Migraines and strokes both affect your brain, and the warning signs can look alike. Doctors warn that you should always treat a possible stroke as an emergency, because blocked blood flow can damage brain cells within minutes.
The key difference between migraine and stroke is the cause. A stroke happens when blood flow is cut off by a clot or bleeding in the brain. A migraine is a repeated brain headache problem where nerve pathways become overactive and sensitive. Both can cause vision change, numbness, and speech problems.
Table of Contents
ToggleDifference Between Migraine and Stroke
In migraine , waves of brain activity move across the surface of the brain and change blood flow for a short time. In a stroke , part of the brain does not get enough blood at all, and cells can start to die.
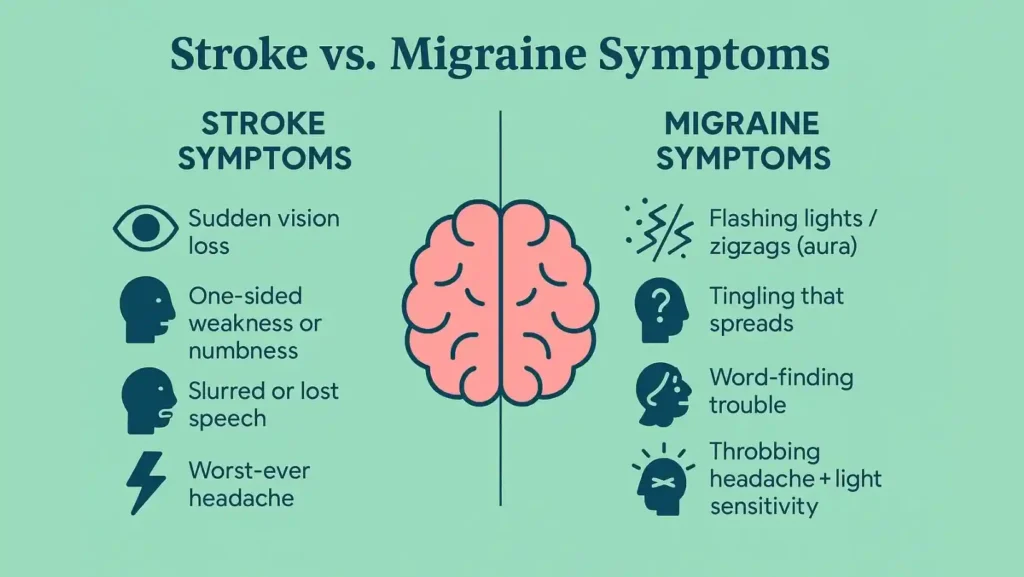
Quick Comparison Of Neurological Features
In a stroke , you often notice loss of function. One side of the face may droop. One arm or leg may go weak. You might not see out of one side of your vision. These problems usually appear on one side of the body.
In a typical migraine , especially with aura, you may notice bright flashing lights, zigzag lines, or a shimmering blind spot that grows, along with tingling that spreads slowly.
How Onset Timing Differs
Symptoms of stroke usually start suddenly. One minute you feel normal; the next minute you cannot move your arm or talk clearly. In a TIA (mini stroke), symptoms also start at once.
With migraine , aura symptoms usually build over at least five minutes, then spread and change over 5 to 60 minutes before they fade. You may see a flashing spot that slowly grows and then feel tingling in your hand and arm. This slow spread is a key clue that leans toward migraine instead of stroke .
Distinguishing Triggers And Patterns
Another difference between migraine and stroke lies in triggers. Migraine attacks often follow a pattern. Lack of sleep, stress, bright light, skipped meals, or some foods can bring an attack.
A stroke is not usually set off by a single short-term trigger. Instead, it links to long-term risks such as high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, or heart rhythm problems.
Symptom Duration Differences
In migraine , aura signs usually last between 5 and 60 minutes and then fully clear, although the head pain can last much longer. In a TIA or stroke , symptoms can last longer than an hour and may not fully improve. When symptoms clear in under a day but look like a stroke , the event is called a TIA, often named a mini stroke in clinics.
Stroke vs Migraine Symptoms
Both stroke and migraine symptoms can cause trouble with vision, body sensation, and speech, so you need to know how doctors sort migraine and stroke during that first urgent visit.
Visual Changes In Stroke Vs Aura
In migraine , especially with aura, you often have “positive” visual symptoms. These are things added to your sight, such as flashing lights, zigzags, bright spots, or waves in your vision that spread over time.
In a stroke , vision loss is more likely to be “negative”. You may suddenly lose the left or right half of what you see, or lose sight in one eye, without bright colors or patterns.
Aura tends to grow and move. Stroke vision loss arrives suddenly and stays until treated or slowly recovers.
Numbness Pattern Differences
Numbness and tingling can appear in both migraine and stroke . In migraine , tingling often starts in the fingers, then moves up the arm, and sometimes to the face or tongue, step by step over several minutes. In a stroke , numbness or weakness usually hits one side of the body all at once and does not “march” up the limb.
Speech Difficulty Vs Migraine Confusion
Both migraine and stroke can affect speech. A stroke in the language centers of the brain can make your words slurred or strange, or you may not find any words at all. In a migraine attack, you may feel slow, have trouble finding words, or mix up sentences, often during aura or strong pain.
Because the same sign appears in both, speech trouble is one of the main times when a migraine feels like a stroke . Doctors advise you to treat any sudden new speech problem as a possible stroke until tests prove otherwise.
Severe Headache Differences
Head pain alone cannot separate migraine from stroke . Many people have stroke with no headache. Others have a bleeding stroke with the “worst headache of life”. In migraine , head pain is common and often throbbing, with sensitivity to light and sound and sometimes nausea.
Because pain level does not clearly show the difference between migraine and stroke , doctors focus more on how fast symptoms start, where they appear, and whether you have other brain signs such as weakness, vision loss, or confusion.
Migraine vs TIA (Mini Stroke)
When doctors talk about migraine vs TIA (mini stroke) , they focus on short-term brain problems that suddenly appear and then clear. TIA stands for transient ischemic attack, which means a brief block of blood flow to the brain without lasting damage on scans.
Brief Neurological Deficits Overview
In a TIA, you may suddenly lose strength, feel numb on one side, lose vision, or have trouble speaking. These are called neurological deficits, which means a part of the nervous system stops working for a short time. In migraine , you can also have visual changes, numbness, and speech trouble, but they often build slowly and follow a pattern you have seen before.
Reversible vs Non-Reversible Symptoms
Both migraine aura and TIA symptoms can fully reverse. That is the tricky part. In migraine , the aura phases are designed to be reversible brain events. They often last between 5 and 60 minutes and then settle, although a headache may follow.
In TIA, the blood flow block is brief, so symptoms usually clear in under 24 hours. The brain scan can look normal, yet the event is still a serious warning sign for stroke in the next hours or days.
When Sudden Changes Suggest TIA
Doctors think of TIA when symptoms fit stroke vs migraine symptoms and start all at once. For example, you suddenly cannot see out of one eye, your arm and leg on one side become weak, or your speech turns unclear without gradual spread.
If you have never had migraine aura before and you are older or have risk factors such as high blood pressure or diabetes, sudden problems are more likely due to TIA or stroke than to migraine . In this setting, migraine is not something you can safely judge at home.
Diagnostic Urgency For Suspected TIA
Because TIA can be a warning for a full stroke , guidelines from major heart and stroke groups push for urgent evaluation in an emergency department or stroke clinic. You may need a brain scan, vessel imaging, heart tests, and blood work in the first hours.
Acting fast helps doctors lower your risk of a later stroke with medicine and lifestyle changes. When there is any doubt between migraine and stroke or TIA, emergency care is the safest plan.
Migraine With Aura vs Stroke Signs
Many people worry about migraine with aura vs stroke signs because aura can look dramatic. Aura means a short brain symptom that comes before or with the headache, such as visual changes, tingling, or speech trouble.
Gradual vs Sudden Symptom Onset
In migraine , aura symptoms usually grow over at least five minutes and may move from one area to another. In a stroke , loss of function appears suddenly and all at once.
So the time pattern is one of the main clues in migraine with aura and stroke signs . Gradual spread leans toward migraine . Sudden fixed loss leans toward stroke .
Positive vs Negative Visual Disturbances
In migraine , you often get positive visual signs, such as flashing lights, zigzag lines, or bright shapes that move across your field of vision. In stroke , you more often lose part of your vision without extra lights, as if a curtain blocks one side.
Sensory Symptom Spread Patterns
Sensory symptoms in migraine aura often move. Tingling may start in your fingertips, then travel up your arm, then reach your face. This spread over minutes is classic for aura. In stroke , numbness or weakness usually appears in the whole area at once and stays there at first.
When Aura Becomes Concerning
Aura needs a fast medical review when it lasts longer than an hour, starts for the first time after middle age, happens with strong weakness, or looks very different from your usual pattern.
In those situations, even classic aura can mark a problem when migraine feels like a stroke , and doctors often order brain scans to rule out a real stroke .
When Migraine Feels Like a Stroke
There are times when a migraine feels like a stroke so closely that even trained specialists cannot be sure at the bedside. Research shows that migraine vs stroke symptoms can overlap in studies of patients who arrive at stroke units.
Overlapping Sensory Symptoms
Both conditions can cause vision loss, face or arm numbness, dizziness, and problems with balance. In hemiplegic migraine , a rare type, temporary weakness on one side can almost copy a stroke . This overlap makes it very hard to separate stroke vs migraine symptoms without imaging.
Confusion And Speech Difficulty Overlap
During a strong migraine , especially with aura, you can feel confused, struggle to find words, or have slurred speech. A stroke in the language areas of the brain causes very similar speech problems. Because of this, any sudden change in speech or understanding is treated as a possible stroke , even if you have a long history of migraine .
This is one of the classic cases when migraine feels like a stroke , and emergency teams often use stroke protocols until scans are done.
Head Pain Differences
Head pain does not clearly distinguish between migraine and stroke . Many ischemic strokes have no pain at all. Bleeding strokes can cause a sudden, extreme headache. Migraine usually brings throbbing or pulsing pain with light and sound sensitivity, but some people have aura without any headache.
Evaluating New Or First-Time Symptoms
Any first-ever attack of aura, first episode of one-sided weakness, or new pattern of symptoms in migraine should lead you to urgent care. Medical teams would rather find out that it is only migraine after a scan than miss a treatable stroke in the early window.
Causes & Risk Factors
Causes of migraine and stroke differ, but there is some shared ground. Understanding this helps you see why migraine vs stroke is a short-term and long-term issue.
Migraine Triggers Overview
In migraine , the brain becomes more sensitive to certain inputs. Common triggers include irregular sleep, stress, hormone shifts, some foods, and bright or flickering light. These triggers do not cause permanent brain damage, but they set off symptom cycles that repeat over time.
Stroke Risk Factors Explained
For stroke , the highest risks include high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, obesity, and heart rhythm problems such as atrial fibrillation. These problems injure blood vessels and make clots or bleeding more likely. When doctors look at stroke symptoms , they always check if you also have these long term risks.
Shared Vascular Influences
Several large reviews show that people with migraine , especially with visual aura, have a higher risk of ischemic stroke over life, even when attacks themselves are reversible. The exact reason is still under study, and experts note that some of the link may be due to shared risk factors or misdiagnosed TIAs.
Lifestyle Factors For Prevention
Healthy daily habits help lower stroke risk and can also reduce migraine frequency. Regular sleep, a balanced eating pattern, enough water, exercise that fits your health, no smoking, and limited alcohol use all support brain and vessel health.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Tell The Difference
When you reach the hospital with possible migraine vs stroke symptoms, the team follows a clear path to protect your brain.
Neurological Exam Basics
First, a doctor or stroke nurse does a neurological exam. This checks your strength, vision, reflexes, speech, balance, and the way you feel touch and pressure. Differences between one side and the other can point toward stroke . A normal exam after symptoms clear may fit migraine , TIA, or other transient problems.
Imaging Tests For Stroke
If there is any concern for stroke , brain imaging is done as fast as possible. A CT scan is often the first test to look for bleeding. MRI scans can show early ischemic damage. Vessel imaging with CT angiography or MR angiography can reveal blocked arteries.
These tests are crucial in sorting stroke vs migraine symptoms and in deciding whether you can receive clot-busting treatment.
When Migraine Needs Imaging
Not every migraine attack needs a scan. Imaging is more likely when you have your first strong headache after age 40, a sudden “worst ever” headache, a big change in pattern, new seizure, or new focal signs such as weakness.
In all those cases, doctors must ask again about migraine vs stroke and rule out bleeding, tumors, infections, or other serious problems.
Red-Flag Symptoms Requiring ER Visit
You should go to the emergency room or call emergency services right away if you notice sudden face drooping, arm weakness, speech trouble, loss of vision, severe sudden headache, or loss of balance with one-sided symptoms. Stroke groups teach the FAST or BE FAST signs to help you remember these warnings.
Treatment Pathways
Treatment differs strongly between migraine vs stroke because the causes are not the same.
Acute Stroke Emergency Steps
If doctors confirm an ischemic stroke , they may give clot-busting medicine within a limited time window or use a catheter procedure to remove the clot in large vessel strokes. Blood pressure, oxygen, and blood sugar are managed tightly to protect brain tissue. Dosage and drug choice depend on your age, scan findings, and other health issues.
Migraine Abortive Treatments
For migraine , treatment in the short term aims to stop the attack. Doctors may use pain relievers, specific migraine drugs that act on serotonin pathways, or newer targeted medicines. Nausea drugs and fluids may help if you are vomiting or dehydrated. The exact choice and dose vary by age, other diseases, and how often you have attacks.
Long-Term Migraine Prevention
If migraine attacks are frequent or disabling, preventive therapy is considered. Options include blood pressure tablets, anti-seizure drugs, antidepressant medicines, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) blockers, or Botox injections, depending on your profile. Lifestyle steps and trigger tracking are always part of long-term care.
Rehabilitation Needs After Stroke
After a stroke , many people need rehab to regain strength, speech, and daily skills. Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy start as early as possible. This long recovery phase shows how serious stroke symptoms can become if brain cells are lost.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention looks at both everyday choices and medical care so that migraine vs stroke becomes less likely to harm you.
Stroke Prevention Essentials
Stroke prevention focuses on controlling blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and heart rhythm. Doctors may prescribe blood pressure medicine, statins for cholesterol, drugs to prevent clots, or treatments for heart rhythm problems. Exact drug types and amounts depend on your personal risk.
Migraine-Specific Prevention
Preventing migraine involves keeping a regular sleep schedule, not skipping meals, staying hydrated, limiting screen glare, and managing stress where possible. Many people also use preventive medicines when attacks happen often.
With good prevention, times when migraine feels like a stroke may become less common, because aura and focal symptoms are less frequent.
Controlling Vascular Risk Factors
Because migraine with aura is linked to higher stroke risk in studies, controlling vascular risk factors is important for you, even at a young age. That means no smoking, watching blood pressure, checking cholesterol and sugar, and discussing hormonal birth control risks with your doctor if you are eligible.
Lifestyle And Dietary Recommendations
A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy fats supports brain and vessel health. Reducing processed foods, high salt snacks, and sugary drinks helps control weight and blood pressure. Regular moderate activity can reduce both migraine frequency and stroke risk when matched to your health status.
FAQ
Can A Migraine Mimic A Stroke?
Yes. A migraine with aura can copy many stroke signs, including vision loss, numbness, and speech problems, which is why when migraine feels like a stroke you still need emergency assessment to stay safe.
How Do I Know If It Is Migraine Aura Or Stroke?
Migraine aura usually spreads gradually, while stroke symptoms start suddenly. Yet real life is not always clear, so any new one-sided weakness or speech change in migraine must be checked fast.
Can Migraines Increase Stroke Risk?
Studies show people with migraine , especially with aura, have a slightly higher stroke risk over life, so doctors pay close attention to blood pressure, smoking, and hormones when discussing the difference between migraine and stroke .
When Should Migraine Symptoms Send Me To The ER?
You should go to the ER whenever stroke symptoms include sudden face droop, arm weakness, vision loss, or speech trouble, or a very sudden severe headache, even if you have had migraine for years.
Is Migraine With Aura More Likely To Look Like A Stroke?
Yes. Visual, sensory, and speech aura can resemble stroke , which is why migraine with aura and stroke signs often confuse people and why urgent scans are used to avoid missing a treatable brain attack.
Can Dehydration Trigger Stroke-Like Migraine Symptoms?
Dehydration can trigger migraine and make aura stronger, so in those moments when migraine feels like a stroke the overlap is worse, but dehydration alone does not replace medical checks for real stroke .
Does Numbness During Migraine Mean Stroke?
Tingling that slowly spreads in migraine aura is common, but sudden fixed numbness on one side fits more with TIA or stroke , so any event that feels like TIA (mini stroke) needs urgent review.
What Tests Confirm Stroke Vs Migraine?
Doctors use neurological exams plus CT or MRI scans, and sometimes vessel imaging, to sort migraine vs stroke and other causes, since stroke can overlap and only imaging shows blocked or damaged brain tissue clearly.
Can Stress Cause Migraine Symptoms That Resemble Stroke?
Stress is a frequent trigger for migraine , and severe attacks can involve confusion, aura, and speech trouble that copy stroke , so during migraine uncertainty, you should always seek emergency care instead of waiting.
About The Author

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Chandril Chugh, Board-Certified Neurologist, providing expert insights and reliable health information.
Dr. Chandril Chugh is a U.S.-trained neurologist with over a decade of experience. Known for his compassionate care, he specializes in treating neurological conditions such as migraines, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease. Dr. Chugh is highly regarded for his patient-centered approach and dedication to providing personalized care.
→ Book a consultation to discover which remedies suit your needs best.