice self-care and surround yourself with support. Together, we can make a difference.
FAQ
What is postpartum depression rage?
Postpartum depression rage is a serious mental health issue. It affects many new mothers. It's a mix of postpartum depression and intense anger or irritability.
How common are mental health issues among women?
Studies show 1 in 5 women face mental illness. This is compared to 1 in 8 men. Women are nearly twice as likely to have anxiety and depression.
What are the common mental health challenges faced by women?
Women are more likely to face anxiety, depression, and PTSD. This is due to biological, psychological, and societal factors.
How do gender-specific risk factors impact women's mental health?
Stress from interpersonal conflicts, caregiving, and work-life balance affects women. These factors contribute to their mental health challenges.
How do cultural and ethnic perspectives influence women's mental health?
In some cultures, mental illness is seen as weakness. This makes it hard for women to seek help. Some ethnic groups show mental health issues physically, making diagnosis tough.
What is the impact of discrimination and gender-based violence on women's mental health?
Gender discrimination and violence can cause serious mental health issues. This includes PTSD, depression, and anxiety.
How can women's mental health needs be addressed across different life stages?
Mental health strategies should vary by life stage. For example, addressing anxiety and body image in teens. Supporting new mothers with postpartum depression and rage.
What are effective strategies for promoting mental well-being in women?
Self-care and stress management are key. Seeking support from healthcare, loved ones, and community resources also helps. These actions improve mental health and well-being.
Source Links
- Best Neurologist In Patna, Author Dr Chandril Chugh
- Postpartum depression | Office on Women's Health
- Digital Health Needs of Women With Postpartum Depression: Focus Group Study
- House Subcommittee Examines Postpartum Depression - Women's Congressional Policy Institute
- Postpartum Rage: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Low Testosterone and Depression in Men: Exploring the Link | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Have you ever felt unusually tired, irritable, or lost interest in things you once enjoyed? What if the cause isn’t just stress or aging, but something deeper – a hormonal shift that often goes unnoticed?
Low testosterone and depression in men is a serious and often hidden link that many ignore until it's too late.
In this blog, we will explain how testosterone affects your mental health, why it's not "just aging," and how early action can save your mood, energy, and relationships. If you're feeling "off," read this carefully. It might be the missing piece in your health puzzle.
Understanding Testosterone and Its Role in Men’s Health
Before diving into the link between hormones and mental health, let’s understand what testosterone does for men.
What is Testosterone?
Testosterone is a hormone made mainly in the testicles. It controls many male traits and body functions. From facial hair and muscle mass to sex drive and mood, it plays a big part in your everyday life.
- Helps build and maintain muscles
- Supports a healthy sex drive (libido)
- Controls sperm production
- Affects mood and brain function
If testosterone levels drop, these functions can be disrupted. And over time, it can take a toll not only on your body but also your mind.
Also Read: Foods That Cause Penis Odor: Dr. Good Deed’s Guide to Managing It
Why Testosterone Declines with Age
Testosterone doesn't stay steady forever. In fact, it naturally declines as you get older.
- Most men see about a 1% drop per year after age 30
- By age 60, many men have low levels without even knowing it
Here’s a simple chart showing how testosterone typically drops with age:
| Age Range | Average Testosterone Level (ng/dL) |
|---|---|
| 20-30 | 600-700 |
| 31-40 | 500-600 |
| 41-50 | 400-500 |
| 51-60 | 300-400 |
| 60+ | 250-350 |
This steady drop can lead to physical and emotional changes in men, which many mistake as just "getting older."

Common Symptoms of Low Testosterone in Men
Men often live with low T (testosterone) for years without realizing it. Here are the most common signs:
- Feeling tired all the time (fatigue)
- Loss of interest in sex (low libido)
- Trouble building or keeping muscle
- Foggy thinking or poor memory (brain fog)
- Mood swings, sadness, or lack of motivation
According to the American Urological Association, about 2 in 10 men over age 60 have low testosterone. And many aren’t diagnosed or treated.
Causes of Low Testosterone in Men
Let’s now understand why testosterone levels drop. It’s not always age alone.
Age-related decline (Andropause)
Just like women go through menopause, men go through andropause. This is the natural drop in male hormones as they age.
- Begins around age 30
- Slowly reduces testosterone by 1% each year
- Can lead to both physical and mental issues over time
Lifestyle Factors
How you live plays a huge role in your hormone levels. Common causes of low testosterone include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Chronic stress from work or relationships
- Poor diet low in nutrients
- Alcohol or drug abuse
Fixing your lifestyle can often help improve your hormone balance.
Medical Conditions
Certain health issues can cause low testosterone:
- Type 2 diabetes (insulin resistance harms hormone production)
- Sleep apnea (disrupts hormone cycles during sleep)
- Chronic diseases like kidney or liver issues
These medical problems also raise the risk of depression.
Low Testosterone and Depression in Men – What’s the Connection?
Now let’s look at how low testosterone and depression in men are connected. This is not just a theory. It’s backed by science and real cases.
How Hormones Affect Brain Chemistry?
Hormones like testosterone don’t just affect your muscles or sex life. They also help keep your brain in balance.
- Testosterone boosts dopamine and serotonin, two brain chemicals that affect happiness and motivation
- Low testosterone can reduce these levels, leading to low testosterone and mood disorders
- It affects brain areas linked to motivation, memory, and focus
When testosterone drops, so does your brain's "feel-good" chemistry. That’s why many men with low T feel sad, anxious, or numb.
Evidence from Clinical Studies
Research shows a strong link between low T and mental health:
- A 2020 meta-analysis found that men with low testosterone had higher depression scores
- Men who received testosterone replacement therapy and depression treatment saw better mood results than those on antidepressants alone
- In some cases, testosterone therapy alone improved mood without needing extra meds
These findings prove that the mind and body are closely connected.
Depression Symptoms Often Overlap with Low T
Many signs of depression and low testosterone are the same. This can confuse both doctors and patients.
| Symptom | Seen in Depression | Seen in Low T |
| Low energy / fatigue | Yes | Yes |
| Sadness or low mood | Yes | Yes |
| Poor sleep | Yes | Yes |
| Low sex drive | Sometimes | Yes |
| Trouble focusing | Yes | Yes |
| Irritability or anger | Yes | Yes |
According to JAMA Psychiatry, men with low testosterone are 2 to 3 times more likely to have clinical depression.

How to Know if Low Testosterone is Affecting Your Mood?
You might wonder: is it low T or something else? Let’s talk about how to find out.
Self-assessment Questions
Ask yourself:
- Do I feel tired all day?
- Is my sex drive much lower than before?
- Am I feeling down, numb, or irritable?
- Am I gaining weight or losing muscle?
- Am I forgetting things or feeling foggy?
If you answered yes to 3 or more, it's time to speak to a doctor.
Medical Diagnosis
Doctors use simple tests to check your hormone levels:
- Blood test: Measures total and free testosterone
- Depression screening tools: Checks your mood symptoms
- Hormone panel: Checks other hormones that may affect mood
Yet, only 5% of men with low testosterone ever get diagnosed or treated. Don’t be part of that 95%.
Treatment Options for Low Testosterone and Depression in Men
You can do something about it. There are many safe ways to treat low testosterone and depression in men.
Lifestyle Modifications
Small changes make a big difference:
- Exercise: Resistance training boosts testosterone naturally
- Healthy diet: Foods rich in zinc, vitamin D, and healthy fats
- Stress control: Better sleep, meditation, and less screen time
These changes help fix both body and mood.
Read: Best Multivitamin for Men: How to Choose the Right One for Your Health
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
TRT replaces lost testosterone using:
- Gels or creams (applied to skin)
- Injections (weekly or monthly)
- Pellets (inserted under skin)
Benefits:
- Boosts mood and focus
- Improves energy and sex drive
- Increases muscle mass
Risks:
- Can affect fertility
- May cause acne or oily skin
- Needs regular monitoring
A study in Psychoneuroendocrinology found that 56% of men on TRT had better mood within 6–8 weeks.
Read: Boost Male Fertility: Top Strategies & Tips
Antidepressants vs TRT – Or Both?
Some men may need both treatments:
- SSRIs help balance brain chemicals
- TRT helps restore hormone balance
- Combining them may offer better results than either alone
A doctor can help you decide what’s best for your body.
Mental Health Support Beyond Hormones
Medicine isn’t the only solution. Mental health care matters too.
Read: Men’s Health and Mental Health: Why It Matters
Therapy and Counseling
Talking helps. Especially for men who keep emotions inside.
- CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy) teaches new thinking patterns
- Helps men express emotions in healthy ways
- Breaks stigma around asking for help
Role of Support Systems
You’re not alone.
- Talk to your family and involve them
- Join men’s health groups or online forums
- Share your story to help others
The Impact of Low Testosterone on Mental Health
Men's well-being is closely tied to low testosterone and mental health. Testosterone is key for both physical and mental health.
Research shows a clear link between low testosterone and mental issues. This includes depression, anxiety, and mood swings. 34% of men with low testosterone face major depression and mood disorders. Symptoms like fatigue, low libido, and trouble focusing can really affect your life.
But, there's hope. Treating low testosterone and its mental health effects can greatly improve your life. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) can boost your mood, focus, and energy. It also makes you feel better overall.
Changing your lifestyle is also important. Eating well, exercising, managing stress, and staying connected with friends can help. These steps, along with TRT, can help you feel better mentally and physically.
If low testosterone is affecting your mood, get help. Healthcare experts can guide you to the right treatment. Don't let low testosterone hold you back. Take control of your health today.
Breaking the Stigma: Why Men Often Suffer in Silence?
Too many men ignore their symptoms due to shame or fear.
Societal Pressure and “Toughness”
Boys are told to "man up." This can be dangerous.
- Many men don’t talk about their feelings
- They hide depression until it’s serious
- Hormone changes are often mistaken for weakness
Why Early Diagnosis Can Save Lives
Men with depression are more likely to take extreme steps, like suicide.
- Depression in men often shows as anger, not tears
- Emotional pain hides behind physical complaints
- Testing early can prevent tragedy
Seeking Professional Help for Depression
If you're struggling with depression, getting help is key. A doctor or mental health expert can check your symptoms and health. They'll suggest the best treatment, like lifestyle changes, counseling, or medicine.
Don't be afraid to ask for help. Getting treatment early can greatly improve your life. Depression affects many men, and sadly, some die from it. Asking for help shows you're strong, not weak.
There are many resources to support you. Talking to a mental health professional can help you understand your depression. They can also teach you ways to manage your feelings. Medicines and therapies like TMS and ECT are options for severe cases.
Self-help methods like meditation and exercise can also help. Remember, you're not alone in this fight. Asking for help is the first step to a better life.
Start by talking to an expert like Dr. Chandril Chugh, a US-trained neurologist who treats both mind and body together.

Take the First Step Toward Better Mental Health with Dr. Chandril Chugh
If you’re facing fatigue, mood changes, or low sex drive, don’t brush it off. Low testosterone and depression in men is real and treatable. Acting early can protect your relationships, work life, and future.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a US-trained, board-certified neurologist with deep expertise in male hormone imbalance, mood disorders, stroke recovery, and more. He treats patients with both care and clinical excellence.
Don’t let silence keep you sick. Reach out today and get your life back.
Book a consultation with Dr. Chugh now to take charge of your brain and body
FAQ
What is the link between low testosterone and depression in men?
Studies show a strong link between low testosterone and depression in men. When testosterone drops, men may feel sad, hopeless, and tired. They might also lose motivation.
What are the symptoms of low testosterone in men?
Low testosterone causes physical and emotional symptoms. Men might lose muscle, gain fat, and have less hair. They could also feel depressed, anxious, and have trouble concentrating.
What are the causes of low testosterone levels in men?
Many things can lower testosterone levels. Age is a big factor, as levels drop about 1% each year after 40. Obesity, diabetes, and stress can also play a role.
How is low testosterone diagnosed?
A blood test is used to check testosterone levels. Doctors look at total, free, and bioavailable testosterone. It's important to talk about the results with a doctor.
What are the treatment options for low testosterone?
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is a common treatment. It uses injections, gels, or patches to raise testosterone levels. This can help with symptoms like depression.
How can lifestyle changes help boost testosterone levels naturally?
Eating well and exercising can naturally boost testosterone. A diet rich in protein and healthy fats is key. Exercise, especially weight training, also helps. Stress management and enough sleep are important too.
What should I do if I'm experiencing symptoms of depression?
If you feel depressed, get help right away. A doctor or mental health professional can help. They'll suggest treatments like therapy, medication, or lifestyle changes. Don't wait to seek help, as early treatment can greatly improve your life.
Source Links
- Best Neurologist In Patna, Author Dr Chandril Chugh
- Content Posted in 2021 | Providence St. Joseph Health Digital Commons
- The role of testosterone, the androgen receptor, and hypothalamic-pituitary–gonadal axis in depression in ageing Men
- Low Testosterone (Low T): Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
- Is Low Testosterone Causing My Depression?
Postpartum Depression Herbal Treatment: Natural Remedies | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Welcoming a new life is a joy, but it can also bring big challenges for new moms. Postpartum depression affects up to one in seven women, casting a shadow on this special time. But, there's hope, and natural remedies offer a promising way forward. We'll look at herbal treatments, mindfulness, and holistic care for postpartum depression, with Dr. Chandril Chugh's guidance.
Postpartum depression can feel overwhelming, but you're not alone. This article will help you understand postpartum depression and its causes. You'll learn about natural remedies like adaptogenic herbs and mindfulness practices. These are safe, effective, and holistic ways to support your mental health after giving birth.
Understanding Postpartum Depression
Postpartum depression is a serious mood disorder that affects new mothers after childbirth. It brings feelings of sadness, anxiety, and fatigue. These feelings can make it hard for a woman to take care of herself and her baby. Knowing about definition and symptoms of postpartum depression, and its causes and risk factors, is key to getting help.
Definition and Symptoms
Postpartum depression is a type of clinical depression that happens after childbirth. It affects about 15% of women. Symptoms include feeling sad all the time, feeling hopeless, and trouble bonding with the baby.
Other signs are changes in appetite and sleep, and feeling very tired or unmotivated.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of postpartum depression are complex. Hormonal changes, psychological factors, and social issues all play a part. Hormonal shifts during and after pregnancy are a big factor.
Other risk factors include a history of mental health issues, lack of support, stress, and poor sleep and diet.
Some important risk factors for postpartum depression are:
- Personal or family history of depression or other mental health conditions
- Stressful life events during pregnancy or after childbirth
- Lack of social support from family and friends
- Complications during pregnancy or delivery
- Preexisting medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders
- Substance abuse or dependence
Understanding definition, symptoms, causes, and risk factors of postpartum depression helps. It lets new mothers and their loved ones spot the signs early. This way, they can get the support and treatment they need.
Benefits of Breastfeeding for Postpartum Depression
If you're dealing with postpartum depression, breastfeeding might help. Studies show women who only breastfeed have an 89% lower risk of depression. It releases oxytocin, a hormone that calms you and boosts your mood.
Postpartum depression hits about 1 in 7 new moms. Lack of omega-3s and Vitamin B-2 can increase your risk. But breastfeeding can help with these issues and support your mental health.
Breastfeeding also has physical benefits for your recovery. It helps your uterus shrink back, cuts down on bleeding, and might lower cancer risk later. It's a strong tool against postpartum depression.

If postpartum depression is overwhelming, get help. Talk to your doctor about adding breastfeeding to your treatment. With the right care, you can beat this and enjoy your baby's early days.
Herbal Remedies for Postpartum Depression
If you're dealing with postpartum depression, natural herbal remedies might help. Certain herbs and plants can ease symptoms. Let's look at some promising options.
Adaptogenic Herbs
Herbs like ashwagandha and rhodiola help your body handle stress. They can also help manage postpartum depression. These herbs aim to balance your body and improve your mood after giving birth.
St. John's Wort
St. John's Wort is known as a natural mood booster. It can help with postpartum depression by lifting your mood and easing anxiety. But, talk to a doctor first because it can affect other medicines.
While herbal remedies can be useful, always talk to your doctor. They can help create a plan that's right for you. Combining natural and medical treatments might be the best way to fight postpartum depression.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Adding mindfulness and relaxation to your daily life can really help with postpartum depression. It helps you stay in the moment and forget worries. This can make you feel less stressed and anxious, helping you sleep better and feel happier.
Practices like mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can calm your body. They make you feel more relaxed and happy.
Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation is about being in the now, without judgment. It helps you stop thinking about worries that come with postpartum depression. Studies show it can really help, with up to 85% of people feeling better.
Yoga and Deep Breathing
Doing yoga and deep breathing every day can also help. They help your body relax, making you feel less stressed and anxious. Research says these activities can lower the risk of depression by 25% during and after pregnancy.

By using mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing, you can manage postpartum depression better. These natural methods are great for improving your mood and well-being. They are powerful tools on your path to recovery.
Postpartum depression herbal treatment
If you're dealing with postpartum depression, you're not alone. Herbal remedies can help manage your symptoms. They support your mental health during this tough time. By using adaptogenic herbs, mood-boosting plants, and relaxation techniques, you can find natural ways to feel better.
Adaptogenic herbs like ashwagandha and rhodiola help your body handle stress. St. John's Wort is used to treat mild to moderate depression. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil and vitamin D can also help with postpartum mood disorders.
- Ashwagandha and rhodiola: Adaptogenic herbs that help the body manage stress
- St. John's Wort: Traditional herb used to treat mild to moderate depression
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Help prevent and treat postpartum mood disorders
- Vitamin D: Can be a beneficial supplement for postpartum depression
Mindfulness practices like meditation and deep breathing can calm your mind. Aromatherapy with scents like lavender and citrus can also improve your mood.
Always talk to a healthcare provider before trying new herbal or supplement treatments. This is especially true if you're already taking medications. With a holistic approach, you can find natural remedies that meet your needs. This will help you on your journey to postpartum wellness.
Dietary Changes for Postpartum Depression
Postpartum depression can be tough, but diet changes help. Cut down on caffeine and alcohol. They can mess with your sleep and mood.
Caffeine, in particular, can make you feel anxious and jittery. This can make postpartum depression worse.
Eating sleep-promoting foods is also good. Foods with melatonin, magnesium, and tryptophan help you sleep better. Some good foods are:
- Almonds
- Bananas
- Oats
- Fatty fish (such as salmon)
- Leafy greens
- Whole grains
These diet changes support your body and mind after having a baby. A balanced diet is key to managing postpartum depression symptoms and staying healthy.

Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise can help manage postpartum depression. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming can reduce anxiety and improve mood. This leads to better sleep and overall well-being.
Yoga and deep breathing are also good for new moms. These practices help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Starting slowly and getting a healthcare provider's advice is key.
The benefits of exercise for postpartum depression are clear. Studies show it can be as good as medicine or therapy for depression. Exercise programs have also helped reduce depression in many women, including those in Taiwan.
If you're dealing with postpartum depression, try these exercises:
- Brisk walking or jogging
- Swimming or water aerobics
- Gentle yoga or Pilates
- Strength training exercises
- Pelvic floor therapy
Start slow and listen to your body. With your healthcare provider's help, you can do more and more. Regular exercise is a strong tool for postpartum wellness.
Importance of Support System
Having a strong support system is key when dealing with postpartum depression. Family, friends, and community connections offer emotional, practical, and social support. This is crucial for new mothers to get through tough times.
Studies show that more support means lower depression scores. A recent study found that less social support during COVID-19 increased depression and anxiety in new moms. It also hurt parent-infant bonding.
Support groups or counseling are great for moms with postpartum depression. They offer a safe place to talk, share, and get advice from experts and others who understand.
You don't have to face this alone. Asking for help and staying connected can really help your recovery. Don't be afraid to ask for help and seek professional advice when you need it.

Integrating Herbal and Conventional Treatments
Managing postpartum depression can be done by mixing herbal remedies with traditional treatments. This way, we tackle the condition from all sides. It helps with both the body and mind.
It's important to work with a healthcare provider for this approach. They can figure out the right mix of treatments for you. This ensures everything works well together.
Research shows that some Chinese herbs can help when used with therapy or medicine. This mix can make symptoms of depression better and improve your overall health.
Choosing a mix of herbal and traditional treatments is a big step towards getting better. It lets you find what works best for you. This approach helps you regain your health in a personal way.
Conclusion
Postpartum depression is common and can be treated. There are many natural remedies for postpartum depression to help new moms. These include adaptogenic herbs, mindfulness, diet changes, and a strong support system.
It's key to remember that seeking help for postpartum depression is vital. A mix of natural and medical treatments works best. With the right support, you can enjoy motherhood more.
You're not alone in this journey. Exploring natural remedies can help you feel better. It's a big step towards happiness and fulfillment as a new mom.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of breastfeeding for postpartum depression?
Breastfeeding can help with postpartum depression. Studies show women who only breastfed had 89% less chance of getting it. It releases oxytocin, which calms the mind and lifts the mood.
What are some effective herbal remedies for managing postpartum depression?
Some herbs can help with postpartum depression. Adaptogens like ashwagandha and rhodiola help the body handle stress. St. John's Wort is also used to help with depression.
How can mindfulness and relaxation techniques help with postpartum depression?
Mindfulness and relaxation can help with postpartum depression. Mindfulness meditation reduces stress and improves sleep and mood. Yoga and deep breathing also help by calming the body.
What dietary changes can be beneficial for managing postpartum depression?
Eating right can help with postpartum depression. Avoid caffeine and alcohol to improve sleep. Foods that help sleep, like melatonin, are good too.
How can regular exercise and physical activity impact postpartum depression?
Exercise is good for postpartum depression. Activities like yoga and deep breathing reduce anxiety and improve mood. Start slow and talk to a doctor before starting.
Why is having a strong support system crucial for managing postpartum depression?
A strong support system is key for managing postpartum depression. Family and friends offer emotional and practical help. Support groups and counseling also help.
How can an integrative approach combining herbal and conventional treatments be effective for postpartum depression?
Combining herbal remedies with conventional treatments can be effective. Work with a healthcare provider to find the right mix. It's complex but can be very helpful.
Source Links
- 5 Effective Strategies For Sleep Maintenance Insomnia Relief
- Meghan Cliffel on LinkedIn: #maternalmentalhealth #postpartumpsychosis #mentalhealth #paidleave… | 21 comments
- Treating postpartum depression with complementary or alternative medicine | Your Pregnancy Matters | UT Southwestern Medical Center
- Postpartum Depression - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Breastfeeding and Postpartum Depression: An Overview and Methodological Recommendations for Future Research
Symptoms of Depression in Children: What Parents Need to Know | Dr. Chandril Chugh
Depression in children is a serious issue. It can really affect a child's happiness and health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says about 2.7% of kids aged 3-17 have depression.
It's very important for parents to know the signs of depression in kids. They should look for these signs and get help from experts. Dr. Chandril Chugh, a top neurologist, has written this article to help you understand depression in children. He also shares ways to support your child's mental health.
Understanding Depression in Children
Prevalence and Impact
Many parents don't know how common depression is in kids. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says 3.2% of kids aged 3 to 17 have depression. Depression can hurt a child's school work, friends, and happiness.
Causes and Risk Factors
Depression in kids comes from many things. It can be because of genes, body changes, or life events. Kids with a family history of mental health issues or who have been through tough times are at higher risk. So are kids with chronic illnesses or low self-esteem.
There are different types of depression in kids. Major depressive disorder (MDD) is when depression is very bad and lasts over two weeks. Persistent depressive disorder (PDD) is when it's milder but lasts over a year. Other types include seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD).
Symptoms of depression in children
As parents, it's key to spot the emotional, behavioral, and physical signs of depression in kids. These signs can show up in many ways and affect a child's happiness and health.
Emotional and Behavioral Signs
Children with depression might feel sad all the time, get easily upset, and lose interest in fun activities. They might also feel they're not worth much or guilty, and have trouble focusing. They could start sleeping or eating differently, pull away from friends, or act out more.
Physical Symptoms
Depressed kids might also have headaches, stomach problems, or feel very tired. These physical signs can make them miss school, even if they're not sick.
Parents should watch for changes in their child's mood, actions, and health. Spotting the emotional signs of depression in children, behavioral signs of depression in children, and physical symptoms of depression in kids helps. This way, parents can get help and support for their child.

With the right help and support, kids with depression can learn to handle their feelings and feel better again.
Recognizing the Warning Signs
It's key to spot the signs of depression in kids early. Parents should watch for big mood and behavior shifts. Look out for ongoing sadness, anger, or mood swings. These signs might mean a child is depressed.
Changes in Mood and Behavior
Depressed kids show many emotional and behavioral signs. They might:
- Feel sad, hopeless, or empty all the time
- Get angry or moody easily
- Stop enjoying things they used to love
- Stay away from family and friends
- Have trouble sleeping or feel very tired
- Have trouble focusing or making choices
- Feel guilty, worthless, or very hard on themselves
Academic and Social Difficulties
Depression can also show up in school and social life. Parents might see their child struggling with:
- Doing poorly in school and having trouble focusing
- Not wanting to hang out with friends or join in activities
- Missing school or avoiding it
- Having trouble making and keeping friends
If you see these signs in your child, get help right away. It's important to address depression in kids and offer the support they need.
Age-specific Manifestations
As children grow, depression symptoms change. It's key to know how depression shows up in kids at different ages. This helps spot it early and get the right help.
Young kids, 5-10 years old, might act out more. They could have more tantrums, feel scared when apart from parents, and have trouble controlling their feelings. They might also get sick more often, like stomach aches or headaches. Their sleep and eating habits might change too.
- Behavioral changes, including increased tantrums or defiant behavior
- Separation anxiety or difficulty being away from parents
- Emotional dysregulation and mood swings
- Physical symptoms like stomach aches and headaches
- Changes in sleeping and eating patterns
Older kids and teens, 11-18 years old, might feel more emotional. They could feel worthless, guilty, or even think about suicide. They might also struggle in school, getting lower grades, or pull away from friends.
- Feelings of worthlessness, guilt, or hopelessness
- Suicidal thoughts or attempts
- Academic problems and declining grades
- Social withdrawal and isolation
Knowing how depression looks in kids of different ages helps us help them sooner. By understanding these differences, we can give each child the right care. This way, they can fight this tough mental health issue.

Depression in Children vs. Normal Sadness
As a parent, knowing the difference between normal sadness and depression in kids is key. Normal sadness is a natural part of growing up. But, if sadness lasts a long time and gets in the way of daily life, it might be depression.
Understanding the Difference
Normal sadness happens when kids face tough times, like losing a pet or fighting with friends. It usually goes away quickly and doesn't stop kids from doing things they love. Depression, however, is a serious condition that lasts a long time. It can make kids feel really down, tired, and unhappy all the time.
When to Seek Help
If your child feels sad, angry, or just doesn't want to do anything for weeks, it's time to get help. Look out for these signs that your child might be depressed:
- Feeling hopeless or worthless all the time
- Changes in sleep or eating habits
- Having trouble focusing or making choices
- Not wanting to be around friends or family anymore
- Thinking about death or wanting to hurt themselves
Remember, asking for help for child depression shows you care. With the right help, kids can feel happy and full of life again.
Evaluation and Diagnosis
Dealing with childhood depression needs a full plan. This plan includes using special tools and getting help from experts. Doctors use special questionnaires to learn about a child's feelings. These tools, like the Children's Depression Rating Scale, help find out if a child is depressed and how bad it is.
But, getting a real diagnosis is key. Doctors like pediatricians or child psychiatrists do a deep check. They look at the child's mental health and might do tests to find any health problems. This way, they can make a plan that really helps the child.
Screening Tools: Identifying the Signals
- The Children's Depression Rating Scale (CDRS) is a semi-structured interview designed for children aged 6-12 to diagnose and assess the severity of depression.
- The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a structured rating scale suitable for all ages, serving as both a diagnostic and severity assessment tool.
- The Mood and Feelings Questionnaire is a structured rating scale for parents and children aged 6-17, used for screening, diagnosis, and severity assessment.
- The Reynolds Adolescent Depression Scale is a structured rating scale for 11-20-year-olds to evaluate the severity of depressive symptoms.
Professional Assessment: Uncovering the Whole Picture
Getting a real diagnosis is very important. Doctors like pediatricians or child psychiatrists do a deep check. They look at the child's mental health and might do tests to find any health problems. This way, they can make a plan that really helps the child.

It's very important to find and treat depression in children early. By using special tools and getting help from experts, doctors can really understand what's going on. Then, they can help the child feel better.
Treatment Options for Childhood Depression
There are many ways to treat childhood depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and family therapy are good options. They help kids learn to cope and improve their relationships.
For more serious cases, doctors might suggest antidepressants. This is often for kids with moderate to severe depression.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, especially CBT, is the best treatment for kids with depression. It teaches them to change negative thoughts and behaviors. DBT is also helpful for teens with severe depression.
Medication Management
For kids with more serious depression, medication might be needed. SSRIs like Zoloft and Prozac are common choices. SNRIs and atypical antidepressants are also used.
It's crucial to watch kids closely on these medications. They should be checked for any signs of worsening symptoms or suicidal thoughts.
Every child's treatment plan is different. It's best to work with a mental health expert. Often, a mix of therapy and medication works best for kids with serious depression.
Coping Strategies for Parents
Parenting a child with depression is tough. But, there are ways to make it easier. Building a strong support system is key. This can include family, friends, support groups, or mental health professionals.
Having people to lean on and getting professional help can be a big help. It gives you the emotional and practical support you need. This support is crucial for your child's mental health journey.
Building a Support System
Getting help from your community is important. Look for local or online support groups for parents of children with depression. These groups can connect you with others who understand your challenges.
Also, include your child's teachers, counselors, and healthcare providers in your support system. They can offer valuable insights and resources.
Self-care for Caregivers
As a parent, taking care of yourself is crucial. Make time for activities that reduce stress, like exercise or meditation. Spending time with friends is also important.
Getting counseling or therapy for yourself can help too. It lets you process your emotions and find healthy ways to cope. Remember, taking care of yourself helps you support your child better.
By using these coping strategies for parents of children with depression, you can face this journey with strength and care. Your child's well-being is very important. With the right support and strategies, you can help them overcome depression.

Prevention and Early Intervention
It's very important to help kids stay mentally healthy and avoid depression. Teaching them how to handle tough times and building strong family bonds can help a lot. Also, dealing with issues like past traumas or ongoing health problems early on is key.
Helping kids feel good about themselves and encouraging them to be active and social is also important. Getting enough sleep is another big part of staying mentally healthy.
Studies show that starting prevention programs early can really help kids feel less anxious and depressed. But, there aren't many programs for the youngest kids that focus on these issues. By starting early, we can give kids the tools they need to manage their mental health.
About 56% of kids and teens with anxiety and depression are getting help. This shows we need more places where kids can get help for their mental health. We need better ways to help kids before they get really sick.
By focusing on mental health, building resilience, and helping early on, we can help kids deal with life's challenges. This sets them up for a bright future.
Here are some important ways to prevent depression in kids and help them early on:
- Teaching kids how to handle tough times and manage their feelings
- Creating a supportive home environment
- Dealing with issues like past traumas or ongoing health problems early on
- Encouraging kids to be active, social, and get enough sleep
- Starting prevention programs early, especially for the youngest kids
- Improving access to mental health services for kids and promoting early help
By focusing on these areas, we can make sure all kids have the support they need to succeed and reach their dreams.
Conclusion
It's very important to spot and deal with depression in kids. This helps them grow up happy and healthy. Knowing the symptoms, risk factors, and treatments helps parents a lot. They can support their child's mental health better.
Early help, working together with many experts, and having a strong support system are key. These things help kids with depression do well.
Dr. Chandril Chugh, a top neurologist, says it's crucial to tackle childhood depression. He urges parents to get help when they need it. With the right help, kids can handle their depression and live happy lives.
Remember, dealing with childhood depression is very important. There are many resources for parents worried about their child's mental health. By working together with doctors, you can help your child get through this and do well.
FAQ
What is the prevalence of depression in children?
The CDC says about 2.7% of kids aged 3-17 have depression.
What are the common symptoms of depression in children?
Kids with depression might feel sad or irritable a lot. They might also feel worthless or guilty. They might lose interest in things they used to like.
They could sleep or eat differently, have trouble focusing, or pull away from friends. They might also get angry or act out more.
They might also have headaches, stomachaches, or feel very tired.
How do I recognize the warning signs of depression in my child?
Look for big mood and behavior changes. Sadness, irritability, or mood swings are signs.
Also, watch for school and social problems. Kids with depression might have trouble concentrating or doing well in school. They might also have trouble making friends.
How do the symptoms of depression differ in children of different ages?
Symptoms change with age. Young kids might throw more tantrums or get really scared when separated.
Older kids and teens might feel more hopeless or even think about suicide.
How do I know if my child is experiencing clinical depression or just normal childhood sadness?
Normal sadness is short-lived and not as bad. Depression lasts a long time and really affects daily life.
If your child is sad, irritable, or loses interest for more than a few weeks, get help.
What is the process for evaluating and diagnosing depression in children?
Doctors use tests and talk to the child to figure out if they have depression. They might ask questions or use special scales.
They also do a full check-up to make sure there's no other health problem.
What are the treatment options for children with depression?
There are many ways to help kids with depression. Therapy, like CBT, can teach them to handle feelings better.
Family therapy helps everyone in the family. Sometimes, doctors might suggest medicine, especially for more serious cases.
How can parents support their child with depression?
It's tough to parent a child with depression. But, having support is key. Build a strong support network.
Take care of yourself too. Do things that make you happy and keep healthy.
How can I help prevent depression in my child?
Teaching kids good ways to handle feelings is important. Make your family a happy place.
Help them deal with tough times and build their self-esteem. Encourage them to exercise, make friends, and get enough sleep.
Source Links
- What Is Teenage Depression: Signs, Causes, And Treatments
- Understanding Anxiety And Depression Symptoms & Treatment
- What is a Behavioral Treatment? - Dr Good deed
- Quick Guide to Depression - Child Mind Institute
- Signs of Depression in Children & How to Help - Children's Health